

Annual Report 2004-2005
1
1.1 Gradual liberalization in international air services
has been a continuous process with the basic
objective of meeting the increasing demand for
travel on international routes. Increased
connectivity, greater capacity and more choices for
passengers have a direct bearing on economic
growth, apart from meeting the needs of business,
trade and tourism. This process was continued
through several initiatives taken during the year.
Some of the major initiatives taken during the year are:-
••
••
• Revised Air Service Agreement with USA:
As per revised Air Services Agreement, both
countries can designate any number of airlines
and can operate any number of services from
any point in the home country to any point in
the territory of other Contracting State with full
intermediate and beyond traffic rights.
••
••
• Liberalization of Entitlements with UK, Australia
and France:
Entitlements between India and UK will be more than
doubled within the next one year and airlines of either
country will be entitled to operate 40 services/week
each by winter 2005. UK carriers have also been
granted access to Bangalore, Hyderabad and Cochin
besides the 4-metro destinations and Indian carriers
to Glasgow, Edinburgh and Bristol in addition to
London, Manchester and Birmingham.
Entitlements on India-Australia sector will also be
enhanced from the existing 2100 seats/week to 6500
seats/week over the next two years. Australian
carriers will also get access to Chennai, Bangalore
and Hyderabad as additional points over this period.
Entitlements on India-France sector have been
increased to 35 weekly services effective
Summer 2005 from 14
weekly services. French
carriers will have access to three additional
points in India namely Bangalore, Chennai and
Hyderabad. Indian carriers will be able to
commence 5
th
Freedom beyond rights to/from
new points in North America from designated
points in France.
••
••
• International Operations by Private Airlines:
Besides the SAARC countries, private domestic
Highlights
1
1

Ministry of Civil Aviation
2
airlines of India having a fleet size of 20 aircrafts and
at least 5 years operations in domestic sector, have
now been permitted to operate to all overseas
destination except Gulf countries.
••
••
• Signing of new ASA:
New Air Services Agreements (ASA) were signed
with the Republic of Slovenia and Morocco on
16.2.2004 and 7.12.2004 respectively. Agreed text of
ASA were initialed with Tunisia and Brazil on
14.2.2004 and 5.5.2004 respectively. The total number
of countries having Air Service Agreement with India
now stands at 100.
••
••
• Policy on Commercial Agreement:
Government will, henceforth, not mandate any
Commercial Agreement between the carriers. The
airlines are however free to enter into co-operative
marketing arrangements as are mutually agreed upon
between them. All existing Government mandated
Commercial Agreements would be reviewed and
phased out over the next five years.
••
••
• Removal of Restriction on Photography:
Aircraft Rules have been amended to permit
photography by passengers of scheduled flights at
the terminal buildings of civil aerodromes and civil
enclaves at Defence aerodromes. In addition
passengers are also permitted to take photographs
from inside an aircraft while in flight or landing/take
off at civil aerodromes.
••
••
• Open Sky Policy during Peak Seasons:
To take care of the peak season rush, like in the
previous years, an Open Sky Policy was adopted by
the Government for the winter 2004-05, under which
designated foreign airlines operated additional
services to/from India subject to the existing terms
of the commercial agreement with Air India/Indian
Airlines.
1.2 AIRPORTS AUTHORITY OF INDIA
• Financial Performance:
Airports Authority of India is expected to earn a profit
(after tax) of Rs.348.32 crores during the year 2004-
2005 compared to Rs.314.96 crores during the year
2003-2004. Airports Authority of India’s contribution
to the national exchequer was Rs. 399.99 crores for
2003-2004 and is expected to be Rs. 436.88 crores for
2004-2005, which includes Income Tax, Dividend,
Interest Payments, etc.
••
••
• Restructuring of Delhi And Mumbai Airports:
Meeting of newly constituted Empowered Group of
Ministers (EGOM) was held on 28.6.2004, in which
proposals for appointment of Legal Consultant,
Global Technical Advisor and changes in key policy
in Expression of Interest (EOI) document were
2

Annual Report 2004-2005
3
approved. 10 EOIs were received and considered by
the Inter Ministerial Group (IMG). Out of the 10 EOIs
received, 9 bidders have been shortlisted. The
consultants have held pre-bid discussions with the
shortlisted bidders on 14-16 December, 2004, as part
of exercise for preparation of Request for
Proposal(RFP) documents. Various transaction
documents have been prepared. The EGOM last
met on 15.2.2005 to take decision on key issues
involved in draft Request for Proposal (RFP) and
other transaction documents. The entire process of
evaluation of bids and handing over of airport to
successful bidders is likly to be over by June, 2005.
••
••
• Modernisation of Kolkata and Chennai Airports:
To improve passenger facilities at the Netaji Subhash
Chandra Bose InternationalAirport (NSCBI) airport,
Kolkata, the following works have been completed:-
– Check-in area in the International Terminal has
been extended;
– New state-of-the-art Flight Information Display
System provided in both the terminals, and
– New Air-conditioning Plants have been
commissioned;
Work is in progress for –
– Construction of an Integrated Cargo Complex;
– Strengthening of main runway including
upgrading the ground lighting facilities to match
with Cat.II Instrument Landing System; and
– International remote parking bays.
State-of-the-art facilitation counter at Terminal-II, IGI Airport
3

Ministry of Civil Aviation
4
A new international Departure Terminal with an area
of 20,000 sqm has also been planned.
The following works have been completed at
Chennai International Airport:-
– A reciprocal Instrument Landing System (ILS)
commissioned;
– Marble cladding of the aerobridge corridor; and
– Vitrified flooring in the Domestic and
International Arrival Terminal.
The existing departure and arrival areas in the old
international terminal are being combined into a
unified international arrival building, which shall
ultimately be merged with new international departure
terminal.
There are also proposals for construction of five bays
and link taxi-track for private Air Taxi Operators,
warehousing facilities for Courier and Charter
Operators and Integrated CargoComplex Phase II and
additional hangars.
••
••
• Greenfield Airports:
The Concession Agreement between Government
of India and Bangalore International Airport Limited
(BIAL) was approved and signed on 5
th
July, 2004.
The Concession Agreement for Hyderabad
International Airport was signed on 20
th
December,
2004.
••
••
• Modernisation/Development of Airport/ATM
Systems:
As part of the ongoing modernization and
development of various airports, state-of-the-art
Instrument Landing System(s)/ Air Traffic
Management (ATM) systems have been installed or
replaced and passenger and cargo terminals have
been expanded at various airports. Further, various
civil/aerodrome/passenger facilitation works have
also been completed at Delhi, Mumbai, Kolkata,
Chennai, Thiruvananthapuram, Bangalore, Jabalpur,
Pathankot, Ahmedabad, Calicut, Dibrugarh, Gaggal,
Lucknow, Bhavnagar, Porbandar, Nagpur, Imphal,
Rajamundry, Amritsar, Agartala, Hyderabad,
Varanasi, Kullu, Jaipur, Lilabari, Leh, Srinagar, Rajkot,
Madurai, Dimapur and Vishakhapatnam airports.
••
••
• I.S.O. Certification:
During the year 2004-05, Airports Authority of India
has been awarded ISO Certification for Pune Airport
and Department of Information Technology at AAI
Hqrs, New Delhi.
4
Proposed New Terminal Building at Srinagar Airport

Annual Report 2004-2005
5
••
••
• Development of Non-Metro Airports:
The Airports Authority of India has drawn a plan for
City Side Development of 25 Non-Metro Airports.
In the first phase 10 Non-Metro Airports namely,
Ahmedabad, Amritsar, Guwahati, Goa, Jaipur,
Lucknow, Mangalore, Madurai, Udaipur and
Trivandrum have been taken up for which Global
Technical Advisor (GTA) and Indian Financial
Consultant (IFC) have been appointed.
AAI proposes to take up similar study for remaining
15 Non-Metro Airports which are Agatti,
Aurangabad, Bhopal, Bhubaneshwar, Coimbatore,
Indore, Khajuraho, Patna, Port Blair, Nagpur, Rajkot,
Trichi, Vadodara, Varanasi and Vishakhapatnam.
Expression of Interest (EOI) have been invited for
appointment of one set of IFC/GTA each for 5 airports
covering these 15 airports.
1.3 INDIAN AIRLINES LTD.
••
••
• New Internationals Services:
Indian Airlines introduced twice weekly flights
between Guwahati-Bangkok-Guwahati from 1.1.2005.
••
••
• Customer Friendly Schemes:
Indian Airlines introduced various customer friendly
schemes viz. Corporate House Scheme, Super Saver
International, Frequent Flyer Programme, Indian
Airlines – Taj Offer, Holiday Packages – IA Flyaways,
IC – Amex Co-brand Credit Card, IC-AMEX Gold
Card, IA AMEX Green Card, IC – ABN AMRO Co-
brand debit Card, Bid and Fly and EMI Scheme.
••
••
• Neticket:
Effective 16
th
Aug 2004, Indian Airlines has launched
a Neticket facility, whereby a passenger can log on
to www.Indian-airlines.com and reserve, buy and print
his ticket image on his own printer. This ticket image
can be presented at the time of check-in in lieu of a
physical ticket. This facility has been extended to IA
approved agents also from 1
st
October, 2004.
••
••
• Financial/Physical Performance:
Indian Airlines earned a net profit (after tax) of Rs.44.17
crores during 2003-2004 compared to a net loss (after
tax) of Rs.196.56 crores during the 2002-2003. During
first six months of 2004-2005 viz. April-September,
2004, the airline suffered a loss of Rs. 66.40 crores
and is expected to close the year with a net profit
(before tax) of Rs. 8.75 crores compared to the
budgeted loss of Rs.24.75 crores. It is expected to
carry 69.46 lakh passengers during 2004-2005
compared to 59.00 lakhs during 2003-2004. Overall
load factor is expected to be 68.6% compared to the
budget estimates of 66.7% during the year 2004-2005.
5

Ministry of Civil Aviation
6
••
••
• Performance of Alliance Air:
Alliance Air (a wholly owned subsidiary of Indian
Airlines) earned a profit (after tax) of Rs.2.05 crores
during 2003-2004 compared to a loss of Rs.82.48
crores during 2002-2003. During first eight months
of 2004-2005 viz. April-November, 2004, the airline
suffered a loss of Rs. 34.43 crores compared to a loss
of Rs.29.14 crores during April-November, 2003. It
carried 15.82 lakh passengers during 2003-2004
compared to 14.19 lakhs during 2002-2003. During
the first eight months of 2004-2005 viz. April-
November, 2004, the airline carried 10.09 lakh
passengers compared to 9.98 lakhs during April-
November, 2003. The airline achieved a load factor of
62.17% during 2003-2004 compared to 59.81% during
the year 2002-2003. During the first eight months of
2004-2005 viz. April- November, 2004, the Airline
achieved a load factor of 63.60% compared to a load
factor of 60.87% in April- November, 2003.
1.4 AIR INDIA LTD.
••
••
• Financial Performance:
Air India earned a net profit of Rs.92.33 crores during
2003-2004 compared to a net profit of Rs.133.86 crores
during 2002-2003. During the first six months of 2004-
2005 viz. April-September, 2004, the airline earned a
net profit (including deferred tax benefit) of Rs.7.85
crores compared to Rs. 40.59 crores during
April-September, 2003. During April-September, 2004,
the airline carried 21.94 lakh passengers compared to
17.84 lakhs during April-September, 2003. During
April-September, 2004, the overall load factor was
62.1% compared to 61.1% during
April-September, 2003.
••
••
• New /Additional Flights
* Twice weekly flights Mumbai/ Ahmedabad/ London
effective March 2004.
* Flights on the following routes increased from two
to three effective March 2004
– Mumbai/Nairobi/Dar-es-Salaam
– Hyderabad/Jeddah/Hyderabad
– Lucknow/Delhi/Jeddah/Lucknow
* Twice weekly Delhi/Amritsar/Delhi hub-n-spoke
flights effective 16
th
April 2004.
* Effective 11
th
June 2004, 3 weekly flights commenced
to Los Angeles via Frankfurt.
* Effective 13
th
June 2004, started 2 weekly flights from
Ahmedabad to Dubai.
* Effective 29
th
November 2004, 4 noon-time departure
flights were introduced on Mumbai/London/
Mumbai.
* Effective 4
th
December 2004, additional flight to
London operated on the routing Mumbai/Delhi/
London/Delhi/Mumbai.
6
Air India Flight during Take-off

Annual Report 2004-2005
7
* Effective 5
th
December 2004, Los Angeles flights
increased to 5 via Frankfurt.
••
••
• Security :
The Security Department of Air India adjudged the
“Outstanding AVSEC Organisation’ by the Mudroch
University of Western Australia at the 7
th
AVSEC
Conference held at Singapore from 14-16
th
April, 2004.
The AVSEC Award has been conferred upon the
Security Department of Air India for the third time in
succession.
••
••
• E-Ticketing:
Air India introduced E-Ticketing (Electronic
Ticketing) through it’s offices in India from August
2004.
1.5 HAJ OPERATIONS 2005
Haj Operations started on 13 December, 2004 and
completed on 26
th
February, 2005. Approximately 82,000
Haj pilgrims carried from India to Jeddah and back.
1.6 TSUNAMI — RELIEF OPERATIONS
Indian Airlines Ltd. operated 79 relief flights from 26
December, 2004 to 7 January, 2005 carrying a total of 4913
passengers and 203090 kgs. of relief material for the
affected people. The helicopter deployed by Pawan Hans
Helicopters Ltd. (PHHL) at Andaman & Nicobar had
carried out relief task in the Islands. Further, the helicopter
deployed at Chennai had undertaken the task of carrying
VIPs to Nagapattinam.
Blue Dart Aviation Ltd. operated 7 relief cargo flights to
Port Blair upto 10.1.2005. Jet Airways operated 18 flights
to Port Blair from Chennai and Kolkata and back till
31.12.2004 airlifting over 1600 stranded residents and
tourists on the islands and it has airlifted over 25,000 kgs.
of relief cargo sent by Government agencies and
recognized voluntary agencies in different parts of India.
They have also carried one tonne of medical relief stores
to Sri Lanka from Chennai.
1.7 EMERGENCY SUPPORT FUNCTIONS
PLAN –2004
As part of Disaster Management, a comprehensive
“Emergency Support Functions Plan-2004” was prepared.
The objective of this plan is to provide necessary support
services / manpower to Ministry of Home Affairs and
also to provide free transportation of disaster relief material
of urgent and essential nature coming from abroad / within
the country.
1.8 AVIATION SCENARIO
••
••
• Scheduled Airlines Operators:
At present, apart from Air India, Indian Airlines and
Alliance Air, Jet Airways, Sahara India Airlines,
Deccan Aviation Pvt. Ltd., M/s Blue Dart Aviation
Pvt. Ltd.(Cargo only) have the permission to operate
domestic scheduled air transport services in the
country. During January-December 2004, a total of
2,50,141 flights were operated by the domestic
scheduled operators carrying a total of 1.76 crore
passengers.
7

Ministry of Civil Aviation
8
••
••
• Non-Scheduled Airlines Operators:
As on 31
st
December 2004, a total of 37 companies
were holding Non-Scheduled Operator’s Permit.
••
••
• Registration of Aircraft:
As on 31st December, 2004, there were 1150 aircraft
(including micro light, gliders and balloons) on the
Indian civil register. Of these, 60 aircraft were
registered and 49 aircraft were de-registered during
the period 1
st
April, 2004 to 31
st
December, 2004.
••
••
• AME Licences:
A total of 6034 Aircraft Maintenance Engineers
(AME) licenses including Basic licenses and 282
Flight Engineers (FE) licenses have been issued so
far, of which 200 AME licenses have been issued
during the period 1
st
April 2004 to 31
st
December, 2004.
••
••
• Approval of Firms:
So far, a total of 1671 firms have been approved for
manufacture, maintenance, testing, storage etc. of
aircraft, aircraft components/equipment. Out of these,
50 are foreign firms.
••
••
• Tourist Charter Flights:
A total of 705 tourist charter flights were operated to
India from January to December, 2004 bringing in
1,55,495 foreign tourists.
1.9 PAWAN HANS HELICOPTERS LTD.
••
••
• Performance of Pawan Hans Helicopters Ltd.:
The company is expected to earn a net profit (after
tax) of Rs. 33.10 crores during 2004-2005. The company
registered a net profit (after tax) of Rs.52.69 crores
during the financial year 2003-2004 compared to a
net profit (after tax) of Rs.15.39 crores during the
year 2002-2003.
1.10 INDIRA GANDHI RASHTRIYA URAN
AKADEMI
During the last seven years, a total of 261 pilots have
completed training and 79 are undergoing training at
IGRUA.
1.11 DEVELOPMENTAL ACTIVITIES TAKEN
UP IN THE NORTH-EAST REGION
••
••
• Alliance Air:
* Alliance Air (a wholly owned subsidiary of Indian
Airlines Ltd.) has taken on lease 4 ATR-42-320 aircraft
for dedicated operations in the North Eastern Region.
These aircraft have been deployed exclusively in the
North East for a period of 5 years on dry lease basis.
The lease period commenced from December, 2002.
* The leased aircraft are being operated in the North
Eastern Region on the basis of agreed budgetary
grant of Rs.35 crores per annum i.e. Rs.175 crores
during the five year period, to be contributed by
Ministry of Development of North Eastern Region.
The deficit, if any, will be met by Alliance Air / Indian
Airlines with increase in fares and other concessions
expected from the Government like reduction of ATF
prices, lowering of Airport charges, including
savings from Landing and Navigation charges in the
North East etc.
8

Annual Report 2004-2005
9
* The first aircraft arrived in India on 19
th
December,
2002 whereas the second aircraft on 23
rd
December,
2002. The remaining two aircraft arrived in February,
2003.
* The inaugural flight took off on 25
th
December, 2002
and operated sector Kolkata-Guwahati-Dimapur-
Agartala-Kolkata.
* The first commercial flight operated on 2
nd
January,
2003.
* Gradually the flight operations increased. The ATR
is operating a total of nine stations i.e. Kolkata,
Guwahati, Silchar, Dimapur, Agartala, Imphal, Aizwal,
Lilabari and Shillong.
* Guwahati made an operational base for 1 ATR aircraft
effective July, 2004.
* Frequency of operations to/from/within North East
increased from 52 flights per week in Winter 2002 to
123 flights per week in Winter 2004 and city pair links
increased from 74 per week to 141 per week.
* Seats offered on North-East routes increased from
7518 per week in Winter 2002 to 9617 per week in
Winter 2004.
• Airports Authority of India:
During the first year of 10
th
Plan i.e. 2002-2003, AAI
spent Rs.30.88 crores and Rs.14 crores have been
spent till October 2003 and likely expenditure during
2003-04 is Rs.27.32 crores. During the current financial
year, North East Council has released Rs.4.5 crores
as share on development of airports in the North
East Region.
• Pawan Hans Helicopters Ltd.:
PHHL operates flights from 24 destinations covering
46 sectors by 120 weekly flights under the agesis of
the State Governments of Meghalaya, Tripura, Sikkim
and Arunachal Pradesh.
* Arunachal Pradesh- PHHL provided a Dauphin
helicopter SA365N to Government of Arunachal
Pradesh from December 1995 which is being utilized
by the State Government for services connecting
Itanagar with Guwahati, Mohanbari, Pasighat, Roing,
Tezu, Ziro, Namsai, Along, Yingklong, Miao,
Changlang, Daporijo etc. In addition one MI-172
helicopter has been deployed from August 2002 for
ferrying passengers and carrying cargo (air
maintenance).
* Meghalaya - PHHL has provided one Dauphin
helicopter on wet lease to the Government of
Meghalaya w.e.f. 15
th
February 1999. The State
Government has been operating daily passenger
flights on the Guwahati-Shillong-Tura sector and
other sectors within the State.
9
Bell Helicopter in North-East

Ministry of Civil Aviation
10
* Sikkim - PHHL has provided a 5-seater Bell helicopter
on wet lease to the Government of Sikkim since 31
st
October 1998. The State Government has been
operating daily passenger/tourist flights on Gangtok-
Bagdogra-Gangtok sector (6 days in a week) and
other flights (joyride to Kanchanjunga) for carrying
tourists.
* Ministry of Home Affairs - MHA has been utilizing
PHHL’s Dauphin helicopter since 1996 every year.
The helicopter is based at Guwahati and being utilized
for transportation of Ministers and Senior Officers
of the Central Government to important centers in
North East.
* Tripura - PHHL has provided a Bell 407 helicopter
on wet lease to the Government of Tripura w.e.f. 25
th
September 2002. The State Government has been
utilizing this helicopter for regular passenger services
within the State.
* NHPC - PHHL has provided a 5 seater Bell helicopter
to NHPC w.e.f. 27
th
October 2000. The helicopter is
based at Itanagar, Arunachal Pradesh and is being
utilized by them to meet their own requirements.
* Oil India Ltd. - PHHL has provided a 3 seater
Robinson R-44 helicopter to Oil India Ltd. w.e.f. 10
th
May 1994. The helicopter is based at Guwahati,
Assam and is being utilized by them to meet their
own requirements
*****
10
Annual Report 2004-2005
11
2.1 INTRODUCTION
The Ministry of Civil Aviation is located in Rajiv Gandhi
Bhavan at the Safdarjung Airport complex in New Delhi
which is a spacious four floor modern building with lush
green lawns and colourful seasonal flowers in its
surroundings, creating an ambience of serenity and peace.
2.2 MAIN FUNCTIONS
The Ministry of Civil Aviation is responsible for the
formulation of national policies and programmes for
development and regulation of civil aviation and for
devising and implementing schemes for orderly growth
and expansion of civil air transport. Its functions also
Rajiv Gandhi Bhawan, Safdarjung Airport, New Delhi
Ministry of Civil Aviation
2
11

Ministry of Civil Aviation
12
extend to overseeing the provision of airport facilities, air
traffic services and carriage of passengers and goods by
air. The Ministry is also administratively responsible for
the Commission of Railway Safety, a statutory body set
up under the Railway Act.
2.3 ORGANISATION
The Ministry of Civil Aviation has under its administrative
purview the following organisations:-
(i) Attached/Subordinate Organisations.
••
••
• Directorate General of Civil Aviation (DGCA)
••
••
• Bureau of Civil Aviation Security (BCAS)
••
••
• Commission of Railway Safety (CRS)
(ii) Autonomous Body
••
••
• Indira Gandhi Rashtriya Uran Akademi (IGRUA)
(iii) Public Sector Undertakings
••
••
• Air India Ltd. (AIL)
••
••
• Indian Airlines Ltd. (IAL)
••
••
• Airports Authority of India (AAI)
••
••
• Pawan Hans Helicopters Ltd. (PHHL)
••
••
• Alliance Air – A subsidiary of Indian Airlines
Ltd.
••
••
• Air India Charters Limited (AICL)*
••
••
• Hotel Corporation of India (HCIL)*
*Subsidiaries of Air India Ltd.
Organisational set-up of the Ministry of Civil Aviation is
at Annexure I.
The Secretary in the Ministry is assisted by one
Additional Secretary & Financial Advisor, three Joint
Secretaries, nine officers of the level of Director/Deputy
Secretary/Financial Controller and nine officers of the level
of Under Secretary/Assistant Financial Controller.
Functions of the Ministry are distributed among sixteen
sections, which form the primary work units.
In addition to framing policies, the Ministry provides
guidance to these organisations in the implementation of
policy guidelines; monitors and evaluates their interface
with Parliament. It also supervises implementation by these
organisations of special programmes of the Government,
particularly those intended for weaker sections.
2.4 ORGANISATION AND METHOD
Instructions were issued from time to time stressing the
need for observance of various provisions of the ‘Manual
of Office Procedure.’ Corrective measures are being taken
on the deficiencies noticed through annual inspections
of sections of the Ministry. Adequate attention was paid
to the delays in disposal. Delays were being regularly
checked by monitoring the pendency position especially
the pendency of VIP and PMO references. In-service
training needs of the officers/staff of the Ministry were
given adequate attention and officers/staff were
sponsored for various training courses through NIC and
12

Annual Report 2004-2005
13
ISTM etc. Cash awards for the best three sections in the
Ministry, for the year 2002-03 were finalized under the
scheme for showing ‘High performance in O&M
Activities.’
2.5 RECORDS MANAGEMENT
Due importance was given to the record management in
the Ministry during the period under report. Various
aspects of record management viz. recording, reviewing,
weeding out of old records/files, were given adequate
attention. Two Special Drives were launched apart from
normal process of recording, reviewing and weeding of
files. Record Retention Schedule of old files/records in
respect of various sections of this Ministry was revised
and sent to National Archives of India.
2.6 MODERNISATION
With the continued active involvement of National
Informatics Centre (NIC) this Ministry has active IT
enabled services . The Main Computer Centre is equipped
with 3 Servers with structured LAN providing Internet
and email facilities to about 80 PCs. This LAN is
connected to NIC’s NICNET through a dedicated 2MBS
leased line and a standby RF Link (High Speed). The mail
services have been made Web enabled so as to access
mail from anywhere in the world. Senior officers have
been provided with NIC’s dial up connectivity at their
residence for accessing Internet and Email facility.
• E-Governance
There has been a consistent effort in implementing various
E-governance packages in different wings and locations
of Ministry of Civil Aviation. A Web enabled version of
the “Office Procedure Automation (OPA)” (File Tracking
software), has been made operational which was earlier
running under client server technology. A separate server
has been setup for the Minister’s office for Web enabled
OPA, which has replaced the older Unix version running
in the DOC cell. A “Composite Payroll System
(CPS)”developed by NIC’s Accounting Informatics
Division, with the involvement of CGA, Ministry of
Finance, for all Central Government offices has been
operational. A web enabled Parliament Question
Software (PQSoft) is already in place in the Ministry. All
Parliament Questions and their replies are being transmitted
electronically to Lok Sabha and Rajya Sabha after question
hour. A web enabled application PGRAMS is also
operational and the Public Grievances are being
transmitted on a regular basis to DAR & PG. Ministry’s
website http://civilaviation.nic.in has been recast to give
more useful information about the Ministry to the public
at large.
In the offices under Director General of Civil Aviation
(DGCA), Civil Aircraft Registration Information System
(CARIS) which was earlier operational under Unix / Fox-
plus has been implemented under Windows environment.
On line query on Civil Aircraft Register has been made
13

Ministry of Civil Aviation
14
available in the Internet through the DGCA Website http:/
/dgca.nic.in. The Medical History information of all the
pilots, from the Flight Crew Licensing System has been
made available to the designated air force medical
authorities through Internet, after incorporating measures
to ensure the security and confidentiality of the data.
The provision for printing of the medical assessments of
all the pilots, who are declared fit by the DGCA doctor,
has also been made through the DGCA Website. The
admitted candidates list for AME/Pilots examination is
published on the Internet through the DGCA Website.
In the office of Bureau of Civil Aviation Security (BCAS)
their Website http://bcasindia.nic.in has been designed,
developed and launched. This site contains up-to-date
information like Organizational details, Training details,
Circulars to Public, Information to air Passengers etc. This
site also contains restricted information pages through
which authorised officials can view circulars, AVSEC
orders & restricted documents.
2.7 PUBLIC GRIEVANCE REDRESSAL
MACHINERY
Public Grievance Redress Machinery (PGRM) in the
Ministry of Civil Aviation is headed by a Joint Secretary
who has been designated as the “Public Grievance
Officer”. All organisations under the Ministry too have
full-fledged grievance redress machinery headed by
designated “Nodal Officer”, for dealing with the grievances
received by them through various sources. Instructions
issued by the Department of Administrative Reforms and
Public Grievances with regard to observance of every
Wednesday as meeting-less day, display of name / details
of the Public Grievance Officer, picking-up of grievances
appearing in newspaper columns for necessary remedial
action, fixation of time limits etc. are being implemented.
Employees with direct public interface are being identified
and sent to training programmes by the respective
organisations so as to sensitize them for careful handling
of the assigned tasks. The position of public grievances
is being closely monitored in the Ministry with all the
organisations under its control.
2.8 ADMINISTRATIVE & STAFF
GRIEVANCE REDRESSAL MECHANISM
Staff Grievance Cells under designated Staff Grievance
Officers are functioning in the Ministry and all its
organisations, for speedy disposal of complaints and
representations of the serving employees.
All cases regarding revision of pension/ family pension
in respect of old pensioners and their families consequent
upon the implementation of the recommendations of the
Fifth Pay Commission have been settled by the Staff
Grievance Cell in the Ministry within the given time frame.
Payment of pension and other retirement benefits were
also promptly settled.
14

Annual Report 2004-2005
15
To ensure punctuality and discipline, periodical and
surprise checks were made. Harmonious relationship was
maintained with the members of the staff.
2.9 WELFARE OF MINORITIES
Government’s 15-point directive about the welfare of
minorities, inter-alia, envisages that when large-scale
employment opportunities are provided by the Railways,
Nationalised Banks and Public Sector Enterprises, it
should be ensured that special consideration is given
to recruitment from minority communities. All public
enterprises under the administrative purview of this
Ministry have been asked to comply with the directive of
the Government and also to continuously monitor the
progress of implementation of this programme. Periodical
returns from all the organisations under the Ministry are
called for to watch the compliance/ progress.
2.10 VIGILANCE MATTERS
The Vigilance Unit of the Ministry is headed by a Chief
Vigilance Officer (CVO) of the rank of Joint Secretary
appointed in consultation with the Central Vigilance
Commission, who functions as the nodal point in the
vigilance set up of the Ministry. The secretarial assistance
to the CVO in the Ministry is given by the Director, Under
Secretary and Vigilance Unit of the Ministry. The Vigilance
Unit in the Ministry inter-alia, monitors and coordinates
vigilance activities of the offices and Public Sector
Undertakings/Autonomous Body under its administrative
control.
Preventive vigilance continues to receive priority attention
with primary emphasis on identification of sensitive/prone
areas for malpractice and temptation. The guidelines /
instructions issued by the Department of Personnel &
Training and Central Vigilance Commission from time to
time in this regard are followed.
The post of Chief Vigilance Officer, Airports Authority of
India was filled up in July 2004 with the approval of
competent authority. However, consequent upon
appointment as Joint Secretary, National Commission
under the Ministry of Small Scale Industries with effect
from the forenoon of 11
th
November 2004 CVO, AAI
demitted the office on the same day. Proposal has been
sent to DOPT for consideration of a suitable candidate
for appointment as CVO, AAI. Vigilance work pertaining
to AAI has been entrusted to the Chairman, AAI in
addition to his own duties with effect from 1
st
December
2004.
In pursuance of Central Vigilance Commission’s
directions, ‘Vigilance Awareness Week’ was observed in
the Ministry from 1
st
November to 6
th
November 2004.
Secretary, Ministry of Civil Aviation administered the
‘PLEDGE’ to all the employees of the Ministry on 1
st
November 2004.
15
Ministry of Civil Aviation
16
In the main Ministry, during the year 2004-2005, there
were 4 pending complaints received from Central Vigilance
Commission. out of 9 pending disciplinary / vigilance
cases 4 cases have since been disposed off.
2.11 WELFARE OF SCs/STs/OBCs
A Cell exists in the Ministry of Civil Aviation for liaison
work relating to reservation for Scheduled Castes and
Scheduled Tribes and Other Backward Classes in posts
and services in the Ministry and its various organisations.
Similar cells also exist in various organisations under the
control of this Ministry. The orders / instructions issued
by the Government in regard to reservation for Scheduled
Castes / Scheduled Tribes and Other Backward Classes
from time to time, are brought to the notice of all the
organisations under the Ministry for implementation. All
periodical returns on the subject are regularly furnished
to the Department of Personnel & Training and Ministry
of Social Justice & Empowerment. Representations/
complaints /grievance petitions received from Scheduled
Castes / Scheduled Tribes employees / Associations are
examined and remedial action taken wherever required.
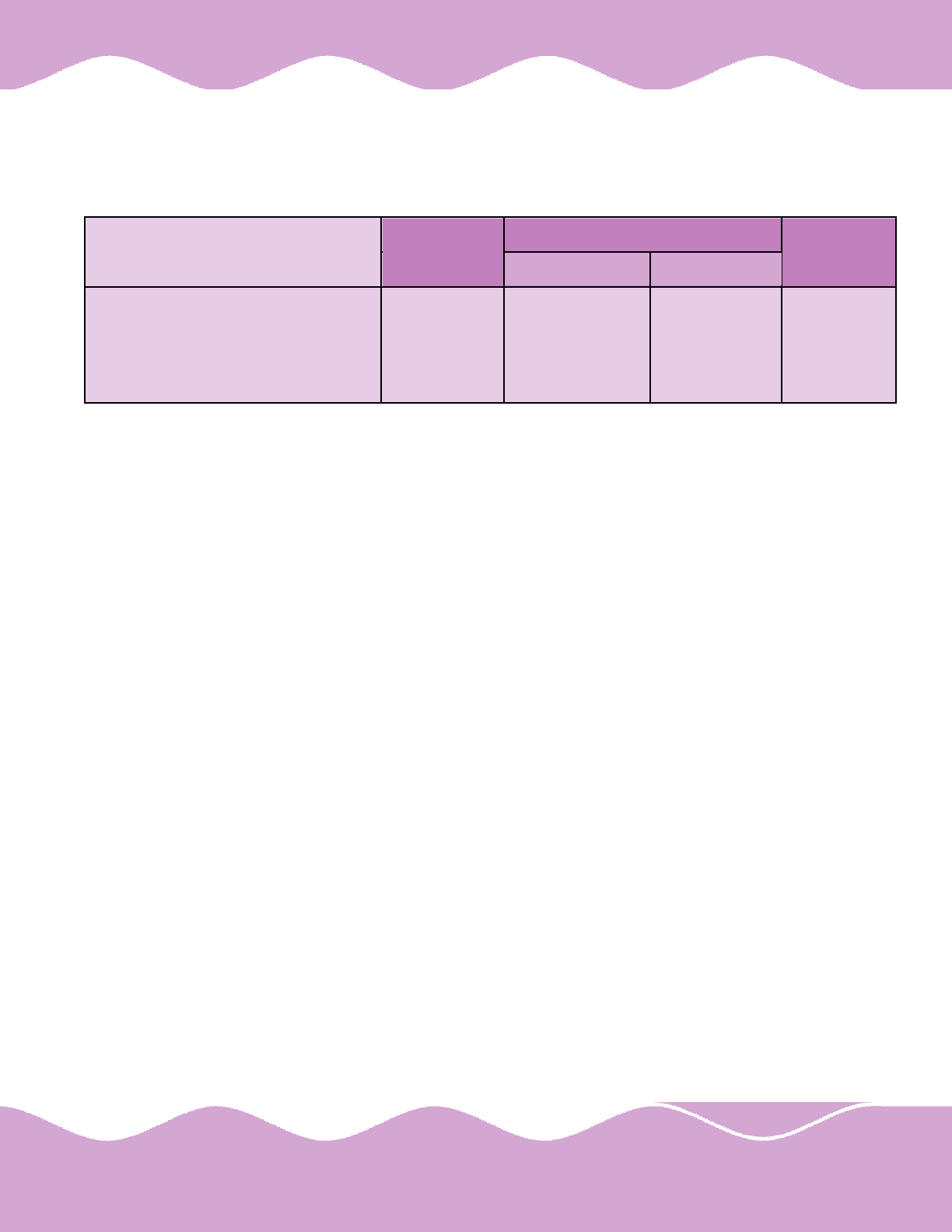
As on 31.12.2004, the representation of Scheduled Castes
and Scheduled Tribes employees in the Ministry and
various Organisations under its control, is as under: -
Name of the Total No. of Total No. Percentage (%) Total No. Percentage (%)
Organisation Employees of SC Employees of ST Employees
(1) (2) (3) (4) (5) (6)
Ministry (Main) 215 46 21.39 9 5.18
DGCA 523 110 21.00 31 5.90
BCAS 237 28 11.81 6 2.53
CRS 130 23 17.70 08 6.15
IGRUA 219 42 19.17 01 0.45
A I 15111 3550 23.49 1043 6.90
I A 18454 3570 19.34 1161 6.29
A A I 19811 5079 25.64 1084 5.47
PHHL 595 89 14.95 39 6.55
HCI 1724 464 26.90 91 5.27
16

Annual Report 2004-2005
17
••
••
• Fix responsibility for any delay caused in
settlement of pension, provident fund, gratuity and
other retirement benefits.
During the lean season, Air India offers special Senior
Citizen fares on the USA / UK/ Europe routes for those
aged 60 years and above. These discounts ranged
between 30-40% and are subject to certain black-out
periods. Air India also offers a 55% discount to senior
Citizens on its domestic routes. These were applicable to
women aged 63 years and above and men aged 65 years
and above. However, effective 6.12.2004, the age limit for
both men and women has been reduced to 60 years and
above. Air India takes utmost care of the senior citizens
and provides special handling at the airports, wheel chairs
on departures/ arrivals, choice of seat allocation on the
flight and choice of any special meal to the requested at
the time of making the reservations.
Indian Airlines offers 50% discount on the fare component
to senior citizens for travel in Economy Class on the
domestic sector. The concession is available for men
who are 65 years and above and women who are 63 years
and above. Special requests of Senior Citizen’s like wheel-
chairs, special meals on board etc. are taken care of.
2.13 PROTECTION OF ENVIRONMENT
Keeping in view the guidelines of the Ministry of Forests
and Environment all the organisations under this Ministry
were given instructions to make every effort to protect
the environment.
2.12 WELFARE OF SENIOR CITIZENS
In accordance with the guidelines issued by Ministry of
Social Justice & Empowerment, as envisaged in the
National Policy on Older Persons, instructions have been
issued to all concerned Organisations under this Ministry
to ensure prompt, fair and humane treatment for older
persons. Instructions were issued to -
••
••
• Remove all physical barriers to facilitate easy entry,
movement and exit at all airports and in airlines;
••
••
• Change the design of the frisking booths in the
security hold area so that older persons are not
required to climb steps and step down while
undergoing security checks;
••
••
• Pay special attention for providing help / assistance
to older persons particularly after alighting from the
taxi at the airports till the person reaches the check-
in counters;
••
••
• Pay special attention to older persons and those
needing assistance at the booking offices of airlines;
••
••
• Give preference in reservation and earmarking of seats
in the airlines;
••
••
• Give widows special consideration in the matter of
settlement of benefits accruing / compassionate
appointments on the demise of the spouse;
17

Ministry of Civil Aviation
18
2.14 OFFICIAL LANGUAGE
In this Ministry, Hindi Salahkar Samiti, under the
chairmanship of the Hon’ble Minister render proper
advice on the implementation of the provisions laid under
Official Languages Act, 1963 and the Official Languages
Rules, 1976 framed there-under. The Samiti met in Delhi
on 18
th
November, 2004 wherein comprehensive
discussion took place to explore measures for progressive
use of Official Language in the Ministry as well as its
Attached/ Subordinate Offices/ Undertakings.
On the eve of Hindi Day, a table-work competition was
held. During the period 23
rd
August to 10
th
September,
2004 all the Officers/ Officials of the Ministry as well as
the Heads of Subordinate Organisations were encouraged
to execute their office-work originally in Hindi. A Review
Committee has evaluated various competitions held in
Hindi during the period. The competition was held
between the officers/ officials in three categories. First
category was between L.D.Cs. to Assistants, second was
between Section Officers to Secretary of the Ministry
and third was between the Heads of all the Subordinate
Organisations under this Ministry and the winners who
discharged their maximum office-work in Hindi were
awarded prizes – First Prize worth Rs.5000/- Second Prize
worth Rs. 4000/-, Third Prize worth Rs.3000/- and Fourth
Prize worth Rs. 2000/- as consolation. In addition, Hindi
Essay-Writing, Hindi-Typing and Hindi-Stenography
competitions were also held. The winners of these
competitions have been awarded the prizes – First Prize
worth Rs. 2500/-, Second prize worth Rs. 2000/-, Third
prize worth Rs.1500/- and Fourth prize worth Rs.800/- as
consolation.
The Ministry and its Organisations carried out
inspections to ensure proper implementation of Official
Language Policy and suggested suitable measures for
improvement.
2.15 ACCOUNTING ORGANISATION
Secretary (Civil Aviation) is the Chief Accounting
Authority of the Ministry of Civil Aviation. The
Additional Secretary & Financial Advisor and the
Financial Controller assist the Chief Accounting
Authority. The accounting organisation of the Ministry
is looked after by the Financial Controller, who performs
duties with the assistance of an Assistant Financial
Controller and 8 Pay & Accounts Officers (PAOs). The
accounting organisation comprises of the Principal
Accounts Office, Internal Audit Wing, 2 Pay & Accounts
Offices at Delhi and three outstation Pay & Accounts
Offices at Mumbai, Kolkata and Chennai. The Principal
Accounts Office consolidates the accounts of the entire
Ministry and other related matters, apart from co-
18
Annual Report 2004-2005
19
ordinating the administrative functions of all the PAOs.
Monthly accounts are compiled by PAOs on computer
with the help of a package called ‘COMPACT’. At the
close of each financial year, the Principal Accounts Office
consolidates accounts of the Ministry through the
package ‘CONTACT’ and are sent to Ministry of Finance,
Controller General of Accounts (CGA). Principal Accounts
Office also compiles Appropriation Accounts, Finance
Accounts and Statement of Central Transactions,
pertaining to the Ministry.
Internal audit - The Internal Audit Organisation in the
Ministry of Civil Aviation is headed by Financial
Controller who is assisted by 1 Assistant Financial
Controller, 1 Sr. Accounts Officer and 4 Asstt. Accounts
Officers. This wing is responsible for internal inspection
of accounts maintained by the Ministry and its
subordinate and attached offices located across the
country. The work of audit is carried out in accordance
with the instructions and procedures laid down in the
Internal Audit Manual. Internal Audit Wing ensures that
rules, regulations relating to accounting and financial
system are properly followed, and serious irregularities /
omissions etc. seen during Internal Audit are brought to
the notice of the Heads of Departments for remedial action.
2.16 AUDIT PARAS
A total of 24 audit paras are outstanding as on 17.1.2005.
Action Taken Notes (ATNs) have been sent to audit in
respect of 18 paras. Of these 18 paras, vetted remarks of
audit have been received in respect of 6 paras and replies
of audit in respect of remaining 12 paras are awaited.
Further action is being taken in respect of those paras
where vetted remarks of audit have been received.
Organisation-wise break-up of pending audit paras is as
under:-
Name of the organisation Pending
Paras
1. Ministry of Civil Aviation (Main) 3
2. Airports Authority of India 9
3. Air India Limited 4
4. Indian Airlines Limited 8
Total 24
Status of audit observations listed in letter No.2100/E.Coord/
2003 dated 8.12.04 from Department of Expenditure has been
indicated in Annexure II
19
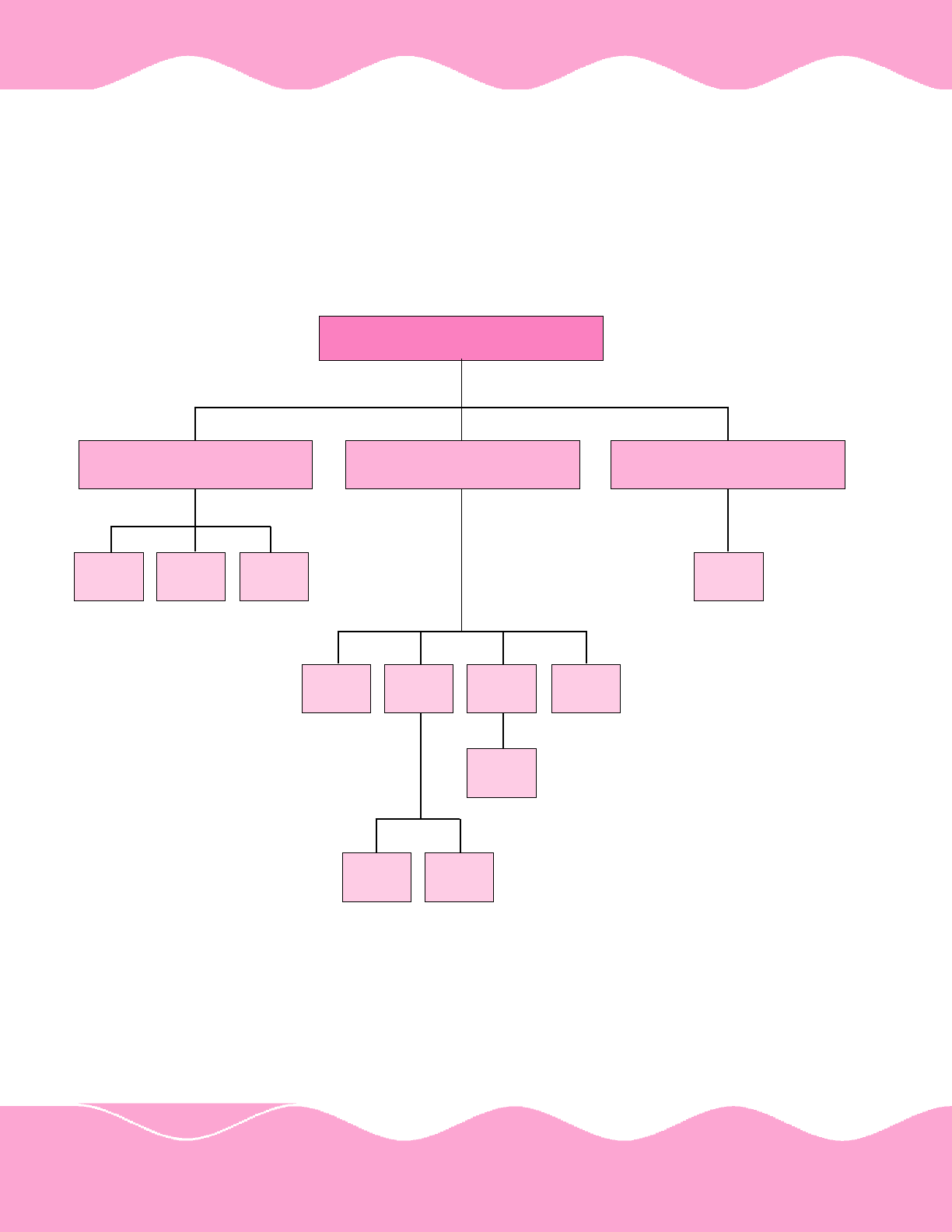
Ministry of Civil Aviation
20
ORGANISATIONAL SET-UP OF THE MINISTRY OF CIVIL AVIATION
Ministry of Civil Aviation
Attached / Subordinate
Organisations
Public Sector Undertakings Autonomous Body
DGCA
BCAS
CRS
IGRUA
AAI AI IA PHHL
HCIL AICL
Alliance
Air
ANNEXURE - I
20
Annual Report 2004-2005
21
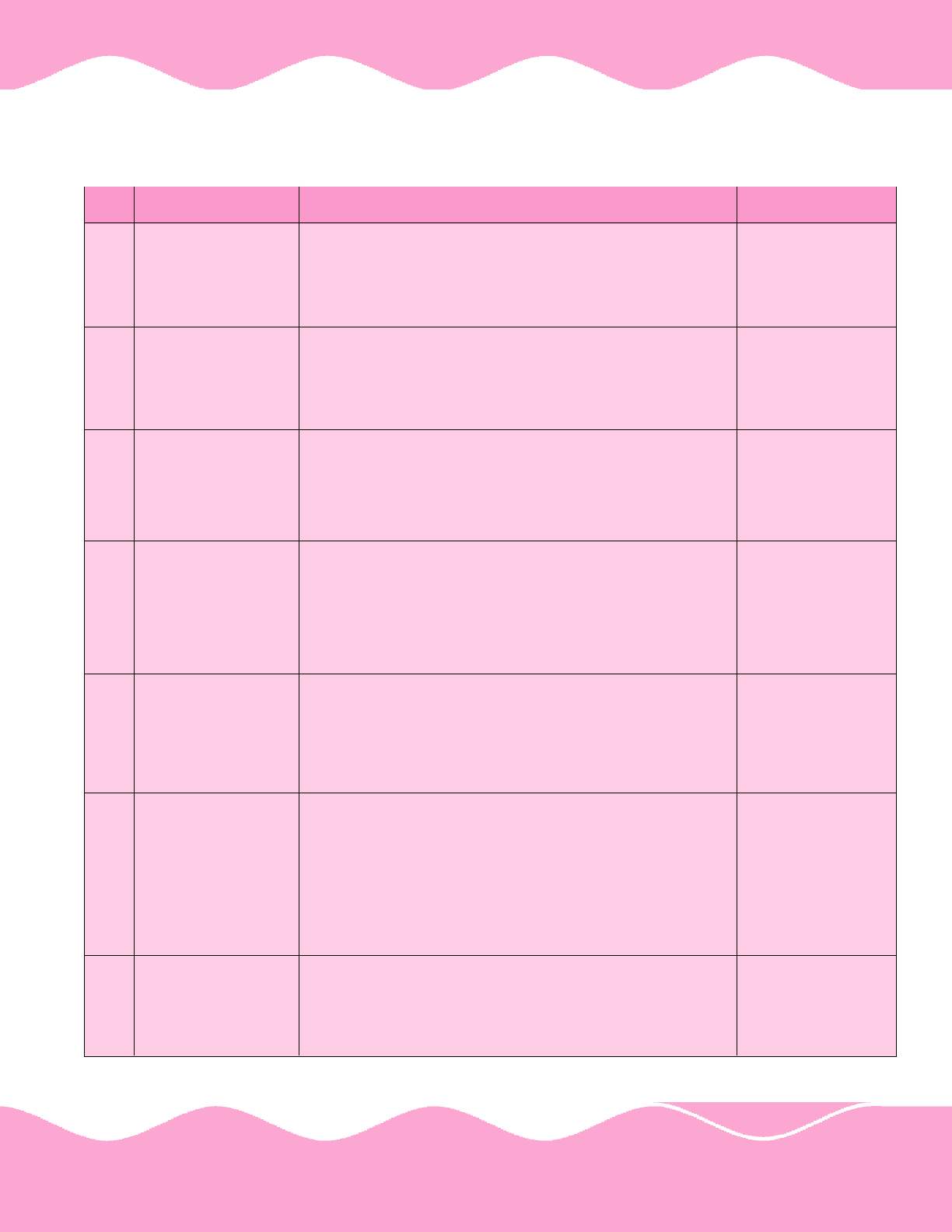
ANNEXURE - II
Para No. 2.1.1 of
Report No.3 of 2004
(Commercial)
Undercharging of lease rent from a private party and
reduction of turnover levy resulted in foregoing of revenue
of Rs.145.69 crore by Airports Authority of India (AAI) over
the lease period from June 2002.
Further comments
of AAI for
preparation of ATN
are awaited.
Para No. 2.1.2 of
Report No.3 of 2004
(Commercial)
AAI incurred infructuous expenditure of Rs.8.23 crore on
extension of runway and construction of boundary wall at
Jammu Airport, as it had to foreclose the contracts in January
2002 for want of clear possession of land.
2. Further comments
of AAI for
preparation of ATN
are awaited.
Para No. 2.2.2 of
Report No.3 of 2004
(Commercial)
Due to negligence AIL did not inform its property status to
the local council authorities at London, which resulted in
avoidable payment of Rs.4.25 crore as council tax till March
2003 and continues to cost Rs.85 lakh per annum till corrective
action is taken by the Management.
3.
Settled. ATN sent to
Lok Sabha
Secretariat on
7.10.04.
Para No. 2.2.1 of
Report No.3 of 2004
(Commercial)
In appropriate decisions of the Corporate Management in
sanctioning advances to its employees, which were
subsequently written off resulted in loss of Rs.26.74 crore up
to March 2002 to the Air India Limited (AIL).
4.
Settled. ATN sent to
Lok Sabha
Secretariat on
27.7.04.
Para No. 2.2.3 of
Report No.3 of 2004
(Commercial)
Absence of effective stores management in AIL resulted in an
avoidable loss of Rs.1.87 crore due to shelf life expiry
perishable and non-perishable aircraft materials, besides loss of
Rs.1.47 crore as interest on blocked funds up to June 2003. In addition
there was customs duty liability of Rs.3.01 crore.
Settled. ATN sent to
Lok Sabha
Secretariat on 5.8.04.
5.
Para No. 2.3.1 of
Report No.3 of 2004
(Commercial)
Indian Airlines Limited lost Rs.3.49 crore incurred on bank
charges and litigation cost up to June 2003 as it had transferred
fund towards lease charges of aircraft without ensuring the
capability of the lessor to arrange aircraft on lease basis.
ATN sent to audit on
2.9.04. Vetted
remarks of audit
received on 1.11.04.
Final ATN is being
sent to Lok Sabha
Secretariat.
6.
Para No. 2.4.1 of
Report No.3 of 2004
(Commercial)
Pawan Hans Helicopters Limited has incurred infructuous
expenditure of Rs.9.86 crore up to March 2002 on injudicious
procurement of stores and spares.
Settled. ATN sent to
Lok Sabha
Secretariat on
16.7.04.
7.
Gist of audit observation Status as on 17.1.05
S. N.
Para/ Report No.
1.
21
Ministry of Civil Aviation
22
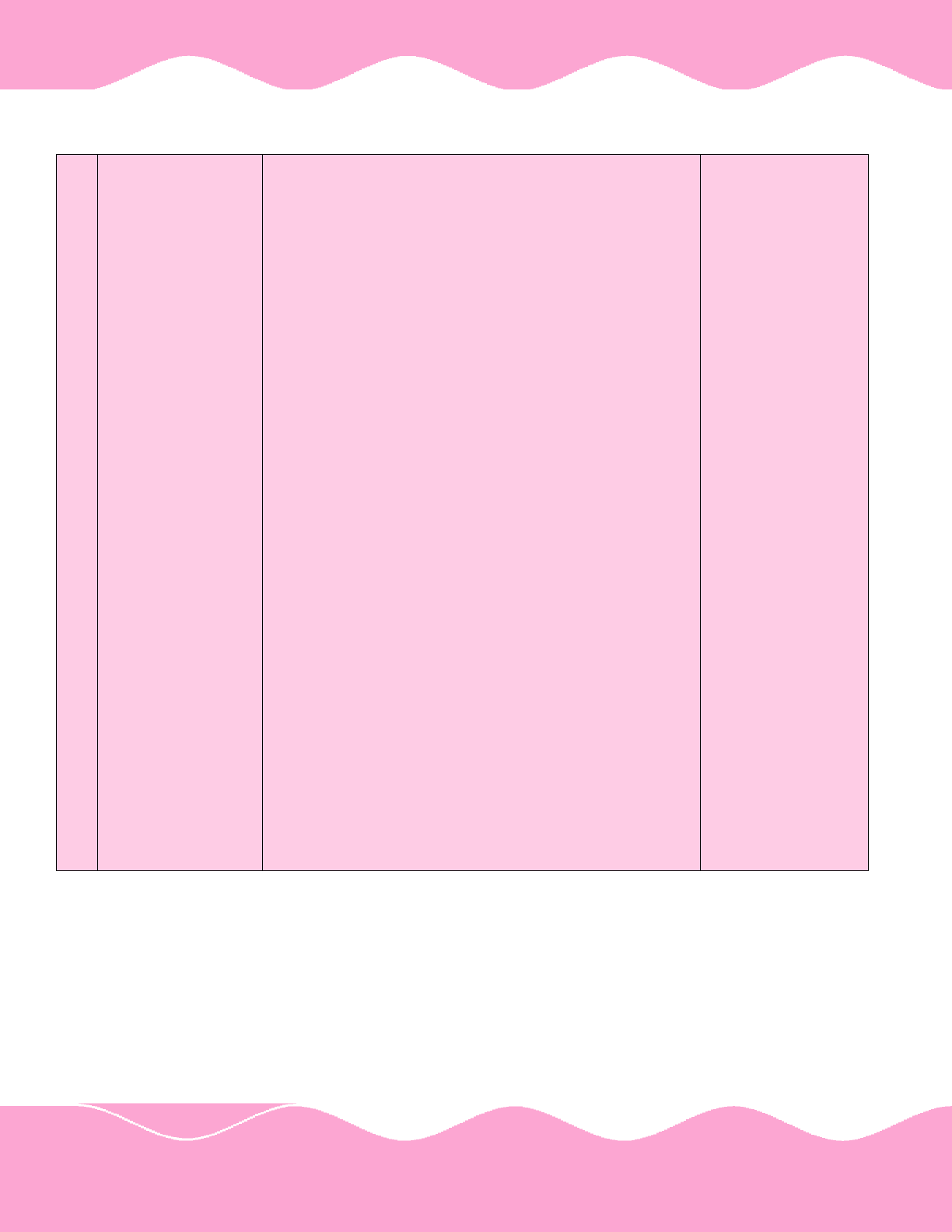
Chapter II of Report
No.4 of 2004
(Commercial)
Indian Airlines Limited(Company) formulated various
schemes for the payment of wages, allowances and
productivity linked incentives (PLI) to its employees during
the last five years ended March 2003 without linking them to
financial performance of the Company, continuance of which
would have adverse impact on the financial viability and
sustainability of the Company on short and long-term basis.
Despite the increased payment of PLI, the overall profitability
of the Company did not improve. As the Company did not
follow its approved wage policy, this resulted in outflow of
resources in excess of inflow. Thus, the Company made total
PLI payment of Rs.1449.02 crore during April 1998 to March
2003 which exceeded the losses of Rs.585.83 crore incurred
during above period. Although the number of employees of
the Company had decreased by 10.93 per cent during the
period 1998-99 to 2002-03, the total employee cost increased
by Rs.143.05 crore. The Company had to pay increased cost
of employees out of additional revenue of Rs.708.57 crore
generated from the periodical upward revisions of fare.
The Company has paid productivity allowance/fixed
productivity allowance/special productivity allowance
amounting to Rs.248.12 crore from April 1998 to March 2003
without measurable linkage to the performance level
achieved by the employees. The Company also paid Rs.13.57
crore to its Cabin Crew and Pilots as out of pocket expenses
over and above the terms of settlement entered into with
their respective Unions.
8.
ATN sent to audit on
28.6.04. Vetted
remarks of audit
received on 27.9.04.
Comments of IA on
vetted remarks of
audit are awaited.
*****
22
Annual Report 2004-2005
23
3.1 INTRODUCTION
The Directorate General of Civil Aviation is the principal
regulatory body in the field of civil aviation. It is not only
responsible for regulation of air transport services to/
from/within India, for formulation and enforcement of civil
air regulations, air safety and airworthiness standards
but also co-ordinates all regulatory functions with
International Civil Aviation Organisation (ICAO).
3.2 ORGANISATION
The Directorate General of Civil Aviation has its
Headquarters in New Delhi. This organisation is
headed by the Director General of Civil Aviation
who is assisted by Joint Director General and Deputy
Director General. The Director General has the following
Directorates under him: -
– Directorate of Regulation & Information.
– Directorate of Air Transport.
– Directorate of Airworthiness.
– Directorate of Air Safety.
– Directorate of Training & Licensing.
– Directorate of Aerodrome Standards.
– Directorate of Flying Training.
– Directorate of Flight Inspection.
– Directorate of Research & Development
– Directorate of Administration.
Directorate General of
Civil Aviation
3
3.3 FUNCTIONS
The main function of the Directorate General of Civil
Aviation is to regulate all civil aviation matter. Some of
the salient functions are as under:-
• Regualtion of air transport services to /from/within
India in accordance with the provisions of the Aircraft
rules, 1937, including bilateral and multilateral
agreements with foreign countries and the policy
pronouncements of the government;
••
••
• Registration of civil aircraft;
••
••
• Laying down airworthiness requirement for civil
aircraft registered in India and grant of Certificate of
Airworthiness to such aircraft;
••
••
• Licensing of pilots, aircraft maintenance engineers
and monitoring of flight crew standards;
••
••
• Licensing of aerodromes and air carriers;
••
••
• Rendering advice to the Government on matters
pertaining to civil aviation;
••
••
• Processing amendments to Aircraft Act, 1934 and
the Aircraft Rules 1937, and other Acts relating to
aviation, with a view to implementing in India the
provisions of the Chicago Convention and Annexes
thereto and other International Conventions relating
to aviation;
23

Ministry of Civil Aviation
24
••
••
• Co-ordination of the work relating to International
Civil Aviation Organisation and sending replies to
state letters after consulting the concerned agencies;
••
••
• Investigation of minor air accidents and incidents
and rendering technical assistance to the Courts/
Committees of Inquiry;
••
••
• Supervision of training activities of Flying/Gliding
Clubs;
••
••
• Development of light aircraft, gliders and winches;
••
••
• Type certification of aircraft.
3.4 AIR SERVICES AGREEMENTS
During 01 April 2004 to 31 December,2004, bilateral air
talks were held with Brazil, Australia and United Kingdom
to review the existing bilateral arrangements, as a result
of this, additional capacity to the tune of 12,000 seats per
week was granted to the designated airlines of India and
the respective foreign countries.
The designated airlines of Sri Lanka and ASEAN
countries were permitted to operate any number of
services to specified 18 points of tourist interest in India,
including Cochin, Trivandrum and Calicut subject to India
receiving reciprocal rights.
3.5 AIR TRANSPORT
••
••
• Tourist Charters
The tourist charter guidelines have been further
liberalized vide Aeronautical Information Circular No.
5/2004 dated 29-07-2004. Now Indian Passport holders
are also permitted to travel by tourist charter flights
under Inclusive Tourist Package (ITP). The ITP flights
can operate to any airport in India without any
limitation on frequency of flights or size of aircraft.
The earlier clause requiring a minimum expenditure
by each tourist in foreign exchange has been
abolished. A total of 705 charter flights were operated
to India from January to December, 2004 bringing in
1,55,495 foreign tourists. Relief flights to Sri Lanka,
Maldives, Thailand and Indonesia were granted
priority in issuing permission to bring relief for the
Tsunami victims.
••
••
• Non-Scheduled Operator’s Permit
As on 31
st
December, 2004, a total of 37 companies
were holding Non-Scheduled Operator’s Permit.
••
••
• Domestic Scheduled Operators
In addition to Air India, Indian Airlines and Alliance
Air, the following private operators had the
permission to operate domestic scheduled air
transport services:
– Jet Airways
– Sahara India Airlines
– Deccan Aviation Pvt. Ltd.
– Blue Dart Aviation Pvt. Ltd (only cargo)
During January to December, 2004, a total of 2,50,141 flights
were operated by the domestic scheduled operators
carrying a total of 17.589 million passengers.
24

Annual Report 2004-2005
25
3.6 INTERNATIONAL CO-OPERATION
••
••
• The following activities were undertaken for
International co-operation. COSCAP-SA Steering
Committee Meeting was held at Hotel Ashok, New
Delhi, India from 29
th
November to 1
st
December 2004.
The meeting was attended by the Directors General
of Civil Aviation or their representative of the
participating SAARC States (India, Pakistan, Nepal,
Bhutan, Bangladesh and Maldives), representatives
from ICAO Headquarters Montreal and its Regional
Office for Asia Pacific Region Bangkok, Federal
Aviation Administration (FAA) of USA, Joint
Aviation Authority ( JAA) of Europe, European Union
(EU), donor agencies like aircraft manufacturers -
Boeing and Airbus and other international aviation
agencies like the International Air Transport
Association (IATA) and the European Aviation
Safety Agency (EASA). The programme was aimed
at assisting the participant States in developing their
air regulations and standards and to improve their
independent oversight capabilities.
••
••
• One session of Indo-Russian Working Group on Civil
Aviation was organized this year. This session was
held under the bilateral agreement between the
Government of Russia and Government of India to
finalize the Implementation Procedures of
Airworthiness (IPA) for mutual acceptance of civil
aeronautical products.
••
••
• A meeting between representatives from Civil
Aviation Authority of Israel (CAAI) and Directorate
General of Civil Aviation (DGCA), India, was
organized this year. This session was held to discuss
the modalities of Bilateral Aviation Safety Agreement
(BASA) between the Government of Israel and
Government of India, for them to accept and operate
HAL manufactured ALH Helicopter (DHRUV).
••
••
• Flight Inspection Directorate organized 8 courses
under EU-India Civil Aviation Project and one course
under COSCAP-SA.
• The European Union Project aimed at establishing a
solid relationship to simulate
co-operation and to further business linkages
between the EU and the Indian aviation sector has
been finalized. The project will increase Indian
awareness of the EU industry practices including
airworthiness and safeguard standards of aviation
safety in the region. Further, the project will provide
for the development of Indian companies in the sector
to enable full growth potential to be met in part
through the assistance in the development of airport
management, modern product support maintenance
and overhaul techniques and commercial pilot
training. The project will concentrate on a programme
of co-operation between European industry and
regulatory authorities and Indian industry in 7 specific
areas of Airworthiness, Airline management, Air
25

Ministry of Civil Aviation
26
SAARC countries, namely India, Pakistan, Nepal,
Bhutan, Bangladesh, Sri Lanka and Maldives. The
programme is aimed in assisting the participant States
in developing their air regulations and standards and
to improve their independent oversight capabilities.
The programme is managed by a Steering Committee
consisting of the Directors General of the seven
States. ICAO Headquarters and Regional Office
Bangkok carry out overall supervision and provide
guidance to the programme. The seven participating
States contribute finances to the programme in
accordance with the services rendered to the
individual State and as determined by ICAO,
Headquarters. During the past five years, a large
number of officers of DGCA and people from the
aviation industry have been trained under the
programme.
Following courses have been conducted under the
COSCAP during the period January, 2004 to December,
2004.
* Workshop on Safety Management systems.
* ETOPS Course.
* Aviation Medicine Course.
* Cabin safety workshop course.
3.8 EXAMINATION
Central Examination Organisation has been conducting
examinations throughout the year for the issue and/ or
extension of Flight Crew and Aircraft Maintenance
Engineer’s License at various Examination centers and
the schedule of examinations of the complete year is
Traffic Management, Product Support, Cooperation
of technologies for economies success in the
Aerospace industry, Pilot/instructor training and
Airport Activities.
3.7 AIRWORTHINESS
••
••
• Registration of aircraft
As on 31st December 2004, there were 1150 aircraft
(including micro light, gliders and balloons) on the
Indian civil register. Of these, 60 aircraft were
registered and 49 aircraft were deregistered during
the period 1
st
April to 31
st
December 2004.
••
••
• Licensing of Aircraft Maintenance Engineers
A total of 6034 Aircraft Maintenance Engineers
(AME) Licenses including Basic Licenses and 282
Flight Engineers (FE) Licenses have been issued so
far, of which 200 AME licenses have been issued
during the period 1
st
April to 31
st
December 2004.
••
••
• Approval of firms
So far, a total of 1671 firms have been approved for
manufacture, maintenance, testing, storage etc. of
aircraft, aircraft components/equipment. Out of these,
50 are foreign firms.
••
••
• Co-operative Development of Operational Safety
and Continuing Airworthiness- South Asia
(COSCAP-SA)
The Co-operative Development of Operational
Safety and Continuing Airworthiness-South Asia
under the aegis of ICAO is a joint programme of seven
26
Annual Report 2004-2005
27
placed well in time on DGCA web site www.dgca.nic.in.
The detailed data of the examinations conducted during
the period from 1
st
April 2004 to 31
st
December 2004 are as
follows: -
3.9 TRAINING AND LICENSING OF
AIRCREW
••
••
• Basic Flying Training
The flying /gliding training is provided by various
Flying/ Gliding Clubs and institutes spread all over
the country. Presently there are 39 flying clubs/
institutes. IGRUA is also imparting flying training to
student pilots in India. Eleven of the above mentioned
institutes are privately owned.
A Government Gliding Centre at Pune run by the
Directorate General of Civil Aviation provides gliding
training. Besides this there are 5 gliding clubs having
5 gliding branches.
A total of 22896 instructional hours were performed
by the Flying Clubs during April to December 2004.
A total of 10021 launches were performed by the
Gliding Clubs during this period. DGCA released an
amount of Rs. 14,11,694/- to the flying clubs under
the flying subvention scheme. DGCA also conducted
examination to select 40 SC/ST candidates for award
of free flying up to PPL. Nine oral exams for FIR(A)/
AFIR(A) and 19 inspections of Flying Clubs have
been carried out. Nine approvals have been granted
to CFI/CFII in various flying clubs.
••
••
• Licensing of air crew
During 01
st
April to 31
st
December, 2004, a total of 778
pilots’ licences/ ratings were issued by the DGCA.
In addition, 97 foreign pilots licenses were validated
under the Aircraft Rules, 1937.
3.10 FLIGHT INSPECTION
During the year 2004, Flight Inspection Directorate carried
out the following major activities: -
••
••
• Surveillance checks of Scheduled Operators were
conducted including 80 Cockpit En-route
Inspections, 27 Cabin Inspections, 20 Station Facility
Inspections and 23 Ramp Inspections were carried
out in respect of scheduled airlines.
AME PILOT TOTAL
Technical General
No. of applicants 11,874 4,045 5,049 20,968
No. of papers 22,163 6,611 10,889 39,663
No. of special Examinations held 02 20 15 37
The results of successful candidates are also displayed on DGCA Website www.dgca.nic.in besides being made available on E-mail
addresses to all Regional/ Sub-Regional offices of the DGCA.
27

Ministry of Civil Aviation
28
••
••
• Simulators of Air India and Jet Airways at Mumbai,
Indian Airlines at Hyderabad and of Indira Gandhi
Rashtriya Uran Academy (IGRUA) at Rae Bareilly,
were evaluated/approved.
••
••
• Approval of Indira Gandhi Rastriya Uran Academy
(IGRUA) as Flight Training Institute was revalidated.
••
••
• Three training Institutes of Ministry of Defence were
revalidated. Flight Training Device (B.737-300) of M/
S Jet Airways was evaluated and approved.
••
••
• Main Base Inspections of Indian Airlines, Jet
Airways, Sahara Airlines and Air India were
conducted.
••
••
• 48 Training Captains of various scheduled airlines
were granted approval to function as Check Pilot/
Instructors and Examiners.
••
••
• Training approvals were granted to 110 pilots/ co-
pilots of Air India, Indian Airlines and Jet Airways
were authorized to carry out ILS CAT-II/ CAT-IIIA/
CAT-IIIB Operations.
••
••
• Three Standard Operating Circulars were issued to
enhance safety of aircraft operations.
••
••
• M/S Air Deccan and M/s Kingfisher Airlines were
given approval for A.320 Endorsement Training
Programme in respect of their pilots for Scheduled
Operations.
••
••
• 101 Flight Dispatchers of scheduled airlines were
approved/ revalidated.
••
••
• During the year 2004, Standard Operating Procedure
for operations to 9 new stations and critical airfields
were examined and approved.
3.11 A ER ODR OME STANDARDS
During the year 2004, the following important activities
were undertaken:
••
••
• The operational authorization for scheduled airline
operations both domestic and international to/from
Cochin International Airport (CIAL) was renewed.
••
••
• Renewal of operational authorization was granted to
Air Deccan for helicopter operations from Katra and
Sanjhichhat helipads owned by Mata Vaishno Devi
Shrine Board.
••
••
• Operational authorization was renewed to privately
owned rooftop helipad, of M/s ESSAR at Mumbai
and at Sahara Shahar, Lucknow and renewal of
licences in private category for sixteen airfields was
carried out.
••
••
• Handling court cases regarding demolition action
under Section 9A of the Aircraft Act, 1934 w.r.t.
Hyderabad airport and also arranging for appeal
against the already issued demolition orders for the
removal of obstructions at Hydrabad airport. In
addition Court Cases regarding compensation at Port
Blair and coordination with MCA and Ministry of
Law for appointment of arbitrator under the
Aircraft Act, 1934.
••
••
• Surveillance and monitoring of CAT-II/IIIA
installation of visual guidance facilities at the IGI
Airport.
••
••
• Finalized Airspace Structure of Bangalore
International Airport and submitted to MCA and also
finalized Airspace structure of proposed Hyderabad
International Airport Ltd. (HIAL) in association with
AAI and other concerned agencies.
28

Annual Report 2004-2005
29
••
••
• Availability of extended runway at Port Blair for
operations of IAL A-320 aircraft by removing the
obstacles. IAL A-320 operations commenced from
March 2004.
••
••
• Participated in meeting for ATS co-ordination in Bay
of Bengal with neighboring countries, RVSM
implementation annual review, ATS route network
review, Special Implementation Project (SIP) for filing
the differences conducted under the aegis of ICAO.
••
••
• Rules for Aerodrome licensing have been revised
and notified in accordance with ICAO guidelines and
Issued Civil Aviation Requirements on ‘Rules of
The Air’
••
••
• Inspected site for proposed aerodrome at Pokyang
by Government of Sikkim.
••
••
• Associated with proficiency checks of ATCOs of
AAI at Delhi and Chennai airports to ensure
standards of their performance.
••
••
• Finalisation of danger area near Barnalla in
association with IAF and AAI.
••
••
• Processing and issue of NOC for Slaughter-house to
be constructed by MCD at Ghazipur.
••
••
• Follow-up of Universal Safety Oversight Audit
Program (USOAP).
••
••
• Coordination with AAI and flying clubs for air space
closure/ restriction for Independence Day/ Republic
Day celebration.
••
••
• Processing request for night operation at private
airfield JVSL Vidyanagar and at Sahara Shahar,
Lucknow.
••
••
• Inspection of aerodromes for commencing schedule
operations from airfields like Dehradun, Kanpur,
Jabalpur, Surat, Kolhapur etc. which were not having
schedule flight operations.
••
••
• Processing of applications for rooftop helipad at
Aditya Birla Foundation, Pune and Taj Wellington
Mews at Mumbai.
3.12 AIR SAFETY
••
••
• General
The Air Safety Directorate had carried out its duties
and responsibilities relating to investigation of minor
accidents and incidents, prevention of accidents/
incidents and birds strike prevention programme.
Under the accident prevention programme, in-flight
inspections of airlines, safety audits of airline
operators and various aerodromes along with the
facilities therein were carried out. Follow up action
was also taken on the recommendations emanating
from the inquiry reports of aircraft accidents/
incidents. The bird strike prevention programme was
undertaken at the airport level.
••
••
• Aircraft Accidents:
During the period 1
st
April to 31
st
December 2004,
there have been 4 notifiable accidents to Indian Civil
Registered Aircraft. All the accidents have been
investigated / are being investigated to find out
circumstances leading to the accidents. There were
516 incidents to various scheduled / non-scheduled
airlines. Out of these, 17 were serious incidents and
15 were air miss incidents. Action is taken on the
recommendations made in the investigation reports
to prevent reoccurrence.
29

Ministry of Civil Aviation
30
••
••
• Prevention Work
* Safety Audit of Airlines/ Operators:
Dedicated Safety Audit Teams of Air Safety
Directorate carried out safety audit of the
airlines/ operators for their operational,
engineering and other aviation oriented
management activities. During the period 1
st
April
2004 to 31
st
December 2004, nine safety audits of
airlines, Flying Academies & Institutes were
carried out along with three surveillance
inspections. The deficiencies pointed out in the
safety audit reports/ surveillance inspections
have been brought to the notice of the operators/
airlines/ concerned agencies for taking
necessary remedial action.
* Implementation of Recommendations made by
the Court/ Committee of Inquires/ Inspector of
Accidents: The safety recommendations
emanating from various court/ committee /
Inspector of accidents inquires into aircraft
accidents are followed up with various
concerned aviation agencies for their early
implementation.
* In-flight Cabin Inspection: Only one in-flight
inspection was carried out during this period
and necessary action was initiated on the
deficiencies observed.
* Pre-flight medical Check: During the period the
regional Air Safety Offices carried out random
checks with the help of breath analyzer for
presence of alcohol in the breath of operating
crew. A total of 12-flight crew were found
positive. Necessary action was taken by the
airlines on the concerned crew.
* Aerodrome Inspection: Six aerodrome
inspections were carried out during this
period and necessary actions were initiated
on the deficiencies observed.
3.13 RESEARCH & DEVELOPME
••
••
• Type Certification
The Type Certificate and Technical Certificates have
been issued to Advance Light Helicopter “ALH-Civil
Skid Version” (DHRUV) designed and developed by
M/s HAL, Banglore. A large number of documents
including design reports, drawings, flight test
reports, etc, were scrutinized by R&D Directorate
prior to this certification.
R&D Directorate is extensively involved in work
relating to type certification of ‘SARAS’ aircraft
being designed and developed by M/s.
National Aerospace Laboratories, Bangalore.
The structural assembly of SARAS has been
completed and the assembling of various
systems is under progress. The test flights of
this aircraft are in progress.
••
••
• Type Approval
R&D Directorate has been very actively involved in
coordinating the design, development and
qualification testing of a large number of indigenously
designed and developed products, appliances and
equipment for ALH and SARAS. Most of these units
are developed by M/s HAL, Lucknow. Type approval
of twenty-six items/accessories of ALH-Civil has been
accorded.
••
••
• Development of Certification Requirements
With a view to upgrade the Indian Civil Aviation
requirements at par with international standards, CAR
30

Annual Report 2004-2005
31
21 which describes the certification procedures of
aircraft and related products, has been developed in
consultation with European experts.
••
••
• Training of Officers
An expert from Joint Aviation Authority of European
Union is positioned at DGCA Hqrs. About 12 courses
were conducted on various topics, which were
attended by the officers of this directorate.
••
••
• Laboratory Activities
* More than 200 samples of aviation fuel and lubricants
were tested for the purpose of monitoring quality
control including VVIP flight fuel samples.
* About 2014 CVR cassettes and 711 FDR read-outs
drawn from various aircraft for monitoring crew
performance and recording integrity of recorders were
analysed and corrective action recommended.
* Assistance was provided by the R&D Directorate in
the laboratory investigations of failed components
of aircraft involved in accidents/incidents.
Investigation of 20 such cases were carried out.
* About 155 Welded specimens were tested for
issuance of welder competency certificate and 57
specimens of indigenously developed upholstery,
seat cover and carpets used for interior furnishing of
passenger aircraft were approved.
* All the approved Design Organizations have been
asked to update the Design & Engineering
Organisation Manual (DEOM) in line with the CAR-
21 requirements.
* One HANSA-3 aircraft manufactured by M/s
National Aerospace Laboratories, Bangalore was
procured by DGCA on 22.12.2004 and is being handed
over to a needy Flying Club/ Institution for training
of student pilots. R&D Directorate did all the
administrative work for this procurement and
allotment.
* The work of setting a new CVR/ FDR laboratory with
state-of-art equipment for routine monitoring of
performance and also for conclusive study/decoding
of CVR/ FDR data in case of incidents/ accidents is
almost complete. New premises have been
constructed for the laboratory. Computers along with
software and hardware required for analysis of flight
data have been procured.
3.14 ADMINISTRATION
••
••
• Implementation of official language policy
All the general orders, establishment orders and
notifications were issued bilingually in the office of
the Director General of Civil Aviation. Air Accident
Report, Statistical Report and Annual Report were
brought out in bilingual form.
During the year 20, employees were imparted training
in Hindi workshops. Various experts from other
offices were invited to deliver lectures in this
workshop. According to the instructions of Official
Language Department, some cassettes and
documentary films regarding progressive use of
Official Language were screened in this workshop.
Two employees were trained on Hindi typing and
one on Hindi stenography under the Hindi Teaching
31

Ministry of Civil Aviation
32
Scheme. In order to promote Hindi work on computers
‘Leap Office’ Hindi software was made available to
all the sub-ordinate offices.
During this period, various Hindi Competitions were
conducted and Hindi Day was celebrated
enthusiastically. The Director General gave
commendation certificates and cash awards to the
winners.
Eight officials were given cash awards for doing their
maximum work in Hindi under the Incentive Scheme
of Official language Department for doing original
noting/drafting in Hindi. One officer was given cash
award for giving maximum dictation in Hindi. Four
typists got incentive allowance for doing Hindi typing
along with English.
Hindi books were purchased from library fund to
ensure implementation of Official Language Policy.
Meetings of Official Language Implementation
Committee were conducted regularly in every quarter.
Subordinate offices were also inspected.
••
••
• Vigilance Activities
During the period, Shri P.K. Chattopadhyay, the Joint
Director General continued to function as Vigilance
Officer for DGCA office. Large size painted boards
have been displayed at all prominent places showing
the name, official and residential address and
telephone number of the Chief Vigilance Officer and
Vigilance Officer. Other instructions on the vigilance
matters, as and when received from the Ministries/
Central Vigilance Commission are scrupulously
followed and circulated.
Out of the eight (08) disciplinary cases pending at
the beginning of the year, five (5) cases have been
disposed off. No new case has been initiated during
the year.
*****
32
Annual Report 2004-2005
33
4.1 INTRODUCTION
The Bureau of Civil Aviation Security is an attached office
of the Ministry of Civil Aviation with its headquarters at
New Delhi. The Bureau works under Commissioner
(Security), an officer of the rank of DGP. The
Commissioner (Security) is the designated “Appropriate
Authority” to ensure development, maintenance, updation
and implementation of National Aviation Security
Programme for India.
The main objective of the Bureau is to safeguard Civil
Aviation operations against the acts of unlawful
interference. To achieve this objective, the Bureau lays
down standards and recommended practices for anti-
sabotage and anti-hijacking measures. Further, the Bureau
is mandated to conduct regular inspections and security
audits to ensure that the laid down procedures are being
complied with.
Being designated as the “Appropriate Authority”
responsible for fulfilling all international obligations in
Civil Aviation Sector and meeting the standards laid down
by ICAO Security Manual Annex-17, the Bureau is
responsible not only for training personnel in aviation
security but also testing and certifying them. Planning
and coordination of all aviation security related activities
being the core responsibility of Bureau of Civil Aviation
Security, four regional offices: one each at Delhi, Kolkata,
Mumbai and Chennai have been established under a
Deputy Commissioner of Security. The Bureau has four
“Bomb Detection and Disposal Squads” positioned at
the four metros alongwith Dog Squads to render
immediate assistance in explosive detection. Srinagar has
also been provided a Dog Squad to tackle the operational
emergencies.
4.2 BROAD TARGETS
• Modernisation
BCAS has formulated an IT Plan for modernization
& automation of Office Procedures. Computerization
work is in progress in the BCAS. All the staff members
have been trained for basic operation. All
documentation both in Hindi and English is being
done on computer, leading to the development and
administration of Databases and Electronic Data
Processing. All computers are internally Net-worked
in Local Area Network. Financial Software Package
has been obtained from the NIC and Official Human
Resource Management Software Package is also
being installed.
Bureau of Civil Aviation
Security
4
33

Ministry of Civil Aviation
34
• Training
a) The Bureau has brought out a “National Civil
Aviation Security Training Programme”
(NCASTP). Thus consolidating the training
curriculum so far developed by BCAS for security
personnel of various categories/levels. Training
Programmes organized by BCAS during the year
2004 are as under:-
* BCAS conducted tests for certifying of screeners
Total number of 1720 screeners from APSU/
Airlines attended, and out of which 1050 have
been certified.
* 37 Basic ABSEC courses conducted and 1058
security personnel have been trained.
* During AVSEC Awareness Programme organized
at different airports in the country, 4401 personnel
working at airports in different agencies attended
the programme.
* Officers of BDDS have also trained 5556 staff of
the airport in recognition of improvised explosive
devices (IEDs) and Bomb Threat Procedure
during the year 2004.
b) The details of foreign training attended by
officers of BCAS are as under:-
One Deputy Commissioner of Security(CA) attended
the Auditors course conducted by the ICAO
Regional Training Centre, Singapore. At the ICAO
Regional Training Centre, Penang, Malaysia one
Assistant Commissioner attended Instructors Course
while two Asstt. Commissioners attended the Cargo
Security Course.
••
••
• Contingency Plan
In order to test the efficacy of Contingency Plan and
Operational preparedness of the concerned agencies,
Mock exercise are being conducted regularly at the
airports.
••
••
• R&D Database for AVSEC :
All officers of BCAS are feeding details of Inspection
Reports, follow-up action, feedback reports, Security
Audit Reports, detailed documentation of Incident
Investigations etc. on the server through networked
desk station. In due course of time, Bureau expects
to accumulate volume of reliable database for data
mining EDP and R&D purpose. Database on Security
related technology is also being created.
••
••
• Initiatives taken to improve security at Airports
Dummy exercises were conducted by RDCOS at
regular intervals at international and domestic airports
in their regions, to test the efficacy of security staff
deployed by various agencies.
A Security Audit of IGI Airport has been carried out
by International Security Auditors under the auspices
of International Civil Aviation Organisation (ICAO)
w.e.f 10
th
Jan to 19
th
Jan, 2005.
34

Annual Report 2004-2005
35
••
••
• Security Programme of Scheduled/Non Scheduled
Air Carriers
To ensure the prescribed Security Standards the
Security Programmes of the Airlines (both Scheduled
& Non-Scheduled Carriers) are scrutinized & vetted
by this Bureau. So far Security Programmes of 58
Foreign Airlines and 107 Domestic Operators of
Scheduled and Non-Scheduled Airlines were
approved for operations up till now.
••
••
• Photo Idendification Card (PIC) System
To ensure the secured access control to the Airport
Premises, the Bureau scrutinizes & approves the
applications for issue of Airport Entry Photo Identity
Cards (PIC) through the PIC Committees and issues
airport entry passes and Photo Identity Cards to
officers and staff of various organizations who are
directly connected with the Civil Aviation operations.
Modern Computerized System of Photo Identity Card(PIC)
has been procured & installed at BCAS' Headquarter &
its four Regional Offices, by the Bureau in December 2002.
Validity of all the permanent PICs which have expired on
31.12.2004 has been increased from one year to three years
for the convenience and smooth operation of Civil
Aviation.
Bureau has submitted a detailed Study Report and Proposal
for introduction of Smart Card and Biometrics Based
Assess Control and Data Base Management System for
airports.
4.3 ACHIEVEMENTS OF BDDS
••
••
• During this year, the squads responded to 368 Bomb
Threat incidents at four International Airports, and 1
Bomb Threat at Domestic airport.
••
••
• 348 Bomb threat calls for unclaimed baggage, 10 bomb
threats for terminal building, 11 aircraft calls which
includes 1 Aircraft/Airlines not identified, 2 Foreign
aircraft inside country, 3 Private Airlines , 3 Indian
Airlines inside the country, 1 by Air India inside the
country/ aircraft were attended, which resulted in
huge financial gain to the airlines and also good-will
from passengers. Because of the dedication and well
trained BDDS of this Bureau, no flight was cancelled
due to bomb threat during the year 2004.
4.4 IMPLEMENTATION OF OFFICIAL
LANGUAGE
During the year, a “Hindi Week” was celebrated in Sept.
2004. Besides, Extempore speech competition, Hindi
Typing, Hindi Dictation, Hindi Essay, Noting & Drafting
and Quiz Competitions were organized during the “Hindi
Week”.
A Hindi Workshop for the Officers and Staff was also
organized. Inspections were carried out in all the four
Regional Offices to ensure the progressive use of Hindi
in the Regional Offices of the Bureau.
Official Language Implementation Committee meetings
were held in time in the Bureau’s Headquarters and its
Regional Offices.
35

Ministry of Civil Aviation
36
through employees own initiatives and contribution to
the efforts towards a pollution free atmosphere. BCAS
ensure that all new vehicles are “Bharat-II” Certified.
Bureau also provides a “Smoke-free Environment” to its
employees.
4.7 WELFARE ACTIVITIES
A small library facility and Reading room has been made
available to the employees to keep abreast of the current
affairs. From time-to-time informal gatherings are arranged
so that the work relationships remain amicable.
Educational video sessions on various Human Resource
Development and Management are proposed to be held
in the newly renovated Training Hall, in an effort to
train and motivate the employees for efficient and
competent output.
4.5 STAFF GRIEVANCES CELL
In pursuance of Government instructions, a Staff
Grievances Cell operates in the Bureau with the Addl.
Commissioner of Security, Civil Aviation as Staff
Grievances Officer, to deal with the grievances of officers/
staff working in the Bureau and its four Regional Offices.
The grievances of BCAS staff, if any, are promptly
attended to.
4.6 POLLUTION CONTROL
Pollution test for all vehicles is ensured and the Pollution
Check Certificate to this effect, is pasted visibly on the
wind screens of all BCAS vehicles. All newly constructed
office buildings of the Regional Offices at Delhi, Chennai
& Kolkata ensure clean & green working environment
*****
36

Annual Report 2004-2005
37
5.1 BRIEF HISTORY
The Commission of Railway Safety deals with matters
pertaining to safety in rail travel and operation and for
this purpose performs certain statutory functions laid
down in the Railway Act and the rules framed thereunder.
Formerly called the ‘Railway Inspectorate’, it functioned
under the control of the Railway Board till May, 1941
when it was separated from its control to secure its
independence from the authority administering the
Railways, pursuant to the recommendations of a
Committee called the ‘Pacific Locomotive Committee’
which was endorsed by the Central Legislature. After its
separation, it was attached to the air wing and placed
under Department of Communications. It came under the
administrative control of the Ministry of Tourism & Civil
Aviation in May, 1967, subsequently when that Ministry
was redesignated as the Ministry of Civil Aviation.
5.2 ABOUT THE ORGANISATION
The Commission is headed by the Chief Commissioner of
Railway Safety, who is also the principal technical adviser
to the Government of India in all matters concerning the
Commission. The headquarters of the commission is
located at Lucknow. The Chief Commissioner directs the
technical activities of the Commission and issues
instructions for the guidance of Commissioners of
Railway Safety in respect of holding statutory inquiries
into serious railway accidents, inspection of new lines
including electrification of existing lines prior to their
opening for public carriage of passengers and sanction
for running of new locomotives/rolling stock. He also
co-ordinates the work of the commissioners in their
dealings with the Railway Board and the railway
administration. He communicates his views whenever
necessary to the Ministry of Railways (Railway Board)
on design, standards, specifications and procedures for
Commission of Railway
Safety
5
37

Ministry of Civil Aviation
38
construction, working and maintenance of assets in all
branches of railway engineering and operation including
civil, mechanical, electrical and signal engineering etc.
The Chief Commissioner is assisted by a Deputy
Commissioner of Railway Safety (General).
There is a technical wing attached to the Chief
Commissioner at his headquarters which has four Deputy
Commissioners of Railway Safety drawn from the
mechanical, electrical, signalling, telecommunication and
operating disciplines of Indian Railways.
The Commission has 9 circle offices – two with
headquarters at Mumbai, three with headquarters at
Kolkata, and one each with headquarters at Bangalore,
New Delhi, Lucknow and Secunderabad. Each circle
office is under the charge of a Commissioner. There are
two Deputy Commissioners of Railway Safety
(Signalling and Telecommunication) headquartered at
Mumbai and Kolkata. Each Commissioner is an
independent statutory authority under the Railway Act,
1989.
5.3 DUTIES AND RESPONSIBILITIES
The Commisioners have been provided with duties/
functions under the Railway Act, 1989 under which rules
are framed and executive instructions issued from time to
time. A gist of main functions are as follows:
••
••
• to conduct statutory inquiries into serious railway
accidents and suggest safeguards.
••
••
• to inspect new lines with a view to determining
whether they are fit to be opened for the public
carriage of passenger and to sanction their opening
after inspection on behalf of the Central Government.
••
••
• to sanction the execution of all new works and
installations on the running track affecting the safety
of the travelling public such as rebuilding of
bridges, remodeling of station yards, line capacity
works, resignalling works, etc.
••
••
• to make periodical inspections of railways and report
to the Central Government on any condition which
may endanger the safety of the travelling public
and make recommendations.
••
••
• to examine the technical aspects of new rolling
stock and advise on their introductions on open
lines and to sanction their running on other section
and increase in speeds.
••
••
• to authorise the carriage of oversized consignments
stipulating the conditions for their movements.
••
••
• to recommend and sanction infringements to the
schedule of dimensions prescribed by the
Government of India.
••
••
• to grant dispensation from general rules under
approved special instructions subject to stipulated
safeguards.
38

Annual Report 2004-2005
39
••
••
• to oversee the accident prevention efficacy of the
zonal railway administrations by reviewing the
reports of departmental enquiries into less serious
accidents.
The Chief Commissioner submits an annual report on
the working of the Commission, which is laid on the table
of both the Houses of Parliament.
5.4 ACTIVITIES/ACHIEVEMENTS
The main activities of the Commission of Railway Safety
during the years 2003-04 and 2004-05 upto 31.01.2005
year 2004-05. Upto September, 2004, the A B & C region
circle offices of the Commission had corresponded 99.15,
97.75 and 99.08 % in hindi respectively. The Commission
published its 2004 edition of Hindi Home Magazine
“Suruchi” on 14
th
September, 2004 during the
5.5 PROGRESS IN USE OF HINDI
According to the target scheduled in the annual
programme of effective use of Hindi for the year 2004-05,
Commission of Railway Safety has stressed towards
achieving the target of 100% hindi correspondance in the
39
S. MAIN ACTIVITIES 2003-04 2004-05 (till
No. January 2005)
1. Statutory inquiries held into serious railway accidents. 34 18
2. Lines inspected and authorized (in kms.)
(i) New lines 130.228 383.526
(ii) Double lines 186.163 195.949
(iii) Section electrified 1168.900 400.280
(iv) Conversion of guage 1097.915 630.91
3. No. of applications for new major works sanctioned 3107 2617
4. Periodic inspection conducted (in kms) 20073.628 14266.576
5. New types of locomotives/ rolling stock recommended for 98 94
placement and sanctioned for extended runs.
6. Application for condonation of infringements dealt with 28 20
7. No. of over dimentioned consignments authorised for movement 15 10

Ministry of Civil Aviation
40
commencement of Hindi Fortnight. The Central Circle of
Commission was awarded with the Rajbhasha shield for
its outstanding work in Hindi. Northern Circle and
Technical Wing were awarded with Second and Third
prize respectively.
All the Circle Offices of the Commission observed the
Hindi Day in the month of September, 2004 in which
Rajbhasha Medals, Suruchi Medals and cash awards for
various Hindi competitions viz. essay, typing, debate etc.,
were distributed in the function. The Commissioners of
Central Circle and Southern Circle were awarded with the
cash award of Rs.1000/- each for producing Accident
Reports in Hindi.
‘NARAKAS’ Lucknow awarded the Technical Wing with
a Shield and a Certificate as it stood second among the
140 Central Govt. Offices located in Lucknow. The
Commission also do publish a quarterly ‘News Letter of
Commission’.
5.6 POLLUTION CONTROL
All possible steps are being taken to control pollution in
the offices of Commission of Railway Safety. The office
premises are kept always neat and tidy. Smoking is strictly
prohibited in the office premises. The vehicles used by
the officers and staff are free from pollution.
5.7 HALF YEARLY JOURNAL
The Commission has started publishing six monthly
journals of accidents inquiry reports after receiving the
comments of Railway Ministry in abstract form as
proposed by CCRS.
*****
40
Annual Report 2004-2005
41
6.1 INTRODUCTION
Indira Gandhi Rashtriya Uran Academy (IGRUA), the
premier institute for flying training in India under the
Ministry of Civil Aviation was set up in 1986 as an
autonomous body to bring about a quantum improvement
in the standards of flying and ground training leading to
issue of commercial pilots licences to the trainees. The
Academy is headed by a Director, who is assisted by
departmental heads who are in charge of flying, ground
instruction, engineering and administration. The aim of
IGRUA is not only to provide training to make pilots but
also to train the pilots by adopting airline oriented flying
training to become an effective systems manager in the
cockpits of modern aircraft. The flying trainees in the
academy acquire the requisite standards in flying &
technical knowledge for their easy transition into the
cockpits of modern jets of the airlines.
The Academy is equipped with the most modern and
sophisticated single engine trainer TB-20 aircraft (13 Nos.)
and twin-engine King Air Turbo prop aircraft (2 Nos.),
up-to-date audio visual training aids including computer
based training systems, centrally air-conditioned
classrooms, flight simulators besides having its own
airfield with 5600 ft. runway, night flying facilities and
dedicated Air Traffic Control and airspace. It also has its
own refueling station, safety services, two fully closable
hangars for housing the aircraft and carrying out
maintenance including approved workshops for aircraft
instruments, radio and battery servicing. The airfield has
recently been equipped with modern navigational aids
like DME/VOR and also landing aids like ILS and PAPI.
The total approved strength of officers and staff at IGRUA
including Instructors is 249. The Academy is fully
residential having 72-room Hostel Accommodation with
messing facilities for the trainees. Separate Hostel
Accommodation for Girls are provided in the campus,
which also has 82 residential accommodations for the
employees.
6.2 COURSES OFFERED
The courses offered in the Academy during the year are :-
• Abinitio to CPL trainee with B.Sc.Aviation degree
(24 months).
• CPL course for PPL holders with B.Sc. Aviation degree
(18 months).
• Multi-engine endorsement/Instrument rating
courses.
• Ground Refresher courses for Chief Flight
Instructors/Pilot Instructor In charges of flying clubs.
• Training to foreign nationals and Indian Airlines
flight engineers upto CPL requirements.
Indira Gandhi Rashtriya
Uran Akademi
6
41

Ministry of Civil Aviation
42
6.3 TRAINING
The total number of hours flown for training purposes
during the year 2004-2005 amounts to 2077 hours. A total
of 42 trainees were inducted during the year making a
total of 75 trainees undergoing various stages of training
i.e. Ground Classes followed by Simulator & then actual
flying.
6.4 RECRUITMENT
During the year, Air India & Indian Airlines conducted
recruitment of pilots exclusively from IGRUA trainees.
15 Ex-IGRUA trainee pilots got placement with Air India
and 14 Ex –IGRUA trainee pilots got placement with Indian
Airlines.
6.5 POLLUTION CONTROL
The Academy has taken the following steps with regard
to pollution control:-
• All vehicle engines and power generators are
properly maintained and pollution levels monitored.
• Solid waste is burnt in a closed environment so as to
cause minimum fumes. Power Generators are run in
closed environment with proper exhaust system.
• Forestation and gardening is actively pursued to
maintain a green environment.
The Academy has a proper underground drainage system
and has its own independent sewerage treatment plant to
avoid pollution in water sources.
6.6 PUBLIC GREVIANCES AND SENIOR
CITIZENS
An officer in the Academy has been designated at the
nodal point to look into public grievances and during the
year 2004, there had been no public grievances. In
accordance with the guidelines of the Government on
national policy on older persons, instructions have been
issued to all concerned and reiterated to ensure prompt
fair and human treatment to elderly persons.
6.7 OFFICIAL LANGUAGE
All steps are taken for ensuring the provisions of the
official language Acts and Rules. Employees are given
training in Hindi including Hindi typing. Incentives are
given to employees for successfully qualifying Hindi
typing test. Computers have been modified with software
for use in Hindi and are in operation. Workshops have
been held for encouraging use of Hindi in official works.
6.8 MODERNISATION
The website on IGRUA is functional with domain address
http://www.igrua.com. All necessary information about
IGRUA including admissions for new courses is displayed
and kept Upto-date and all under enquiries for
procurement are offloaded as per CVC guidelines.
6.9 ACHIEVEMENTS
The major achievements of the academy during the year
are as follows:
• Training to foreign nationals and Indian Airlines
flight engineers upto CPL requirements.
Completion of a Indoor sport complex comprising of
squash court, badminton court and gymnasium hall
to ensure fitness of trainee pilots.
• Training to foreign nationals and Indian Airlines
flight engineers upto CPL requirements.
The procurement of Six Zlin Z 242 single engine
trainer aircraft has since been finalized and orders
placed with the manufacturers.
••
••
• The ILS and VOR-DME installed at the airfield was
commissioned after flight calibration checks and made
operational.
*****
Ministry of Civil Aviation
42
Annual Report 2004-2005
43
7.1 INTRODUCTION
Airports Authority of India (AAI) continued to make
further strides in providing quality infrastructure at
various airports and further upgraded its CNS – ATM
facilities as per the ICAO standards. Modern Terminal
Buildings with futuristic design and latest technology
are under construction at various airports.
The old Passenger Terminal Buildings at IGI Airport, Delhi
and CSI Airport, Mumbai are being completely
refurbished as time bound turn key projects to augment
the passenger handling capacities and facilities.
At NSCBI Airport, Kolkata which serves as a gateway to
Eastern India, a new international Departure Terminal of
20,000 sqmtr. area has been planned for which an
international design competition was held and a
consortium headed by M/s. ADPi of France has been
selected as Architects for designing this new terminal.
The Consortium is in the process of preparing detailed
design for the new international departure terminal. Work
is in progress for construction of a modern Integrated
Cargo Complex at a cost of Rs.49.66 crores and
strengthening the main runway including upgrading the
ground lighting facilities at runway 19L to match with
Cat. II Instrument Landing System and International remote
parking bays at a cost of Rs.16.95 crores.
At Chennai Airport, reciprocal Instrument Landing System
(ILS) has been commissioned at Runway 25 end. Other
passenger facilities like Marble cladding of aerobridge
corridor, vitrified flooring in the Domestic Terminal and
International Arrival Terminal have also been provided.
There are plans for further development of Chennai
Airport. The existing departure and arrival areas in the
old international terminal are being combined into a unified
international arrival building which shall ultimately be
merged with new international departure terminal already
commissioned. There are also proposals for construction
of five bays and link taxi-track for private Air Taxi
Operators, warehousing facilities for Courier and Charter
Operators and Integrated Cargo Complex Phase II and
additional hangars.
The Authority continued to maintain its growth and
profitability and has been paying dividend since inception.
In the year 2003-04, an amount of Rs. 70 crores was
paid as dividend to the Government of India, the highest
so far paid.
Airports Authority of India
7
Annual Report 2004-2005
43
Ministry of Civil Aviation
44
7.2 ORGANISATION
The Board of Airports Authority of India as on 31.12.2004
comprised of a Whole-time Chairman, Whole-time
Member(Finance), Whole-time Member (Personnel &
Administration) and four other Part-time Members
comprising the Director General of Civil Aviation,
Additional Secretary & Financial Advisor, MCA, Joint
Secretary, MCA and CMD, Indian Airlines Limited.
44
7.3 FINANCIAL PERFORMANCE
••
••
• The operating results for the year 2003-04 and the revised estimates for the year 2004-05 are as follows:
(Rupees in crores)
Particulars 2003-04 2004-05
(Actual) (RE)
a. Revenue 2630.59 2769.65
a. Expenditure 2086.63 2169.32
b. Profit Before Tax 543.96 600.32
c. Profit After Tax 314.96 348.32
••
••
• Financial Highlights
(Rupees in crores)
Particulars 1998-99 1999-2000 2000-01 2001-02 2002-03 2003-04 2004-05 (RE)
a. Revenue 1591.27 1691.28 1873.44 2244.84 2384.49 2630.59 2769.65
b. Expenditure 1255.49 1346.55 1514.36 1767.86 1887.44 2086.63 2169.32
c. Profit Before Tax 335.78 344.73 359.08 476.98 497.05 543.96 600.32
d. Provision for Tax 127.37 133.35 145.00 210.00 215.00 229.00 252.00
e. Profit After Tax 208.41 211.38 214.08 266.98 282.05 314.96 348.32
Annual Report 2004-2005
4545
••
••
• Capital Structure of AAI as on 01.04.2004 and 01.04.2005
(Rupees in crores)
Particulars 01.04.2004 01.04.2005(RE) Details of Capital Structure of AAI as on 1.4.2005 (RE)
Govt. Capital 416.63 432.90 Capital Reserve 276.53
Reserves & Surplus 2602.53 2737.03 General Reserve 1778.18
Long Term Loans 145.23 104.89 Fixed Asset Replacement Reserve 413.85
Ne t Wor th 2617.95 2903.40 Obsolescence Reserve 60.73
Capital Employed 2698.26 2982.67 Contingency Reserve 60.73
Other Reserves (CISF) 147.01
Total 2737.03
* The capital outlay for the year 2005-2006 (BE) is Rs. 898.50 crores.
••
••
• Capital Structure
(Rupees in crores)
Particulars 1.4.99 1.4.2000 1.4.2001 1.4.2002 1.4.2003 1.4.2004 1.4.2005
(RE)
Govt. Capital 337.63 350.13 365.09 388.79 405.59 416.63 432.90
Reserves & Surplus 1273.53 1534.73 1715.58 2023.49 2317.07 2602.55 2737.03
Long Term Loans 466.06 445.82 394.77 315.81 225.73 145.23 104.89
Ne t Wor th 1417.23 1691.15 1880.32 2142.01 2370.93 2617.95 2903.40
Capital Employed 1437.03 1852.45 2047.89 2396.59 2534.68 2698.26 2982.67
Working Capital 261.45 404.59 492.50 741.62 820.52 896.70 976.70
Ministry of Civil Aviation
46
••
••
• Contribution to Exchequer
(Rupees in crores)
Particulars 1998-99 1999-2000 2000-01 2001-02 2002-03 2003-04 2004-05
(RE)
Income Tax** 149.43 158.20 184.35 206.29 255.65 317.42 356.00
Dividend*** 41.68 42.28 50.00 55.00 62.00 70.00 70.00
Tax on Dividend 4.17 9.30 5.10 0.00 7.94 8.97 9.15
Interest Payments 6.41 7.83 5.93 2.42 2.83 1.90 0.52
Loan Portion of Budgetary 3.18 2.96 2.74 2.55 2.18 1.70 1.21
Support Guarantee Fees
Interest on Loan Portion of 12.40 11.27 10.08 14.13 2.14 0.00 0.00
Commencing Capital
Total 217.27 231.84 258.20 280.39 332.74 399.99 436.88
* * This represents Advance Tax & TDS.
* * * Dividend shown for the year 2003-04 has been paid in 2004-05. Dividend for 2004-05 is provisional. Final dividend will be
decided by Board.
7.4 TRAFFIC
Traffic handled during April to March 2004-05 vs. April to March 2003-04:
Particulars April to March April to March %
2004-05* 2003-04 Change
Aircraft Movements (in Nos.)
International Airports 158191 132934 19.0
Domestic Airports 571827 506042 13.0
Total 730018 638976 14.2
Passengers (in Nos.)
International Airports 19451146 16624911 17.0
Domestic Airports 40095663 32076530 25.0
Total 59546809 48701441 22.3
Cargo (in tonnes)
International Airports 824876 693173 19.0
Domestic Airports 465036 375029 24.0
Total 1289912 1068202 20.8
* Traffic projections based on actual traffic handled for the period April to November 2004.
46

Annual Report 2004-2005
47
AAI has joined the AETRA Programme [A Joint Venture
between International Air Transport Association (IATA)
and Airport Council International (ACI)] to ascertain the
Customer Satisfaction of Delhi and Mumbai airports and
benchmark it against leading airports of the world.
7.5 WORKS COMPLETED AND FACILITIES
PROVIDED DURING 2004-05
••
••
• Navigational & Landing Aids Provided at Airports
* Communication, Navigation and Surveillance
equipment installed at various airports were
further upgraded.
* New ILS was installed at Port Blair and
Bhavnagar airports. The existing ILS at
Khajuraho airport has been replaced with a new
State-of-the-art ILS.
* New DVOR was installed at Vijaywada airport.
The existing VORs at Hyderabad, Ahmedabad,
Mumbai, Mohanbari, Visakhapatnam and Bellary
have been replaced with new DVORs.
* AAI has also installed High Power DME and
DVOR at Indira Gandhi Rashtriya Uran Academy
(IGRUA), Fursatganj, U.P., free of cost.
* New Low Power DMEs were also installed at
Bhavnagar, Raipur, Mohanbari and Agartala
airports.
* New High Power DMEs have been installed as
replacement at Port Blair, Belgaum,
Bhubneshwar, Chennai, Lucknow, Trivandrum,
Jaipur and Varanasi airports.
* The existing NDBs installed at Jaipur, Delhi, Kota,
Calicut, Coimbatore, Bhopal, Khajuraho,
Reengus, Lucknow, Amritsar, Shimla, Ludhiana
and Trichy were replaced with new equipment.
* Close Circuit TV Cameras have been installed at
Guwahati, Bagdogra, Agartala, Imphal, Bhopal,
Mangalore and Ranchi airports.
* At Delhi, Allahabad, Chennai, Trivandrum,
Bangalore and Nagpur airports, Ultra High
Frequency links (UHF-Link) have been installed.
Further the Digital Airport Terminal Information
System (DATIS) has been installed and
commissioned at Ranchi and Dibrugarh airports.
Computer-aided Flight Data Processing System
(FDPS) has been installed and commissioned at
Nagpur, Thiruvananthapuram, Varanasi and
Ahmedabad airports.
* The Flight Inspection Unit at Delhi has been
provided with a new State-of-the-art Automatic
Flight Inspection System for carrying out
calibration of navigational aids at various
airports.
* A project for installation of V-SAT equipment at
80 locations is under implementation.
••
••
• Gagan Project
AAI in collaboration with ISRO is implementing GPS
and GEO Augmented Navigation (Project ‘GAGAN”)
– an augmentation system to enhance the accuracy
and integrity of GPS signals to meet precision
approach requirements in civil aviation. A technology
demonstration system will be ready by early 2006 in
47

Ministry of Civil Aviation
48
first phase and the same will be upgraded to a full
operational capability system in the second and third
phase. When implemented, this will cover area far
beyond Indian airspace and would replace most of
the ground based navigational aids and it would be
possible to provide precision approach and landing
guidance up to category I to aircraft hitherto not
available due to terrain conditions precluding the
provision of Instrumental Landing System.
••
••
• Aerodrome Works
The development of the international airports as well
as domestic airports received focused attention both
in terms of speed and construction as well as
introduction of latest technology in futuristic
terminals:-
* IGI Airport, Delhi
Passenger facilities were further improved at IGI
Airport, Delhi. The major areas where
improvements have been made / facilities
upgraded related to replacement of conveyor
belts, escalators, provision of apron lighting,
false ceiling work, provision of vitrified flooring
tiles, provision of more commercial facilities like
airline transfer desk, transfer lounge, plasma TV,
wireless fidelity in internet facility, CUTE system,
home theatre, etc. All these facilities have further
enhanced quality of services provided at these
airports.
48
Newly renovated Customs Arrival area IGI Airport

Annual Report 2004-2005
49
* CSI Airport, Mumbai
Number of passenger facilities were provided
which include additional escalators in Terminal
2A, additional conveyor belts at Terminal 2C,
new taxi parking area and additional space in the
security hold area. In addition, more comfortable
cushioned sofa chairs were placed at Terminal 1
and 2 at CSI Airport.
* Chennai International Airport
At Chennai Airport, marble cladding was
provided in the aerobridge corridor, the floor
tiling at the domestic terminal and international
arrival terminal were replaced with vitrified tiles,
automatic flight information system introduced
and additional X-ray machines provided at the
domestic terminal.
* NSCBI Airport, Kolkata
At Kolkata Airport a new air-conditioning plant
was commissioned for improved passenger
comfort. New Flight Information Display System
consisting of Split Flap Board, 42” Plasma
Monitors, 29/21” Monitors have been provided
in both the terminals. Check-in area of
International Terminal has been extended. Snack
bar counter in main concourse of International
Terminal Building has been established from
September 2004 and the area has been further
expanded.
* Trivandrum International Airport
Strengthening of main runway 14-32 and taxiway
was completed at Trivandrum. Flooring of
Terminal-2 has been replaced by vitrified tiles.
Touch free security system has been
commissioned.
* Other Airports
The following major works have been completed
at other airports:-
A new Terminal Building at Pathankot,
construction of fire station at Calicut airport,
construction of DVOR building at Dibrugarh
airport, construction of Technical Block cum
Control Tower and extension and strengthening
of runway and provision of CAT-II lighting
system at Lucknow airport, runways, apron,
taxiways, etc. were expanded / strengthened at
Lucknow, Bhavnagar, Porbandar, Nagpur,
Rajahmundry, Kullu, Hyderabad, Jaipur and
Varanasi and construction of Isolation Bay at
Calicut, Amritsar, Hyderabad, Ahmedabad and
Varanasi airports. Construction of boundary wall
and Earthren Bund at Vishakhapatnam airport.
Provision of runway lead in lights at Calicut
airport.
* Schemes completed at airports in NER
Resurfacing of runway and construction of
Isolation Bay at Imphal airport. Strengthening
49

Ministry of Civil Aviation
50
of apron, construction of boundary wall around
the newly acquired land and widening of link
taxiway at Agartala airport. Earthwork and
Grading in critical area for installation of Glide
Path & In Transition Area at Dimapur airport.
••
••
• Other Facilities
* Schemes are under preparation to implement
inline baggage scanning system by means of
explosive detector X-ray machines for the
Airports of Delhi, Chennai, Kolkata, Mumbai,
Ahmedabad, Calicut & Srinagar. The system is
meant to improve security at the airports.
* Flight Information Display System have been
installed at Kolkata, Trivandrum and Delhi
Airports with a provision of large scale Split Flap
Display Boards and Plasma Monitors.
* Expressions of interest have been invited for
implementation of CUTE (Common User Terminal
Equipment) System at 16 Airports in India. The
system is proposed to be implemented by middle
of this year.
* 20 modern big sized colour X-Ray machines have
been installed at 4 metro airport and some
domestic airports.
* Walk in cooler for perishable cargo centre
established at Coimbatore airport in May, 2004.
* The 2
nd
phase of Web based Electronic Data
Interchange (EDI) with trade partners of AAI
through internet has been implemented at IGIA
(1.11.04), Chennai (29.11.04), Kolkata (4.12.2004)
and Mumbai (10.12.2004).
* The 3
rd
phase of EDI (introduction of Bar Code
System ) is being progressed.
* AAI is implementing Bar Code System at Air
Cargo Terminals of Delhi, Mumbai, Kolkata &
Chennai airports to enable fast movement of
cargo with complete accuracy through automatic
data capturing. The complete system is expected
to be operational by 31.3.2005.
* AAI, at its four metro airports i.e. IGIA Cargo
Terminal, New Delhi, Air Cargo Terminals of
Chennai, Kolkata & Mumbai, has commissioned
Electronic Data Interchange (EDI) connectivity
with trade partners such as Airlines, Banks,
Customs House Agents, IATA Agents, etc. for
EDI connectivity, the netTransaction Hub (nT
Hub) has been established at AAI Operational
Offices, New Delhi. AAI has hosted its e-
commerce website, www.airports-ecom.gov.in, in
order to provide online cargo tracking &
business transactions to the public & trade
partners through Internet. With online EDI
connectivity through Internet, public & trade
partners are in a position to track import & export
cargo and also clear their consignments after
payment of applicable charges to AAI.
••
••
• Air Traffic Management
* Minimum Flight Altitudes [MFAs] were
established for many segments of International
50

Annual Report 2004-2005
51
and Domestic ATS Routes under Safety
Management System – compliance report for
implementation of provision of Annex 11. AIP
Supplement No.02/04 was published on the
subject.
* Air Traffic Flow Management Plan – Operational
trial of the traffic originating from South East
Asian airports was implemented in February
2004, only due to full support from AAI.
* New ATS Routes:-
– M-890 – a by-pass route to avoid flying
over Delhi. This route is 17 NM shorter and
has been appreciated by ICAO, IATA and
other countries.
– UM-551 – has been implemented between
Thiruvananthapuram and Salalah in
Sultanate of Oman. UM 551 provides a 106
NM shorter routing and also uses, hither to
underutilized airspace of Republic of Yemen,
thus strengthening AAI’s relation with
immediate neighbours in Arabian Sea.
– P-628 – This route from Kualalumpur to
Jabalpur [ASOPO] has been extended to
Rahim Yar Khan in Pakistan. When fully
operational in Pakistan, P – 628 will be one
of the shortest routes between Europe and
Malaysia / Singapore.
– W – 107 – ATS route between Chennai and
Port Blair has been implemented to provide
shortest routing between the two stations.
This route has been opened for those
international airlines also who operate their
flights through Chennai Airport.
– L – 626 – This route from Kathmandu to
Delhi is finalized. AIP-Supplement shall be
published shortly.
* RVSM airspace over Arabian Sea has been
expanded to make it compatible and contiguous
with the RVSM Airspace of Sana’s FIR, Republic
of Yemen.
* The LOAs on the ATS Co-ordination Procedures
have been signed with Bangladesh, Mauritius,
Republic of Yemen, and Pakistan.
* To increase the safety of opposite direction
flights flying on bi-directional ATS Routes in
Oceanic Airspace AIP Supplement on Strategic
Lateral Offset Procedure has been published.
The procedure will be applicable with effect from
20
th
January, 2005 coinciding with the date of
application of the procedure in the Asia/ Pacific
Region.
* An AIP Supplement has been prepared to
promulgate helicopter routings to ensure
uninterrupted flights of helicopters between
Juhu Airport and Oil rigs in Mumbai High.
* ATS set up has been re-established to support
schedule flight operations at Vijayawada, Hubli,
51

Ministry of Civil Aviation
52
Surat and Kolhapur Airports. Arrangements are
being made to accept schedule flight operations
at Dehradun, Kanpur and Ludhiana also.
* A National Search & Rescue Seminar has been
conducted at Chennai. AAI invited IAF, Indian
Navy, Indian Coast Guards, and ISRO etc. to
participate in the Seminar.
* The conduct of national level Search and
Rescue Seminar is a prelude to the ICAO Search
and Rescue Seminar and Search & Rescue
Exercise (SAREX) to be conducted in March
2005. AAI is making other preparations for the
ICAO Seminar.
* Air-show at Mumbai airport was conducted by
IAF and Air India to commemorate Birth
Centenary of JRD Tata with full support by AAI.
* Repetitive Flight Plan (RPL) System has been
commissioned at Mumbai and Delhi Airport.
* One Engine Start Up Procedure, while the aircraft
is being pushed back, has been drafted and
submitted to DGCA for cancelling DGCA’s AIC
on banning of starting engine while aircraft is
being pushed back.
* In accordance with the ICAO General Assembly
Resolution A33-8, the Safety Oversight by
ICAO covering Annexes 11 and 14 was slated
to start in the year 2004. However, further work
carried out by ICAO revealed that many areas of
Annex 11 and Annex 14 are inter-related to
several other Annexes, and therefore, the safety
audit would not be effective on Annex to Annex
basis.
* During the 35
th
Assembly of ICAO with the
unanimous support of contracting states, it was
decided to restructure USOAP for a
comprehensive systems approach covering all
safety related Annexes. Safety oversight Audit
is scheduled to be carried out from the year 2005
onwards. Safety related Annexes for which the
safety oversight capability of AAI is to be
audited are Annex 1 (Personnel Licensing – Air
Traffic Controllers) and Annex 2 – Rules of the
Air, Annex 4 (Aeronautical charts), Annex 10
(Aeronautical Telecommunications) Annex 11
(Air Traffic Services) Annex 14 (Aerodrome
Design and operations) and Annex 15
(Aeronautical Information Services).
* AAI had already prepared Manual of Air Traffic
Services and Aerodrome Operations Manual,
filled compliance checklists and identified
differences in respect of Annex 11 and Annex
14. Action is being initiated for gearing to
expanded requirements of the programme which
requires massive exercise for preparing manuals,
filling up of revised checklists, institution of
Safety Management System and Human factors
principle, identifying differences with ICAO
SARPS, Certification of Aerodromes etc.
* Instrument Approach Procedure Designing
(PANS-OPS) Course, which is available in very
52

Annual Report 2004-2005
53
few countries, was conducted at CATC
Allahabad to train 10 officers.
* Provided expert advice for designing new
airports near Ludhiana to be developed by Govt.
of Punjab and for development of new runway
at Mysore and Cuddapah Airport.
* Assisted ICAO Expert in conducting
Aeronautical Study at Mumbai.
* Instrument Approach Procedures for Delhi
Airport were revised to implement Khola
Committee Recommendations.
* About 100 AIP charts were amended for AIP
2004 amendment.
* Procedures have been evolved to facilitate pilot
to join VOR DME Arc Procedures from any radial
at most of the airports, which results into saving
of time and fuel.
* The promulgation of instrument approach
procedures was streamlined to meet Annex 15
requirement by persuading DGCA to promulgate
procedures through AIP Supplements direct,
thus saving substantial time.
* AIP supplement 001 to 033 published and
disseminated to all concerned. Amendment 01/
2004 to AIP-India Vth Edition Volume 1 and II
pages has been incorporated.
* During year 2004, a total of 18500 cases were
received for issue of NOC for erection of mast/
antenna. 11100 cases have been cleared.
* During year 2004, a total of 1450 cases were
received for issue of NOC for buildings. Out of
which 1610 cases have been issued NOC – this
includes backlog of 2003.
7.6 DEVELOPMENTAL ACTIVITIES TAKEN
UP IN NORTH EASTERN REGION
Airports Authority of India is laying special emphasis for
development of airports in north-eastern region. Hon’ble
Minister of Civil Aviation has taken up a meeting with
Members of Parliament for monitoring the progress of the
development activities in the north-eastern region.
During first year of 10
th
Plan i.e. 2002-03, AAI spent
Rs.30.88 crores and Rs.14 crores have been spent till
October 2003 and likely expenditure during 2003-04 is
Rs.27.32 crores.
During current financial year, North East Council has
released Rs.4.5 crores as share on development of airports
in the North East Region.
7. 7 I.S.O. CERTIFICATION
AAI is committed to provide effective Quality
Management System (QMS). In this direction AAI, has
already obtained ISO 9001-2000 certification for 7 airports
which are Ahmedabad, Chennai, Coimbatore, Jaipur,
Kolkata, Mangalore and Mumbai. During the year
2004-05, ISO certification was obtained for Pune, Goa,
Madurai, Udaipur Airports and Department of
Information Technology. AAI is striving to bring in more
airports and more areas under this ISO certification which
serves as benchmark for providing quality services/
systems.
53

Ministry of Civil Aviation
54
7.8 RESTRUCTURING OF METRO
AIRPORTS
On 11
th
September 2003, Government accorded its
approval for the restructuring of Delhi and Mumbai
airports by adopting the Joint-Venture route.
The then Finance Minister in his budget speech for the
year 2003-04 announced that two airports at Delhi and
Mumbai will be renovated/modernized along with the
modernization of certain selected sea ports at an estimated
cost of Rs.11000 crores. The Funding mechanism aims at
leveraging public money through private sector
partnership, wherever possible. The two airports at Delhi
& Mumbai will be renovated/ modernized by incorporating
two separate companies.
The AAI Amendment Bill introduced in the Parliament
(Budget session 2003) was passed by the Parliament in
the Monsoon session of June 2003. The Amendment Bill
authorizes AAI to transfer the operations and management
of its existing airports by way of long-term lease to private
players. The Bill inter alia provides for exclusion of private
airports (like BIAL) from the ambit of AAI Act, excepting
security and ATC functions, which will continue to be
discharged by AAI. The Bill also authorizes AAI to charge
Advance Development Fee (ADF) for the development/
upgradation of existing airports and for the setting up of
greenfield airports. In addition, the Bill also seeks to
prevent and remove encroachments of airport land.
AAI is currently in the process of setting up two separate
companies for Delhi & Mumbai airports.
The Government decided to constitute an Empowered
Group of Ministers(EGOM) to take up decisions on
various issues connected with the restructuring of
Mumbai and Delhi airports. Further, to oversee the process
of privatization, the Government constituted an Inter-
Ministerial Group (IMG). The group is chaired by Secretary
(Civil Aviation) with Addl. Secretary & Financial Advisor
of MCA and representatives from the MCA, MoF,
Planning Commission and Ministry of Law, Justice &
Company Affairs and AAI as Members.
To assist Ministry of Civil Aviation (MOCA)/Airports
Authority of India (AAI) in the restructuring process,
AAI has appointed following advisors:
• Financial Consultant (FC): ABN Amro.
• Global Technical Advisor (GTA): M/s Airplan,
Australia.
• Legal Consultant (LC): M/s Amarchand &
Mangaldas Suresh A. Shroff.
• Accounting and Taxation Advisor (ATA): M/s
Thakur, Vaidyanath Aiyar & Co.
Registration of Expressions of Interest were solicited from
interested parties to acquire 74 % equity stake in the JVC
and the complete documentation, in this regard, was
uploaded in the websites of AAI and MCA on 17.02.2004.
The last date for submission of EOI was 04.06.2004.
Subsequent to formation of the new Government, the last
date of submission of Expression of Interest was extended
to 20th July 2004 with a view to addressing certain key /
critical issues.
Government inter-alia, approved the 49% cap on FDI,
restriction of equity participation by Indian scheduled
airlines upto 10%, increasing the deputation period of
employees in the JVCs from 2 to 3 years and also decided
to give weightage to bidders who will induct more
number of employees over and above the mandatory
induction of 40%.
54

Annual Report 2004-2005
55
Ten entities have lodged their EOIs by 20
th
July 2004 (i.e.
last date of the receipt of EOIs).
Nine Consortia of companies have been short listed for
participation in the next stage i.e. Request For Proposal.
The entire process of evaluation of bids and handing
over of airport to successful bidder is likely to be over by
the first half of 2005-06.
The Key Transaction objectives are as under:-
••
••
• World class development and expansion:
Ensure world class phased development and
expansion such that the new JV Companies meet their
commitments through the timely provision of high
quality airport infrastructure (on both the airside and
landside) to meet growing demand; and
••
••
• World class airport management:
Ensure the creation of world class airport management
systems that are implemented in a timely manner
through the selection of serious, committed
successful bidders with suitable operational expertise,
managerial and financial capability, financial
commitment and the commitment to provide quality
airport services.
••
••
• Other transaction objectives:
In addition to the key transaction objectives, other
transaction objectives include:
– Timely completion and certainty of closure, with
minimal residual risks;
– Smooth transition of operations, under
concession agreements;
– Appropriate regulation - achieving economic
regulation of aeronautical assets that is fair,
commercially and economically appropriate,
transparent, predictable, consistent and stable
while protecting the interests of users and
ensuring that the airports are operated in
accordance with world standards;
– Fair and equitable treatment of AAI employees,
including preservation of accrued entitlements;
and
– Diversity of ownership between Delhi and
Mumbai airports, to enhance competition,
encourage innovation and allow competitive
benchmarking.
••
••
• Status – Greenfield Airports – Bangalore
International Airport
– Greenfield airport at Devanahalli near Bangalore
is being implemented on a Build Own Operate
and Transfer (BOOT) basis with Public Private
Participation.
– Government of Karnataka (GOK) through
Karnataka State Industrial Investment
Development Corporation (KSIIDC) and AAI
together hold 26% equity and the strategic joint
venture partners hold the balance 74%. AAI’s
investment in the equity is capped at Rs.50 crores.
– A Memorandum of Understanding to this effect
signed on 3
rd
May 1999 between AAI and
KSIIDC to facilitate further action leading to
implementation of the project.
55

Ministry of Civil Aviation
56
– Based on a Global tendering process initiated
by the State Government in August 1999, a
Consortium lead by Siemens Germany with
Unique Zurich, Switzerland and Larsen & Toubro
India Limited as other members, was chosen as
the strategic Joint Venture Partner in July 2001.
– A Shareholders Agreement was executed
amongst AAI, GoK, Siemens, Unique Zurich and
Larsen & Toubro in January 2002.
– Concession Agreement (CA), was approved by
the Cabinet in January 2004/15
th
June 2004 and
was signed on 5
th
July 2004.
– GoK proposes to extend Rs.350 crores as State
support.
– The approximate cost of the Project is Rs.1300
crores.
– The target opening date of the airport is 33
months from the date of Financial Closure.
– State Support and Land Lease Agreement have
been signed between GoK and BIAL on
20.01.2005.
– CNS/ATM agreement has been approved by the
AAI Board and likely to be signed between AAI
and BIAL.
– The financial closure is expected to be achieved
in early 2005-06.
••
••
• Status – Greenfield Airports – Hyderbad
International Airport
– The Union Cabinet had given their approval on
13
th
April, 2000 for construction of new airport
of international standards at Shamshabad,
Hyderabad under joint venture.
– The Government of Andhra Pradesh (GoAP)
have selected a consortium led by M/s GMR
Infrastructure Ltd. with Malaysian Airport
Holding Berhard (MAHB) as the Developer for
Greenfield Airport at Shamshabad near
Hyderabad.
– Government of Andhra Pradesh and AAI
together hold 26% equity and the strategic joint
venture partners, GMR infrastructure Ltd. with
Malaysian Airport Holding Berhard (MAHB),
hold the balance 74%.
– A Shareholders’ Agreement was executed by
the parties viz. M/s GMR, M/s MAHB
(Sponsors), AAI and GoAP (State Promoters)
on 30th September 2003.
– GoAP has also entered into the State Support
Agreement and the Land Lease Agreement with
the GMR led Consortium on 30th September
2003.
– Government of Andhra Pradesh is extending
Rs.315 crores as State Support and Rs.107 crores
as grant.
– The approximate cost of the Project is Rs.1385
crores.
56

Annual Report 2004-2005
57
CA will facilitate construction of the Greenfield
International airport at Shamshabad near
Hyderabad.
7.9 DEVELOPMENT OF NON METRO
AIRPORTS.
• City Side Development of Non Metro Airport.
The Airports Authority of India has drawn a plan for
City Side Development of 25 Non Metro Airports. In
the first phase 10 Non Metro Airports namely,
Ahmedabad, Amritsar, Guwahati, Goa, Jaipur,
Lucknow, Mangalore, Madurai, Udaipur and
Trivandrum have been taken up for which Global
Technical Advisor (GTA) and Indian Financial
Consultant (IFC) have been appointed. These
Consultants are carrying out a detailed Techno
Feasibility Study for business and financial plan and
model specific to each airport for adoption by AAI.
– The target opening date of the airport is 36
months from the date of Financial Closure.
– The Concession Agreement (CA) to be signed
between Government of India and HIAL was
approved on 15.12.2004. The Concession
Agreement was signed on 20.12.2004.
– The Concession Agreement lays down the
scope of the project, recognition of rights and
obligation of the Government of India and HIAL
and lays down parameters regarding
construction of airport, its operations,
maintenance, monitoring, airport charges,
maintenance of accounts, force majeure, events
of default and consequences, transfer of airport
to Government in certain cases, term of
concession, compensation payable in certain
events, dispute resolution and other
miscellaneous provisions. The signing of the
57
Refurbished Airside Corridor of Hyderabad International Airport

Ministry of Civil Aviation
58
In order to have world class International Terminals,
Architectural design competition have been finalized
in respect of Ahmedabad, Trivandrum, Jaipur, Trichy,
Udaipur and Dibrugarh. Architectural design entry
for Terminal Buildings at Lucknow, Bhubaneshwar
and Madurai are being invited. The Architectural
design consultant and GTA will assist AAI in finalizing
the modalities involved for over all development of
the Airports.
In addition to 10 airports already identified, AAI
proposes to take up similar study for other 15 Non
Metro airports which are: Agatti, Aurangabad,
Bhopal, Bhubaneshwar, Coimbatore, Indore,
Khajurho, Patna, Portblair, Nagpur, Rajkot, Trichy,
Vadodara, Varanasi and Vishakhapatnam.
Expressions of Interest (EOI) have been received for
appointment of one set of IFC/GTA each for 5 airports
covering these 15 airports for submission of Techno
Economic Feasibility Report, Business and Financial
Plan and Model specific to each airport for city side
development and are under evaluation.
7.10 HUMAN RESOURCE DEVELOPMENT &
INDUSTRIAL RELATIONS
The Authority continued to lay stress on Human Resource
Development with focus on training the executives and
other staff for increasing the productivity and for
providing better and customer-friendly service. Industrial
Relations during the year saw some turbulence on
account of the impending restructuring of the Delhi and
Mumbai airports and also the private sector participation
in the development of the city side development of selected
non-metro airports. Meetings were held at the level of
Chairman with Ministry of Civil Aviation for addressing
the concerns expressed by the employees on the process
on restructuring of these two metro airports.
To keep pace with technological changes taking place in
the airport / aviation sector, various Training Programmes
were organized in the following areas:-
– Airside operations
– Airport Terminal Management
– Air Cargo Management System
– Contract Management
Besides the above, training in Hindi Typing and other
knowledge based programmes have helped the employees
of AAI to perform better.
Tournaments were conducted in Table Tennis, Chess,
Carom, Volleyball, Badminton, Cricket and Football. AAI
teams participated in Public Sector Tournaments organized
by All India Public Sector Sports Promotion Board in
Volleyball and Cricket. AAI was one of the co-sponsors
in the All India Public Sector Cricket Tournaments.
7.11 TRAINING
••
••
• National Institute of Aviation Management &
Research (NIAMAR)
58
National Institute of Aviation Management & Research (NIAMAR),
New Delhi

Annual Report 2004-2005
59
The National Institute of Aviation Management &
Research (NIAMAR) conducts courses in Airport
Operations, Airport Engineering, Construction,
Airport Commercial, Airport Finance, Aviation Law,
Human Resource Development including Personnel
Management and Cargo Management including
Dangerous Goods Regulations. Non-scheduled
programmes are also organized and conducted
depending on the needs and requirements of various
functional departments.
It conducted 71 programmes participated by 1045
employees including 30 CISF officers from January
2004 to December 2004.
It conducted the first Joint Seminar with Airport De
Paris Training Center, France, on “Airport
Management for Senior Airport Executives” from 6
th
December to 17
th
December 2004. About 33 officers
of the level of General Managers, Airport Directors,
Addl. General Managers, Dy. General Managers from
Airports Authority of India including two foreign
participants, from Maldives and one Dy. General
Manager (Pers.) from Cochin International Airport
Pvt. Ltd., participated in the Joint Seminar.
In the year 2004, NIAMAR conducted ICAO Regional
Seminar on “Special Implementation Project (SIP)”
from 4
th
to 6
th
October 2004 and 8 foreign participants
from different SAARC countries like Bangladesh,
Nepal, Sri Lanka and Thailand have attended the
programme. It also conducted two workshops on
“Public Grievances & Grievance Redressal” during
the year.
••
••
• Civil Aviation Training College, Allahabad
The Civil Aviation Training College (CATC),
popularly known as CATC-Allahabad, is another
training establishment of AAI dedicated to training
in the area of Air Traffic Management (ATM) and
Communication, Navigation and Surveillance (CNS).
CATC-Allahabad is fully equipped with modern
training aids and has 19 fully air-conditioned
classrooms, 22 lab rooms for CNS equipment, 7 labs
for ATM, Library and Auditorium.
During April, 2004 to December, 2004 129 personnel
in 20 courses were trained in CNS stream and 121
personnel were trained in 12 courses in ATM
totalling 250 trainees in 32 courses.
Twelve trainees from Afghanistan were trained in 8
weeks Area Control (Refresher) Course w.e.f. 5.7.04.
Training for another batch of fifteen trainees from
Afghanistan for ab-initio (ATC) course is in progress
w.e.f. 5.7.04 for 50 weeks duration.
A state-of-the-art Radar Simulator has been installed
at CATC which has been supplied by M/s CS of
France with project cost of Rs.21 crores. This ultra
modern system is capable of ATC Radar training for
approach and enroute air traffic with 10 trainee work
stations. First batch of twelve trainees for RCAP
Course has successfully passed out on 7.1.05
Procurement and installation of Aerodrome
Visual Stimulator at a cost of 7.60 crores has been
taken up.
During the period January 2005 to March, 2005 104
personnel are planned to be trained in CNS stream
and 73 personnel are planned to be trained in ATM
stream, totalling a sum of 177 personnel.
59

Ministry of Civil Aviation
60
••
••
• Fire Services Training College (FSTC), Kolkata
The Fire Services Training College (FSTC), is
engaged in providing Basic, Refresher and Advance
Fire Fighting training to all grades of Fire Service
personnel including officers level and prepares them
for handling aircraft and airport installations fire
protection. The training curriculum is upgraded from
time to time to include requirement of latest Aviation
Technology and it conforms to ICAO requirements.
329 personnel were imparted training at FSTC,
Kolkata during the year.
••
••
• Fire Training Centre (FTC), New Delhi
The Fire Training Centre (FTC) imparts training to
airport Fire Service Personnel with an objective of
preparing meet the highly skilled demand of the
Airport fire service at various airports. The training
imparted at FTC are registered in the ICAO Directory.
146 personnel received training during the year.
7.12 VIGILANCE
As a part of proactive role, the Vigilance Department urged
other key departments for system improvement and
codifying of work procedures. On vigilance initiative many
suggestions were made on corrective preventive
measures in the form of general guidelines and circulars.
Vigilance Awareness Week was observed at all the 124
airports commencing from 1
st
November to 6
th
November,
2004. The focus this time was towards Education of
Customers and Users of the services provided at our
airports and to sensitize officials and public to evil
consequences of corruption. Towards this endeavour
during the week, CCTVs, Plasma monitors and screens at
the airports continuously displayed;
• AAI’s Mission Statement.
• Brief on AAI and Airport Specific
• Complaint redressal system and
• Avenues for redressal of complaints / grievances
available at the airport.
A special feedback campaign was launched at airports to
get responses to the questionaire on quality of services
at the airport and analysis thereon.
A workshop on “Disciplinary Proceedings” was organized
from 2nd November to 4th November, 2004 at our training
institute, NIAMAR. Various competitions were organized
in Hindi and English at different airports to effectively
sensitize officers and students to the adverse effects of
corruption. Observance at the airports drew
overwhelming response from officials and public. A
lecture on “Values of Values” by Swami Nikhilanandji,
Head of Delhi Chinmaya mission was organized on 5th
November' 04 at Headquarters to enlighten AAI officials
on ethics and moral values.
CVC guidelines for putting information on website relating
to all the tenders in AAI has been implemented as a step
towards increased transparency in the tender process.
*****
60
Annual Report 2004-2005
61
8.1 HISTORY
Tata Airlines started the first scheduled airmail service
in India on October 15, 1932. During the thirties, the
airlines used various small single-engined aircraft to
operate domestic services all over India. To emphasise
its new civilian status and its role as a public utility,
Tata Airlines was converted into a Public Limited
Company on 29
th
July 1946 and renamed Air India. At
the end of 1947, Air India submitted a plan to the
Government for the formation of Air India International
Limited with Government participation to operate
international services. The plan was approved and Air
India International launched its first service to London
via Cairo and Geneva on 8
th
June 1948 with
Constellation aircraft. In 1952, the Planning Commission
recommended the nationalisation of Air Transport
Industry, which was effected on August 1, 1953, with
the creation of two nationalised Corporations – Air
India International Limited, which retained its identity
and international flag carrier status, and Indian Airlines,
to operate domestic services.
Air India Limited
8
61
Air India's Boeing 777 Aircraft

Ministry of Civil Aviation
62
On 1
st
May 1992, Air India Ltd. was incorporated as a
Public Limited Company under the Companies Act, 1956
with the main object of succeeding the undertaking of
Air India. The Air Corporations Act, 1953 was repealed
by the President of India on 29
th
January 1994 by
promulgation of an ordinance called “The Air
Corporations (Transfer of Undertakings and Repeal)
Ordinance 1994”. The Central Government thereafter
issued a Notification dated 18
th
February 1994 by which
the undertaking of Air India was transferred to and
vested in Air India Ltd. (a company incorporated under
the Companies Act, 1956) with effect from 1
st
March,
1994.
8.2 BOARD OF DIRECTORS
The composition of Board of Directors as on 1
st
January 2005 is
as follows :
Shri V.Thulasidas Chairman & Managing Director
(effective 22
nd
December 2003)
Shri P.K.Mishra Addl. Secretary & Financial Advisor,
Ministry of Civil Aviation
(effective 30
th
December 2004)
Shri Raghu Menon Jt.Secretary,
Ministry of Civil Aviation
Shri Sunil Arora Chairman & Managing Director,
Indian Airlines
Shri N. Vaghul Chairman , ICICI Bank
Shri K.Ramalingam Chairman, Airports Authority of India
(effective 30
th
December 2004)
8.3 CIVIL AVIATION SCENARIO 2003/04
The World Air Transport Industry, which was reeling
under the impact of many adversities, showed signs of
recovery in the year 2003-2004. Airlines are slowly
emerging from one of the most difficult business
environments. International passenger and cargo traffic
growth continued to exceed expectations, though the
extraordinarily high level of oil prices continued to cast
a shadow on the profitability of airlines.
Closer home, in India, tourist arrivals have reflected
double digit growth rates in each month since June
2003 and, in most of this period, traffic has rebounded
to just above the 2000 levels i.e. before the incidents of
11
th
September 2001. The positive change apparent in
India and the emergence of Chinese economic strength
are expected to boost air traffic in Asia. The industry
was expected to return to profitability in 2004, riding
on the global economic recovery. However, oil prices,
which have moved in the range of USD 44-48 per barrel
in recent times, can seriously affect every airline’s
prospects and plans. According to an IATA estimate,
each dollar added to the average price of a barrel of
Brent over the year adds a USD 1 billion to the industry’s
costs.
Air India, conscious of the challenges posed by
increasing competition, spiraling costs and pressures
on yields, had pursued a strategy aimed both at cost
reduction and increase in revenue. Among the various
measures Air India had taken during 2003/04 were the
augmentation of capacity through dry lease of aircraft
for operations on existing and new routes adding to
62

Annual Report 2004-2005
63
••
••
• Haj 2004 : Haj Movement 2004 was successfully
carried out by Air India in association with Indian
Airlines and Saudi Arabian Airlines. Air India
operated 112 flights from Bangalore, Chennai,
Lucknow, Kolkata, Kozhikode, Nagpur and
Srinagar and carried 34,370 Haj pilgrims while Indian
Airlines carried around 7500 Haj pilgrims. Srinagar
was a new embarkation point for Air India this
year.
••
••
• VVIP Flights : During the year 2003-04 Air India
operated 7 VVIP flights on behalf of the
Government of India. During the period April-
November 2004 another 4 VVIP flights were
operated by Air India.
••
••
• Others : The Company was the recipient of a
Special Communication Project Award for
Effectively Handling Crisis Management, from the
Association of Business Communicators of India.
••
••
• M/s. Dun and Bradstreet have ranked Air-India
30
th
among the top 500 Companies of India based
on turnover. The ranking was based on Net Profit
which was 309 and on capital employed 164.
••
••
• Air-India has been awarded the prestigious
Mercury Award by the International Flight Catering
Association/International Food Service
Association at the IFCA 2004 Conference held
recently at Nice, France.
••
••
• Air India is the only PSU amongst 256 PSUs in the
country with multiple ISO Certificates. The
Engineering, Engine Overhaul, Ground Services
and Security Departments of the Company have
the cash margins, reduction in establishment costs,
formation of subsidiary companies for Ground Handling
and Engineering Services, hiving off non-core
activities, initiation of steps for establishing low-cost,
low-fare operations through its subsidiary on routes
to the Gulf, Middle East and South East Asia,
conclusion of a Strategic Alliance with Lufthansa
whereby both the airlines would, inter-alia, code share
on each other’s services between India and various
points, pursuing similar alliances with other global
carriers and introduction of e-ticketing on certain
domestic sectors.
Leasing tax : The withdrawal of Sec 10 (15A) exemption
in the Finance Bill from 1 September 2004, came as a
severe blow to the national carrier since most of its
expansion activity is being achieved through the
medium of dry lease. On representation by all the Indian
carriers, including Air India, the Government has
deferred the implementation of this provision till 31
March 2005.
8.4 HIGHLIGHTS OF THE ACTIVITIES
DURING THE YEAR
••
••
• Birth Centenary of Late Shri JRD Tata : Air-
India celebrated the birth centenary of J.R.D. Tata,
whose maiden flight heralded the birth of Air-India,
on July 29, 2004. A series of programmes were
organised to commemorate the occasion. The
functions organised included unveiling of a 7’x3"
statue of J.R.D. Tata at Old Airport Complex by
Shri Praful Patel, Union Minister of State for Civil
Aviation at a staff function held at Old Airport
Complex.
63
Ministry of Civil Aviation
64
••
••
• The Engineering and Engine Overhaul
Departments have received JAR-145 Repair Station
Certificate from the European Civil Aviation
Authority – JAA and FAR 145 Certificate from US
Civil Aviation Authority – FAA.
••
••
• On the occassion of the World Woman’s Day on 8
March 2004, Air-India operated its first flight AI-
470 on Mumbai-Delhi-Singapore sector with all
women cockpit crew. Capt. Rashmi Miranda and
Capt.Kshmata Bajpai, piloted the flight, operated
with an A310 aircraft.
••
••
• Air-India, the largest carrier of perishable cargo
from India, has taken over as the sole ground
handling agent at the world-class Perishable Cargo
Centre set up recently in Mumbai by the
Agricultural Produce Export Development
Authority, a body affiliated to the Ministry of
Commerce.
••
••
• The Maharajah Lounge at IGI Airport, New Delhi
has been refurbished and is now fully operational.
The Executive Class passengers can, while awaiting
departure of their flight, avail of an Ayurvedic
massage, in addition to other facilities, such as
Business Centre, Library and Music Centre.
••
••
• During the year 2003-04, Air India has secured
new ground handling contracts of Sri Lankan
Airlines, Air Sahara and Gulf Air at Kochi, KLM
Royal Dutch Airlines, Gulf Air, Royal
Jordanian(Freighter Flights), Singapore
Airlines(Freighter Flights) and Alitalia at Kolkata,
been awarded ISO 9002 Certificates by the Bureau
of Indian Standards. Earlier the Engineering
Department was certified under the old ISO
9002:1994 Standard Quality System Certification
from 1996. Under the new standards, the emphasis
has shifted from documentation of procedures to
customer satisfaction and continuous
improvement.
••
••
• Contact Programmes have been held in various
important cities and towns in Kerala, Goa, West
Bengal, Assam, the North Eastern States, Andhra
Pradesh, Karnataka and Tamil Nadu. The objective
of these Contact Programmes was to make a
concentrated effort to meet those customers who
have not flown on Air India in the past two years.
Our data bank was used to reach out to these
customers and obtain feedback from them to
upgrade our services and to woo these passengers
back to Air India. Both the traveling public and the
trade were openly appreciative of Air India’s efforts
to reach out to its markets.
••
••
• On Time Performance increased from 85% in 1999-
2000 to 88.5% in 2003-04 and RTKM/Employee
improved from 84 in 1999-2000 to 113.5 in 2003-04.
••
••
• Air India handled the following number of flights
during 2003/04 :
Air India 21111
Flts. of foreign airlines 20944
Other flights 1245
64

Annual Report 2004-2005
65
China Airlines(Freighter Flights), Turkish Airlines
and Air Canada at Delhi, Silk Air at
Thiruvananthapuram Thai Airways at Chennai and
Aeroflot at Mumbai.
••
••
• Since January 2004, all Air-India flights between
Delhi and Gulf/Europe and vice versa started
overflying Pakistan air space resulting in saving
of 30 mts to 1 hour of flying time.
••
••
• Air-India had carried out testing of routes
overflying Afghanistan air space on 20, 21 and 29
February, 2004. This was an important step towards
commencement of route search on India/Europe/
UK sectors and would assist us in selecting
minimum cost track of the day, based on minimum
fuel requirement, maintenance time cost, overflying
charges etc. It is expected that the saving on this
account would be about Rs. 7.10 crores per annum.
As and when the dry leased B747-400 aircraft are
fitted with additional passenger oxygen cylinders,
the saving would increase by another Rs.2 crores.
••
••
• Fuel Contract for Salalah was awarded to M/s. Shell
for the period from 01.04.2004 to 31.05.2005.
••
••
• Direct routing is cleared by AAI in co-ordination
with C.A.A. Yemen and Oman between Salahah to
a way point ANGAL in Indian FIR effective 28
th
June, 2004. This will reduce about 20 minutes of
flying for our flights between Salalah to Calicut.
Our Department was continuously pursuing for
the above route.
••
••
• An agreement with M/s. SITA has been signed for
supply of advanced computerised flight planning
system. Optimisation of the fuel requirement
calculation through the new system is expected to
save approx. Rs.6 crores per annum.
••
••
• Medical department has been awarded the
S.M.Dahanukar Trophy for the best medical set
up in the Industrial Medical Health.
• Air-India signed a Strategic Alliance agreement
with Duetsche Lufthansa AG on 10 August 2004
in Mumbai, whereby both the airlines will code
share on each others’ services between India and
various points in Germany such as Frankfurt,
Munich, Berlin, Stuttgart, Dusseldorf, etc. This
agreement was signed by Shri V Thulasidas,
Chairman and Managing Director, Air-India and
Wolfgang Mayrhuber, Chairman of the Executive
Board of Deutsche Lufthansa AG. Air India will
also code share on Lufthansa’s services beyond
Frankfurt/Munich to points in Europe and USA.
Effective 1 October 2004, the code share will be a
free flow code share.
8.5 IMPORTANT ACHIEVEMENTS :
••
••
• Air India achieves third consecutive year of profits
despite increased competition, spiralling fuel costs
and pressure on yields.
••
••
• Augmentation of capacity through dry lease of
aircraft for operations on existing and new routes.
ATKS increase by 19.5%., RTKMS by 13.6% in
2003/04 as compared to last year and fleet strength
to 35 as of 1
st
January 2005 as compared to 29 as of
31
st
March 2003. 17 aircraft inducted on dry lease.
••
••
• New destination introduced in the network viz.,
Newark, Los Angles, Shanghai, London
Terminators via Ahmedabad from Mumbai and
65

Ministry of Civil Aviation
66
enhanced operations on existing routes with
standardized departure timings in the last two years.
••
••
• Production upgradation by reconfiguring F and J
class seats with full flat beds in F class and
slumberette seats in Club class.
••
••
• Refurbishment of existing fleet of B747-400 aircraft
and A310 aircraft.
••
••
• Revenue Passengers carried increased from 3.45
million in 2002/03 to 3.83 million in 2003/04.
••
••
• On-time performance increased from 85% in 1999-
2000 to 88.% in 2003-04.
••
••
• Flights in summer and winter schedules of 2004
increased by 10% over the corresponding period
last year.
••
••
• Aircraft utilisation improved from 3280 hrs. per
annum to 3586 per annum in 2003/04 vis-a-vis last
year.
••
••
• Number of staff decreased from 16068 as of 31
st
March 2003 to 15572 as of 31
st
March 2004 due to
adoption of VRS and retrenchment of staff at
foreign stations including closure of uneconomic
offices.
••
••
• E-ticketing introduced in India effective August
2004. E-ticketing has now been extended to UK
sector from London effective February 2005.
••
••
• Proposed launch of Air-India Express-Budget
Airline-Low Cost Low Fare No Frill Airline to the
Gulf/South and Middle East, East Asia effective
May 2005. Project report was submitted to the
Govt. in December 2004. Meanwhile, 3 B737-800
aircraft are being dry leased with four more to
follow in 2006.
••
••
• Air India Board has approved acquisition of 50
aircraft upto 2012/13 (one third on option).
Meanwhile expansion through dry lease with
proposed fleet strength by Winter 2005 being 50.
••
••
• CMD-Air India was elected as President Elect of
the Aeronautical Society of India for the year 2005.
••
••
• An Advance Check-in Facility has been introduced
for passengers bound for USA/UK/Europe
travelling from Mumbai only with effect from 11
th
January 2005. At least one member of the family
who is travelling must go for the check-in alongwith
passports and tickets of the whole family. The
boarding cards will be given at the time of check-in
and passengers should report back to the airport
directly for immigration/customs clearance at least
90 minutes prior departure.
••
••
• The first B737-800 aircraft, out of the three aircraft
leased for Air-India Express was delivered to Air
India at Seattle on 23
rd
February 2005. The second
of the three B777-200ER aircraft leased for Air India,
joined the fleet on 15
th
February 2005.
••
••
• As per the Budget announcement on 28
th
February
2005, the exemption with regard to payment of
Withholding Tax on leasing of aircraft or aircraft
engines from foreign companies has been extended
till 30
th
September 2005 which will assist Air India
in dry leasing more aircraft for expansion and
growth without payment of Withholding Tax.
66
Annual Report 2004-2005
67
••
••
• Sale of Aviation Turbine Fuel (ATF) to Indian
carriers operating international flights has been
declared as “Deemed Export”, which will enable
the carriers to purchase ATF without payment of
Sales Tax, which ranges from 4% to 39%, which
will enable Air India to reduce its fuel cost structure
substantially.
8.6 C API TA L
The Authorised Capital of the Company is Rs 500 crores
divided into 425636820 Equity Shares of Rs. 10/- each
and 7436318 Redeemable Preference Shares of Rs100/-
each. The Total issued and Paid up share capital of the
Company as on March 31, 2004 is Rs.153.84 Crores.
8.7 SUBSIDIARY COMPANIES
The Company’s investments in subsidiary Companies are as under:
Hotel Corporation of India - Rs.40.60 Crs. (Authorised Capital – Rs.41 Crs.)
Air-India Charters Ltd. - Rs.5.00 lakhs (-“- – Rs.30 Crs. )
Air-India Air Transport Services Ltd. - Rs.5.00 lakhs ( -“- – Rs.100 Crs.)
Air-India Engineering Services Ltd. - — (-“- – Rs.10 Crs. )
8.8 INTERNAL RESOURCES PLOUGHED BACK INTO BUSINESS
As on March 31, 2004 an amount of Rs. 6264.61 Crores has been ploughed back into business.
8.9 FLEET
As of 1
st
January 2005 Air India has the following aircraft in its fleet:
Total Fleet Owned Avg. A ge Leased Avg. Age
B747-200 2 2 24.9 yrs - -
B747-300 2 2 16.2 yrs - -
B747-400 11 6 10.1 yrs 5 14.8 yrs.
B777-200 1 0 - 1 5.8 yrs.
A310-300 19 8 17.5 yrs 11 14.8 yrs
TOTAL 35 18 15.7 17 13.0 yrs.
Note: One B747-200 aircraft is on ground awaiting disposal and is not included in the above fleet.
67
Ministry of Civil Aviation
68
* Flights on the following routes increased from two
to three effective March 2004
– Mumbai/Nairobi/Dar-es-Salaam
– Hyderabad/Jeddah/Hyderabad
– Lucknow/Delhi/Jeddah/Lucknow
* Effective 4
th
April 2004, AI commenced operations
to Salalah with a weekly extension of the Al-Ain
flight to Kozhikode.
* Twice weekly Delhi/Amritsar/Delhi Hub-&-Spoke
flights effective 16
th
April 2004
* Effective 11
th
June 2004, 3 weekly flights
commenced to Los Angeles via Frankfurt.
* Effective 13
th
June, 2004, started 2 flights per week
from Ahmedabad to Dubai.
* Effective 29
th
November 2004, 4 noon-time
departure flights introduced a Mumbai/London/
Mumbai.
* Effective 4
th
December 2004, additional flight to
London operated on the routing Mumbai/Delhi/
London/Delhi/Mumbai.
* Effective 5
th
December 2004, Los Angeles flights
increased to 5 via Frankfurt.
* The total number of flights increased to 162 during
Summer 04 as against 147 operated during
Summer 03.
* In Winter 04 the flights increased to 167 from 152
operated in Winter 03.
* Standardised departures from Winter 2004
timetable
8.10 OPERATIONS
••
••
• The pattern of operations during 2004/2005 were
as follows:
Routes Summer Winter
2004 2004
India/London/New York 7 7
India/London (T) 2 7 *
India/London/Chicago 3 3
India/Frankfurt/Los Angeles 3 5
India/Frankfurt/Chicago 3 3
India/Frankfurt (T) 3 3
India/Paris/Newark 7 7
India/Nairobi/Dar-es-Salaam 3 3
India/Gulf 105 103
India/Bangkok/Tokyo 2 2
India/Tokyo (T) 2 2
India/Bangkok/Shanghai 2 2
India/Hong Kong/Osaka 2 2
India/Hong Kong (T) 3 3
India/Singapore/Jakarta 3 3
India/Singapore/Kuala Lumpur 7 7
India/Singapore (T) 5 5
Note : * 4 services with B777-200ER effective 30
th
December
2004.
••
••
• New Routes
* Twice weekly Mumbai/Ahmedabad/London
flights introduced effective March 2004
68
Annual Report 2004-2005
69
AI now has standardised departures from most
cities in the network except where slots have not
been granted by the local authorities or where
markets require otherwise.
••
••
• Extra Sections : In order to meet the additional
demand during the peak season, 18 extra sections
were operated from India to various points in the
Gulf during the current year. During the first six
months of the current financial year, there has been
an increase of approx. 30% in the timetable hours
as compared to the same period last year. During
the current year, we have also planned operation
of 174 Haj flights in two phases.
••
••
• Joint Ventures and Code Share Arrangements.
Air-India signed a Strategic Alliance with
Lufthansa effective 1
st
October 2004. Many existing
Code Share and Joint Venture Agreements with
foreign airlines were continued. These
arrangements using foreign airlines aircraft are
given below :
To : With :
USA :
Chicao/Denver/Detriot/ Lufthansa–December 2004
Los Angeles/Washington
Los Angeles/San Francisco Singapore Airlines
Los Angeles Malaysian Airlines
San Francisco Asiana Airlines
Europe
Paris/Frankfurt/Berlin Air France
Vienna Austrian Airlines
Zurich Swiss Airlines
Frankfurt/Berlin/ Lufthansa – 01 Oct.2004
Dusseldorf/Munich/
Stuttgart/Amsterdam/Lyons
Geneva/Zurich Lufthansa – subject to
German Govt. clearance
Russia : Moscow Aeroflot
Africa : Mauritius Air Mauritius
Gulf :
Dubai Emirates & Thai Airways
Kuwait Kuwait Airways
Istanbul Turkish Airlines
S.E. Asia :
Singapore Silk Air & Singapore Airlines
Kuala Lumpur Malaysian Airlines
Far East
Seoul Asiana Airlines
Bangkok Thai Airways
In addition to the above, Air-India also implemented Block
Space Arrangements, as follows:
Between With
GULF
Bangkok-Dubai-
Chennai-Dubai Thai Airways
FAR EAST
Bangkok-Shanghai/ Thai Airways
Tokyo/Hong Kong
Air-India also has entered into a code-share with Indian
Airlines for Mumbai/Bangalore – Hyderabad/Chennai
sectors on two flights per week.
69
Ministry of Civil Aviation
70
The Haj 2005 period is
– Phase 1 Dec. 13, 2004 – Jan. 15, 2005
– Phase 2 Jan. 25, 2005 - Feb. 24, 2005
The first Haj flight flagged off from India on Dec. 13,
2004 from Srinagar
Air-India is supporting this programme with a 1-line
747 operation and a 2-line A310 operation. This is being
supplemented by Indian Airlines with a 1-line AB4
operation.
All physical arrangements at the embarkation points
have been finalised and tied up in close coordination
with Indian Airlines, State Haj Committees and Haj
Committee-India.
8.12 FINANCIAL HISTORY
• Debts
* Aircraft Loan : The aircraft loans outstanding as
on 31
st
March 2004 are mainly in respect of six B747-
400 aircraft acquired during 1993-96. These loans
were arranged through External Commercial
Borrowings (ECB) supported with US Exim
guarantee and guarantee/comfort letter furnished
by the Govt. of India. It is pertinent to mention
that due repayment of loans over the years, the
aircraft loan balances have reduced in terms of US
Dollar, but in terms of Indian Rupees the loan
balances have not shown corresponding
reductions primarily due to devaluation of Indian
Rupees as reflected below:
••
••
• Offices (as on December 31, 2004 ):
Online - 55
Offline - 37
Sales Representative - 07
8.11 SPECIAL OPERATIONS
••
••
• Haj Operations 2005 : Air-India continues
to be the nodal agency to coordinate the Haj Programme
on behalf of the Ministry of Civil Aviation. The
highlights of Haj 2005 are as under:
Embarkation Stations: 3 new embarkation stations
have been added for Haj 2005 viz., Guwahati, Patna and
Aurangabad. Patna is a switch with Gaya. The
embarkation stations finalised for Haj 2005 are :
Ahmedabad, Mumbai, Kozhikode, Delhi, Ahmedabad,
Chennai for Saudi Arabian Airlines. Bangalore, Kolkata,
Jaipur, Lucknow, Nagpur for Air-India. Guwahati,
Aurangabad, Patna stations are being covered by way
of an Hub & Spoke arrangement. While Guwahati
pilgrims will be brought to Kolkata to connect Air-India
flights, Aurangabad and Patna pilgrims will be brought
to Mumbai and Delhi to connect Saudi Arabian flights.
The total number of pilgrims being carried from each
station are as under :
Ahmedabad 6054 Mumbai 10643
Kozhikode 9600 Delhi 11790
Hyderabad 5500 Chennai 2738
Bangalore 4080 Kolkata 3528
Jaipur 3800 Lucknow 7800
Nagpur 2969 Guwahati 1670
Aurangabad 1700 Patna 1600
Srinagar 8750
70
Annual Report 2004-2005
71
* Working Capital Loan : Due to financial crunch faced by
Air-India from 1996-97 onwards, Air-India has taken working
capital loans, as shown below:
Loan Balance Rs. / Crores
As on 31.03.1997 260
As on 31.03.1998 951
As on 31.03.1999 1013
As on 31.03.2000 1026
As on 31.03.2001 1102
As on 31.03.2002 1004
As on 31.03.2003 740
As on 31.03.2004 554
As on 30.09.2004 working capital loan is 456 Crores
(Provisional). In addition, Air-India had taken loans for Haj
operations on need basis. Air-India has never defaulted in
servicing its debts and have paid the loans in time.
Aircraft Loan Balance USD/Million Rs. /Crores
As on 31.03.1997 795.689 2899.78
As on 31.03.1998 679.673 2698.35
As on 31.03.1999 571.344 2424.21
As on 31.03.2000 509.6925 2223.29
As on 31.03.2001 447.842 2087.84
As on 31.03.2002 385.789 1882.65
As on 31.03.2003 299.023 1419.91
As on 31.03.2004 210.860 921.77
As on 30.09.2004 the Aircraft Loan is Rs. 815.39 Crores
and estimates as on 31.03.2005 is Rs.636.28 Crores.
• Debt Equity Ratio
The Debt equity ratio of the Company as on 31 March 2004 was 3.0:1 against 4.5 : 1 as on 31 March 2003.
• Summary of Financial Performance for the last 7 years :
Particulars Units 2003-04 2002-03 2001-02 2000-01 1999-00 1998-99 1997-98
Financial Performance
Operating Revenue Rs.Crores 5987.98 5275.91 4751.36 4927.45 4448.05 4135.26 3837.21
Operating Expenses Rs Crores 6104.24 5465.63 4805.89 4924.35 4372.00 4139.84 4029.84
Operating Profit/(Loss) Rs.Crores (116.26) (189.72) (54.53) 3.10 76.05 (4.58) (192.63)
Total Revenue Rs.Crores 6322.07 5689.88 5032.94 5278.84 4772.62 4236.72 4174.16
Total Expenses Rs.Crores 6229.74 5556.02 5017.50 5323.24 4810.25 4411.20 4355.17
Net Profit/(Loss) Rs.Crores 92.33 133.86 15.44 (44.40) (37.63) (174.48) (181.01)
Yield per Rtkm (Schd. Serv. Rs. 25.81 25.80 26.38 26.02 24.43 22.90 21.95
Rev. per Rtkm)
71
Ministry of Civil Aviation
72
8.13. FINANCIAL ANALYSIS
••
••
• Financial Analysis F.Y 2003-04 as against F.Y
2002-03
During the year under review, the total revenue of the
company consisting of Passengers, Excess baggage,
Mail, Cargo, Charter and Handling / Servicing /
Miscellaneous Revenue was Rs. 62364.4Million as
compared to Rs. 56578.7 Million for the year 2002-03
representing an increase of 10%. The total expenditure
of the company likewise was Rs. 62286.0 as compared
to Rs. 55458.7 Million representing an increase of 12%.
The profit of the year before tax was Rs.78.4 Million as
compared to Rs. 1120.0 Million during the year 2002-03.
After providing for taxation and accounting for deferred
tax benefit as per Accounting Standard 22, the net profit
earned during the year 2003-04 was Rs.923.3 Million as
against Rs. 1338.6 Million during the previous year, a
decrease of Rs.415.3 Million.
The factors leading to the decline in profitability were
the SARS outbreak and Pilots’ strike during the first
quarter, April to June, 2003 and the profitability of
operations in the initial phase in respect of the new
routes with dry leased aircraft was not in line with the
estimates.
72
••
••
• Financial Analysis April/September 2004 as against April/September 2003
The results of the Company for the period April/ September 2004 (Provisional) as compared to April / September 2003 are
given below:
(Rs. in crores)
Particulars April to Sept 04 (Prov.) April to Sept 03
Operating Revenue 3350.52 2667.4
Operating Expenses 3448.77 2747.4
Operating Profit/(Loss) (98.25) (80.02)
Total Revenue 3470.76 2812.20
Total Expenses 3462.91 2771.6
Net Profit/(Loss)* 7.85 40.59
(including Deferred Tax benefit)
Annual Report 2004-2005
73
8.14 PHYSICAL PARAMETERS
••
••
• Summary of Physical Performance for the Last 7 Years
Physical Performance 2003-04 2002-03 2001-02 2000-01 1999-00 1998-99 1997-98
Revenue Hours Flown(Total) No. 107886 91318 84468 80380 79289 84391 84065
ASKMs (Total) Millions 22293.6 18715.6 17680.1 17915.6 17821.5 18591.7 18067.3
ATKMs (Total) Millions 2984.0 2495.5 2392.6 2419.2 2415.4 2540.9 2445.7
Pax Load Factor % 70.5 71.6 66.6 73.1 70.3 66.9 67.5
Overall Load Factor % 61.2 64.6 60.8 67.4 65.1 61.5 63.4
8.15 FOREIGN EXCHANGE EARNINGS
The foreign exchange earned / saved by the Company,
computed on the basis of the formula approved by the
Government in 2003-04 was Rs. 1753 crores as against
Rs 1517 crores in the previous year .
8.16 MEASURES TO CONTAIN IMPACT OF
INCREASE IN FUEL PRICES
••
••
• Hedging the Fuel Prices
Global fuel prices continued their upward spiral
during the year 2004. Average fuel prices increased
from USC/USG 113.99 during FY 2003-04 to USC/
USG 156.87 during period Apr.-Dec.04., the peak
being Nov.04 at USC/USG 187.69. AI expects to
spend approx. Rs.500 crores more than what was
budgeted for the FY 2004-05. The company also
pursued its efforts in the direction of hedging fuel
prices by finalising Risk Management Policy and
pursuing the International Swap Dealers
••
••
• Physical Analysis F.Y 2003-04 as against F.Y.
2002-03
Number of Passengers increased from 3.46 million to
3.84 million in F.Y 2003-04 an increase of 11%. The traffic
capacity offered increased by 20% whereas the traffic
carried increased by 11%. The passenger load factor,
however, decreased from 71.6% to 70.5% and Overall
load factor also decreased from 64.6% to 61.2%.
••
••
• Physical Performance April/September 2004 as
against April/September 2003
Particulars April to Sept 04 April to Sept 03
(Prov.)
PKMs(Total) 9208.6 6989.2
ASKMs (Total) 13035.4 10021.5
Pax Load Factor (%) 70.6 69.7
RTKMs (Total) 1066.9 822.6
ATKMs (Total) 1717.3 1342.8
Overall Load Factor(%) 62.1 61.1
Yield Per RTKM (Rs) 25.40 26.36
No of Pax (Schd.Ser) 2193774 1783937
73

Ministry of Civil Aviation
74
Association Agreement with the counter parties.
M/s. Ernst and Young have been appointed as
consultants for “hand holding” during the initial
phase of hedging. Since the fuel price was at its
peak, the hedging activity has not yet commenced.
••
••
• Opening of Air Space
With the opening of Air space over Pakistan for
our flights, various possible ATS route options
like Afghanistan, Turkmenistan, Russia, etc. have
emerged. This enabled us to conduct a route search
to decide the most economical route considering
various factors like Wind Component, Overflying
Charges, etc. It is decided to commence operation
on overflying Afghanistan with Air India aircraft
resulting in a saving of approx. Rs. 9 crores per
annum. Leased aircraft can commence overflying
Afghanistan after modification of passenger
oxygen system.
••
••
• Economic Tankering
As fuel prices vary from airport to airport, Airlines
do take advantage of the fuel price differences and
uplift more fuel at an airport where the price is
cheaper as compared to the next airport of landing,
after taking into account following factors
– Fuel price difference should offset additional
burn-off
– Fuel is available for economic tankering.
– Performance and Payload considerations
permit.
– To avoid undue wear and tear in operating to
maximum landing weight, (additional uplift of
fuel should be normally be restricted upto
maximum landing weight depending on the
type of aircraft).
••
••
• Fuel Surcharge:
In order to meet the spiraling fuel costs, effective
October 2004, fuel surcharges were increased as
follows :
– India to Gulf - USD10
– India to USA/UK/Europe/SEA/Africa - USD15
– India to USA on direct services – USD25
Fuel surcharges were also introduced in cities
across our network wherever implemented by the
National Carriers.
8.17 UPDATE ON DISINVESTMENT IN A
WHOLLY OWNED SUBSIDIARY –
HOTEL CORPORATION OF INDIA
(HCI) LTD.
As per the decision taken by the Government of India,
Air India Limited had appointed M/s. J.P.Morgan
(formerly M/s.Jardine Fleming Securities Limited) as
the Global Advisor for divesting the share of Air India
in the Company including the option of sale of
individual business through the slump sale. Though
the process of disinvestments was started in the year
2000, however, actual transaction in respect of Centaur
Hotel Juhu Beach and Centaur Hotel Mumbai Airport,
Mumbai took place in the year 2002. The business of
Centaur Hotel Juhu Beach was transferred to M/s.Tulip
Hospitality Services Limited in terms of Agreement to
Sell dated 11.03.2002 effective 31.05.2002 at a
consideration of Rs.1530 Million as per the bid accepted
by the Cabinet Committee on Disinvestment in its
meeting held on 10.11.2001 and Centaur Hotel Mumbai
74

Annual Report 2004-2005
75
Airport to M/s.Batra Hospitality Pvt. Ltd., ( presently
known as M/s.Sahara Hospitality Limited) in terms of
Agreement to Sell dated 18.04.2002 effective 05.06.2002
at a consideration of Rs.830 Million as per the bid
accepted by the Cabinet Committee on Disinvestment
in its meeting held on 05.02.2002. The disinvestment of
remaining units could not take place as the bids
received was lower than the reserve price and for
disposal of Centaur Lake View Hotel, Srinagar certain
issues were to be resolved with the State Government.
The process of disinvestment in respect of remaining
units was once again re-initiated in 2003 and Expression
of Interest was called for disposal of Centaur Hotel
Delhi Airport (including Chefair Delhi) and Chefair Flight
Catering (including Dining Facilities, Mumbai) through
an advertisement which appeared on 14.10.2003.
Ministry of Disinvestment had shortlisted 39 parties
out of 46 parties whose response was received and 20
parties have deposited the Earnest Money and shown
the seriousness. It is likely that the process of
disinvestment of these two units would be completed
shortly. As regards disposal of Centaur Lake View Hotel,
Srinagar it was decided by the Central Government to
dispose off the same to the Government of J&K at
negotiated terms. Core issues were identified and the
property has been got valued by an individual Valuer
and very soon a decision in this regard would be taken
to transfer the property to the Government J&K.
••
••
• Disposal of Centaur Lake View Hotel, Srinagar:
In pursuance of the Hon’ble Union Minister of
Civil Aviation’s Letter dated 16
th
August 2003 to
the Hon’ble Chief Minister, Government of Jammu
& Kashmir, the State Government has shown its
willingness to take over the property of Centaur
Lake View Hotel, Srinagar. Several meetings have
taken place between the State Government and
the Central Government. The core issues have
been identified, the assets of Centaur Lake View
Hotel had been evaluated by the Asset Valuers,
and same has been submitted to the State
Government for their views. The Chief Secretary, J
& K Government, has informed that they are
examining the matter and would be reverting. It
was desired by the State Government to introduce
Voluntary Retirement Scheme (VRS) for the
employees of Centaur Lake View Hotel Srinagar,
which was agreed, subject to reimbursement of
the said amount by the Government of Jammu &
Kashmir at the time of transfer.
A meeting took place between the Chief Secretary
and CMD-AI on 3
rd
May 2004 where there were
consensus on the principle issues. However, a
counter claim was given for the first time by the
State Government, which was examined. In this
regard, a meeting was organized alongwith the
Principal Secretary-Tourism, J & K Govt. and
officials of HCI at Centaur Hotel Delhi Airport, on
15
th
October 2004 when the core issues were
discussed and a consensus drawn up. As per the
consensus arrived, a sum of Rs. 4.11 crores is due
to be paid by the State Government to HCI as on
31.3.2004. In the said meeting, it was desired by
the State Government to implement VRS among
the staff of CLVH. A reference was made by the
Ministry of Civil Aviation to the State Government
seeking their confirmation with regard to the cost
of VRS and the consensus on the core issues. In
this regard, a meeting of the Central and State
Committees was held on 6.1.2005 when these issues
were addressed.
75

Ministry of Civil Aviation
76
8.18 PRODUCT DEVELOPMENT
••
••
• The Maharajah Club (TMC) and the Leading Edge
Club (LEC) : Membership to these two elite clubs
is by invitation only. The Clubs were re-launched
effective 15
th
August 2004 till 14
th
August 2007 with
enhanced features. Targeting the high yield
passengers they offer recognition and value added
benefits to retain the loyalty of the members. As
on 30
th
September 2004, there were 2006 Maharajah
Club members and 2150 Leading Edge Club
members.
••
••
• E-Ticketing : Air India introduced E—Ticketing
(Electronic Ticketing) through it’s offices in India
from August 2004. IATA has advised that all airlines
should implement E—Ticketing, as the system of
issuance of conventional paper tickets will be
discontinued by the end of 2007. From the
beginning of 2008, only E—Tickets will be used in
the aviation industry globally. Air India plans to
implement the E—Ticketing programme in a
planned and phased manner to adhere to the
timeline set by IATA for complete switchover from
paper tickets to E—Tickets.
Air India’s E—Ticketing programme commenced
with the cutover of 9 online India stations to E—
Ticketing for domestic bookings. The stations were
Mumbai, Delhi, Chennai, Bangalore, Hyderabad,
Thiruvanathapuram, Kochi, Kolkata and
Ahmedabad. This was completed during the period
August to October, 2004. In the first week of
December, 2004, international bookings for the
India/USA/India route was E—Ticket enabled
through the Air India offices at New York, Newark,
Chicago, Los Angeles and Washington.
Simultaneously, E—Ticketing facility has also been
provided to passengers making bookings directly
through our online booking facility YATRIK.
••
••
• Approval of VVIP kit by DGCA : DGCA had
approved the use of VVIP kit developed in-house
for B747-400 aircraft.
••
••
• Installation of Solid State Digital Audio System :
All the aircraft in Air India’s fleet were retrofitted
with the new generation Solid State Digital Audio
Reproducers of M/s TEAC. This system provides
improved sound quality and has capacity for 16
channel audio output – of which 8 are stereo
channels.
••
••
• Re- delivery of two A310s dry leased from
GECAS: The lease term of the two A310 aircraft
(VT-EVH & VT-EVG) of General Electric Capital
Aviation Services (GECAS) ended in June and July
2004. As per the re-delivery conditions, “C” check
was performed at a JAA approved maintenance
facility and redelivered to GECAS.
••
••
• Catering : On the occasions of Independence Day
and festivals like Diwali, Onam, Pongal and
Ramadan, special meals were uplifted and sweets
were offered to the passengers on flights operating
on that day. Wider choice of duty free items has
been offered to passengers. 21 new items have
been added to the duty free sale items effective
October 1, 2004.
••
••
• Cabin Upgradation : Under the cabin product
upgradation programme, so far First Class and
Executive Class seats of B747-400 aircraft have
been replaced with more comfortable state-of-the-
art seats.
76

Annual Report 2004-2005
77
••
••
• Future Plans : It is proposed to upgrade the fleet
as under :
* A310-300 Aircraft :
At this point of time, it is anticipated that the A310-
300 fleet will not be in the service beyond 5 years.
Considering this, it is proposed to carry out :
Ø Seat Refurbishment : All Executive Class,
Economy Class seats as well as Attendant
seats will be refurbished and all seat belts will
be replaced. This refurbishment is expected
to be completed within 8 to 10 months. The
estimated cost of Seat Refurbishment is USD
2.40 million (Rs. 11 crores) for 8 aircraft.
Ø Cabin Interior Upgradation: Cabin Interior
upgradation involves repainting the interior
in new color scheme, changing all decorative
laminates and replacement of curtains,
upholstery etc. This upgradation package is
estimated to cost little over USD 1.0 million
(Rs. 5 crores) for the fleet and the work will
be completed in 2 months time after it is
taken up.
* B747-400 Aircraft :
The B747-400s are expected to be retained in service
for the next 10 years and the cabin upgradation
programme chalked out for these aircraft is as
under:
Ø Replacement of existing Economy Class
Seats: It would be cost effective to replace
the existing seats in economy class with new
seats which are ergonomically designed to
provide maximum comfort. These new seats
will have provision for individual IFE System
and in-seat power supply for lap top
connectivity. It is estimated that new Economy
Class Seats would cost USD 1.00 million per
aircraft or USD 6.0 million for the fleet (Rs. 28
crores).
Ø Providing latest Inflight Entertainment System
(IFE) with Audio / Video on Demand, internet
and Phone facility for all passengers including
personal monitors. The estimated cost is USD
8 million per Aircraft or USD 48 million for the
fleet (Rs. 220 crores).
Ø Providing Inflight entertainment and new
seats will take 12-18 months.
* Upgrading the Interior of the Cabin: This involves:
Ø Replacement of all decorative laminates
including sidewall panels.
Ø Replacement of Stowage Bin Covers and
Ceiling Panels to give an enhanced and
spacious look.
Ø Replacement of existing Cabin Lighting with
Dynamic Lighting which provides many
options of lighting in the Cabin. Estimated
cost for the dynamic lighting, enhanced cabin
interior and replacement of all decorative
laminates is Approx. USD 1.9 million per
Aircraft or USD 11.4 million for the fleet (Rs.
53 crores). This work will require 4-6 months
for completion after it is taken up.
77

Ministry of Civil Aviation
78
* Replacement / upgradation of existing galleys and
toilets : A need was felt to provide latest
equipments like steam ovens, microwaves, coffee
percolator etc. in the galley. M/s.Jamco,
manufacturer of our existing galley was approached
for a solution. They opined that, such elaborate
changes are not possible with the existing galleys
and new galleys will be required. Estimated cost
of toilet upgradation is USD 6.5 Million for 6
aircraft (Rs. 30 crores)
* Catering:
Ø Planning to uplift branded and Imported Soft
variety of Segment Cheese and Branded
Presentation Chocolate Box in the Executive
Class for Lunch/Dinner service out of all
applicable Indian Meal Stations.
Ø Bone China crockery will replace porcelain
crockery in the First and Executive class.
Ø Metal cutlery will replace plastic cutlery in the
First, Executive and Economy class as per
directives of Security.
Ø Stainless steel tea/bar service items will replace
silver plated tea/bar service items.
Ø Damask linen and Pure wool shawl type
blankets will be uplifted in the First class and
Executive class.
78
In-flight scenario
Annual Report 2004-2005
79
8.19 OTHER REVENUE GENERATING
ACTIVITIES DURING F.Y 2003-04 AND
APR-SEP 2004.
••
••
• The revenue earned by Engine Overhaul
Department during the period April –September
2004 was Rs. 19.16 crores and projected revenue
for the next six month is Rs.8.20 crores (approx.).
• The revenue earned by the Ground Services
Department during the year 2003-04 is Rs.330.27
crores and Security revenue of Rs.58.61 crores
totalling Rs.388.88 crores. The estimated Ground
handling and Security revenue for the financial
year 2004-05 will be approx. Rs. 325 crores and
Rs.60 crores respectively.
••
••
• The Security Department earned a revenue of
Rs.49.84 crores by way of handling customer
Airlines during the year 2003-04.
8.20 AIR INDIA’S FUTURE STRATEGY
••
••
• In August 2004, at a meeting held in the Ministry,
it was decided that Air India would revisit the
aircraft acquisition proposal submitted in January
2004 (detailed in para (a) above), in view of:
Ø Induction of non-stop services to USA by
competitive airlines in the Gulf and South East
Asia and the need for Air India to offer a
competitive product with suitable aircraft.
Ø Low cost, low fare operations with dry leased
B737-800s now envisaged under Air India
Express.
Ø Induction of aircraft on dry lease to meet the
interim capacity of Air India.
••
••
• The Revised Fleet Plan approved by the Board
envisages an increase in the fleet size for Air India
and Air India Express combined from the present
35 to 74 aircraft as follows:
Aircraft Type Present Planned Net
Fleet Fleet Addition
(2012/13)
B747-400 11 6 -5
B747-300 2 - - 2
B747-200 2 - - 2
A310-300 19 - - 19
B777-200ER 1 - -
MCULR - 8 + 8
MCLR-A - 15 +15
MCLR-B - 27 +27
B737-800 - 18 +18
Total 35 74 +39
79

Ministry of Civil Aviation
80
operating pattern for operations in all Economy
seating configuration and with low costs and low
fares, now envisaged under Air India Express. This
revised Project Report was approved by the AICL
Board and the same was submitted to the
Government on 07 December 2004
••
••
• In the context of the recently announced decision
of the Government to allow private domestic
airlines to also operate on all international routes
(excluding the India/Gulf-Middle East routes) – and
the clarification that Air India’s operating plans
will be given due cognizance before allocating
available entitlements to such airlines – it is
essential for Air India and Air India Express to
induct additional aircraft on dry lease during 2005
in order to ramp up its capacity at the earliest.
••
••
• Air-India Express - a wholly owned subsidiary of
Air India Charters Limited, will commence
operations from 27 April 2005 with services
between India and Gulf/ME (except Saudi Arabia)
and SE-Asia hitherto being served by Air India.
Dubai, Singapore and Kuala Lumpur will be served
both by Air-India and Air-India Express
concurrently. Air-India Express flights will be
operated initially with leased B737-800 aircraft. On
mature operations (Summer2006), Air-India Express
••
••
• The Air India Board had approved the Revised
Long Term Fleet Plan - fleet requirements of Air
India and Air India Express - upto the period 2012/
13. This fleet plan was undertaken as a
consequence of the following:
Ø Air India submitted a Project Report for the
acquisition of 10 A340-300 + 18 B737-800W
aircraft to the Ministry in January 2004.
Ø Thereafter, Air India presented its medium term
business strategy and growth plans till 2006
to its Board in March 2004.
Ø The Board decided to launch a separate new
airline, “Air India Express”, for low cost, low
fare operations with B737-800 aircraft on dry
lease till the period upto Winter 2006/07.
Ø Pending aircraft acquisition, the Board further
decided to induct 34 aircraft (3 Medium
Capacity Ultra Long Range + 17 Medium
Capacity Long Range aircraft for Air India and
14 B737-800 aircraft for Air India Express) on
dry lease till the period upto Winter 2006/07.
••
••
• The Board further authorized the Management to
update the earlier Project Report for the acquisition
of 18 x B737-7800W aircraft (submitted to the
Government in January 2004), based on the
80

Annual Report 2004-2005
81
is expected to have a fleet of 14 B737-800 aircraft.
A stand-alone web based Reservation system has
been procured which would enable passengers to
purchase tickets over the Internet, the airline’s
Reservation offices or through the Travel Agents.
The airline will be able to offer attractive pricing
through saving in the following areas:
Ø Booking agency commission would be
reduced from 7 % to 3.5 %.
Ø. Scaled down on-board service- packed snack
boxes will be served.
Ø. Indian and foreign liquor will be served on-
board on payment.
Ø. Duty free liquor and cigarettes would be sold
on-board.
Ø. The aircraft would be all-economy version
with 31-inch pitch.
Ø. Reducing cabin crew complement from ten to
five and ensuring minimum 75 hours flying a
month
Ø Operating crew utilization would be ensured
at 65 hours a month.
Ø. Free Baggage Allowance from Gulf region
pegged at 30 kilos ie.10 kilos extra over
standard FBA of 20 Kg on all sectors.
Ø The airline will have a lean HQ and
organization structure with outsourcing of
non-core activities.
The net operating profit on operations of 127 flights
per week is projected at Rs. 264 crores based on a 25%
reduction in fares and a seat factor of 68 percent.
••
••
• The following routes have been identified for such
capacity expansion in 2005:
– India/London
– India/Frankfurt/Chicago
– India/Frankfurt/Los Angeles
– India/Birmingham/Toronto
– India/Mauritius
– India/Bangkok/Shanghai
– India/Bangkok
– India/Singapore
– India/Kuala Lumpur
– India/Singapore/Jakarta
– India/Hong Kong
– India/Hong Kong/Osaka
– India/Bangkok/Singapore
81

Ministry of Civil Aviation
82
purchasing IATA published full fares in First,
Executive & Economy Class to take along a
companion free of cost. Members of the Flying
Returns programme are entitled to Additional
Mileage Points if they do not avail of the
Companion ticket.
••
••
• Auctions through Indiatimes.com: Introduced
effective 12
th
November 2003, Air-India continued
to auction seats in Economy class through
Indiatimes.com a leading internet portal. Specific
sectors and flights on which there is low demand
are identified and a certain number of seats on
these flights are put up for auction. Till November
2004, revenue of Rs.53.12 lakhs was earned through
these auctions.
••
••
• Pravasi Bharatiya Divas : In order to facilitate
NRIs to attend the Pravasi Bharatiya Divas held in
Mumbai from 7
th
to 9
th
January 2005, special fares
were given to all those registered as delegates for
the event.
• Medical Tourism : Air-India tied up with M/s Vedic
India to tap the growing medical tourism market.
Medical packages including airfares were offered
to all those wanting to undergo treatment in India
upto December 2004.
8.22 AIR SAFETY
Air India maintained a high standards of ‘SAFETY’
during the year 2004-05 till date. There were no incidents
resulting in any significant injury to passenger/crew or
any major damages to aircraft/equipment. The main
••
••
• For additional operations on the above routes, Air
India and Air India Express will need to induct
additional aircraft as follows :
Aircraft Existing Proposed Additional
Type Fleet Fleet Aircraft
(Winter Required on
2005) Dry Lease
in 2005
B747-200 2 - -
B747-400 11 11 -
B747-300 Combi 2 2 -
B747-400 Combi - 1 +1
A310-300 19 21 +2
B737-800 - 7 +7
B777-200ER 1 3 +2
MCLR - 5 +5
Total 35 50 +17
Note: (a) Lease arrangements for 3 x B777-200ER and 3 x B737-
800 aircraft have already been finalized.
(b) 1 x B777-200ER has already been inducted and 2 x
B777-200ER will be inducted shortly.
8.21 MARKETING STRATEGY
••
••
• Expansion through Dry Leasing : Air-India is
planning to increase frequencies to Los Angeles
and Chicago to 7 a week with the induction of dry
leased aircraft.
••
••
• Companion Free Scheme: The Companion Free
Scheme is continued allowing passengers
82
Annual Report 2004-2005
83
8.24 ENGINE OVERHAUL
The department is an approved FAA and JAA repair
station and is endeavouring to get additional third party
work. The department continues to provide all support
in terms of repair and overhaul of various engines and
APUs for Air India’s fleet. The standard for engines
and APUs were continuously reviewed to achieve
improved reliability and control of maintenance cost
per engine flying hour.
8.25 GROUND SERVICES DEPARTMENT
••
••
• During the period April-September 2004, the GSD
handled-
AI Flights : 11,357
Flights of Foreign Carriers : 11,547
Other Flights : 443
••
••
• It is expected that from Oct. till March 2005, the
department will be handling-
AI Flights : 11,350
Flights of Foreign Carriers : 9,902
Other Flights : 3,202
AI Haj flights at BOM & CCU : 218
SV Haj flights at BOM : 66
••
••
• Equipment serviceability during the year 2003-04
was 96.34% and Equipment/Vehicle serviceability
during the year April/September 2004 on an
average was 96.75% and 90.06% respectively.
safety program of the department during the year
included interalia, 100% monitoring of the DFDR,
random monitoring of CVR, investigation of incidents
by the Permanent Investigation Board (PIB), Updating
Air Safety Manual and Contingency Plan, Preparation
of Air Safety Manual for Air India Express and Safety
Audits of all stations.
8.23 ENGINEERING
••
••
• Fleet Utilisation & Despatch Reliability : Aircraft
utilisation and technical despatch reliability for the
period under consideration is given below.
Utilisation is given in terms of average daily
utilisation per aircraft in block time. The technical
delays of duration 15 minutes and above are
considered for the Technical despatch reliability
APR -SEP’04
Aircraft Type Utilisation/day/ Tech. Despatch
acft (Hrs) Reliability (%)
B747-200 3.2 94.9
B747-300 7.9 92.6
B747-400 13.0 97.3
A310-300 9.6 98.5
••
••
• Aircraft Availability : On average, 86.7% of the
fleet (28.6 aircraft) was made available for service
during April - September 2004
••
••
• Additional Operations : During April – September
2004, to cater to commercial requirements, 34
additional flights were operated over and above
the schedule, resulting in an additional 232 hours
of operations.
83
Ministry of Civil Aviation
84
••
••
• On time baggage delivery statistics was 94.74%
and 97.89% at Mumbai and Delhi respectively,
during the year 2003-04. The same for the period
April-September 2004 at Mumbai and Delhi are
93.87% and 98.75% respectively.
••
••
• Air India at present provides ground handling
services to 27 foreign carriers at Mumbai, 21 at
Delhi, 13 at Chennai, 6 at Kolkata, 3 at
Thiruvananthapuram , 11 at Kochi and 7 at
Bangalore.
8.26 INFORMATION TECHNOLOGY
••
••
• ARTICA DCS cutover at Hong Kong on May 23,
2004.
••
••
• Handling of Thai Airways International flights at
Bangalore under ARTICA DCS effective June 07,
2004.
••
••
• LAX Airport flight handling under ARTICA DCS
effective June 11, 2004.
••
••
• Implementation of ARTICA DCS under CUTE for
Nairobi on July 19, 2004 (Flight AI-200). Cargo
Automated Manifest system with US Customs was
implemented effective August 14, 2004.
••
••
• CUTE IP TE development and certification by SITA
was completed on August 27, 2004. CUTE
commissioned on 10 counters at IGI Airport, Delhi.
••
••
• ARTICA DCS has been modified and tested to
check-in passengers with Electronic tickets.
••
••
• E-ticketing implemented for Chennai, Hyderabad,
Bangalore, Ahmedabad and Kolkata on September
22, 2004.
••
••
• Automated Manifest System (AMS) with US
Customs introduced for Chicago Airport on
September 23, 2004.
••
••
• AI/LH thru check-in facility introduced at BOM
on 23.9.2004 and at DEL and BLR Airports on
September 24, 2004.
8.27 INTERNAL AUDIT
In order to provide wide coverage during the current
year ,the following professional firms of Chartered
Accountants were appointed region-wise:
Name of the Audit Firm Region Period Total Audit Reports
M/s G.S.Mathur & Co. Western 2003-04 12 Financial Audit Report
M/s G.P.Kapadia & Co Western 2003-04 14 (9-Finaicial; 5-Inventory)
M/s Kumar Sharma & Co Northern 2003-04 12
M/s K. Varghese & Co. Southern 2003-04 11
M/s Maheshwari & Associates Eastern 2003-04 4
84
Annual Report 2004-2005
85
In appreciation of the contribution to Aviation
Medicine, Dr.S.M.Gaikwad, Director-Medical Services
(O) was elected as a Associate Fellow of the Indian
Society of Aerospace Medicine. The International
Medical Services Academy (IMSA) elected
Dr.S.M.Gaikwad and Dr.N.Vetrivel, Dy.Chief Medical
Officer, Chennai as a fellow of the society recognizing
their contribution especially in the form of the book
“Beat the Blood Pressure Blues”- a text on
Hypertension written by them.
8.29 SECURITY
••
••
• Outstanding AVSEC Organization : The Security
Department of Air India has been a proud recipient
of the International Merit Award for “Excellence in
Aviation Security” and has been adjudged the
“Outstanding AVSEC Organization” by the
Mudroch University of Western Australia at the
7
th
AVSEC Conference held at Singapore between
14
th
to 16
th
April 2004. The AVSEC Award has been
conferred upon the Security Department of Air
India, for the third time in succession.
••
••
• IATA Operational Safety Audit (IOSA) : The
IATA Operational Safety Audit (IOSA) Programme
is an Internationally recognized and accepted
evaluation system designed to assess the
operational management and control systems of
an Airline. IOSA Audit of the department was
conducted between 12
th
Jan to 16
th
January 2004
by a team of Aviation Quality Services (AQS) a
subsidiary Company of Lufthansa. On completion
of the audit, the IOSA Auditors appreciated the
security measures being adopted by the Security
Department of Air India, in its entirety.
The following firms of Chartered Accountants have
been appointed as Internal Auditors region-wise for
the year 2004-05:
M/s G.S.Mathur & Co. Western
M/s Haribhakti & Co Western
M/s Rajnish & Associates Northern
M/s K. Varghese & Co. Southern
M/s Maheshwari & Associates Eastern
Ø The Audit Committee has met 7 times during April
2003 December 2004 and the last meeting was held
on July 29, 2004.
Ø Details about pending CAG Audit Paras/ATNs for
reply are as follows :
Ø Draft Para “Unproductive expenditure of Rs.26.33
crore in the purchase of Master Change “ – Air
India Ltd.
Ø Draft Para “Unproductive expenditure of Rs.159.55
lakhs on Hotel accommodation for Cabin Crew at
Delhi, London & Parils –Air India Ltd.”
Ø Details about pending Draft Audit Paras for reply:
NIL
8.28 MEDICAL
The Medical Service Department’s primary function is
to provide clinical services to its serving and retired
employees. The department tries to keep abreast with
the latest developments in the field of medicine by
taking active part in national, international conferences
and presenting papers relating to health issues.
85

Ministry of Civil Aviation
86
••
••
• Single Agency Concept : In accordance with
AVSEC Order No. 2/2004 dated 6
th
January 2004
issued by the Commissioner of Security (CA),
Bureau of Civil Aviation Security (BCAS) and as
directed by the Ministry of Civil Aviation, Air India
Security Department has taken over the security
controls pertaining to registered baggage for all
International Airlines operating from CSIA Terminal
II 2A & 2C, Mumbai, with effect from 14
th
January
2004.
••
••
• Investigation & Fraud Prevention Cell : The
Investigation and Fraud Prevention Cell, which is
a vital part of the Security Department, deals with
all revenue and property crimes, including policies
to prevent travel of passengers with improper
documents. This section, besides formulating
Security polices for the control of revenue
documents also scrutinizes passenger travel
documents on certain sectors of our flight
operation. The Investigation & Fraud Prevention
Unit has been instrumental in intercepting/
detecting passengers attempting to travel with
forged/fraudulent travel documents on our flights
to UK & USA. During the period October 2003 to
September 2004, the I&FP Cell has intercepted 547
inadmissible passengers attempting to travel on
our flight, thereby saving fine/penalties of Rs. 8.36
crores approx.
8.30 VIGILANCE
The activities of the Vigilance Department till September
2004, are as below:
••
••
• The Vigilance Department is headed by a senior
officer from the IRS cadre who reports directly to
the Chairman cum Managing Director/Central
Vigilance Commission on all matters pertaining to
Vigilance. The objective of this department is to
sustain a high level of integrity, purity and
efficiency of the organization in addition to
executing the anti-corruption measures of the
Central Government.
••
••
• Towards this end, the department conducts regular
and surprise inspections of sensitive spots and
suggests ways and means to streamline procedures
which, if not amended, give scope for
manipulation. Measures for detection of corruption
and prevention are also initiated by the
department, apart from dealing with vigilance cases.
Regular follow up of departmental enquiries is
being done for their expeditious disposal. Periodical
reports are also required to be sent to various
agencies of the Government. Vigilance clearance
for promotions, foreign postings and resignation
of employees are given after the records are
examined.
••
••
• The Vigilance department in consultation with the
Dept of IT, has developed a software for providing
an easily accessible complaint’s interface, online.
The link has been provided on the Home page of
Air India website www.airindia.com.
••
••
• During the period under review a number of
recommendations were made for streamlining of
procedures in the organization, which include:
Ø Formulation of service regulations in respect of
local based staff abroad, including regulations
towards passage, entitlements, medical benefits
etc.
86

Annual Report 2004-2005
87
Ø In order to avoid recurrence of disputes arising
out of submission of Technical and Commercial
bids, it was recommended that the concept of single
envelope in the tender procedure needs to be
clarified to all concerned.
Ø In order to avoid delay in completion of
departmental enquiries due to multi-member
enquiry committees, it was proposed to have a
panel of retired officers of proven integrity for
conducting disciplinary proceedings.
8.31 STEPS TAKEN TO IMPROVE PUBLIC
GRIEVANCE REDRESSAL
MACHINERY
Redressal of Public Grievances is handled in accordance
with the laid down procedures. All complaints are
speedily and effectively actioned and when received
through the Ministry of Civil Aviation, the outcome of
the same is informed to them through the office of the
Director- Corporate Affairs. A system to handle
complaints world wide is already in place and the
procedure followed is both effective and streamlined
to provide maximum passenger satisfaction. All
complaints are replied to our valued passengers within
72 hours of receipt of the complaint. Air-India Limited
is committed to improve its ground and onboard
services and every attempt is made to extend maximum
comfort by way of professional handling with efficiency
and respect to our passengers.
The office of the Manager-Passenger Relations at
Mumbai is provided with a direct telephone number to
speak to the passenger directly and settle the matter. In
addition the travel related problems of the passengers
can also be conveyed to Air-India Limited at
8.32 OFFICIAL LANGUAGE
With a view to implement various provisions of the
Official Languages Act/Rules and the Policy
effectively, the company had adopted a three point
programme viz. Training, Translation and
Implementation.
In compliance with the Directives issued by the
Government, the company is conducting in-service
training in Hindi, Hindi Typing, Hindi Stenography and
Hindi Workshop, for Officers / Staff of the Company.
During the period in question, 92 employees took
advantage of these training programmes. At present
57 employees are undergoing various training.
The Annual Programme for the implementation of
Official Language for the year 2004-2005, issued by the
Department of Official Language, Ministry of Home
Affairs, was sent to all Departmental Heads and on-
line / off-line Station Heads in India and abroad, for
compliance.
Air-India celebrated Hindi Fortnight during 1st to 14th
September, 2004. On this occasion, officers/ staff were
advised to do their maximum work in Hindi, to converse
with the customers, passengers, callers, in Hindi.
To create the Hindi atmosphere amongst the staff,
various Competitions such as, Hindi Patra Lekhan,
87

Ministry of Civil Aviation
88
Hindi Shabda Spardha, Hindi Vichar Lekhan, Hindi
Shabda Gyan & Hindi Slogan were organised during
Hindi Fortnight by the Hindi Section. 90 staff member
participated in these competitions.
Bilingual Software / Fonts were installed on computers
of various Departments / Stations.
One staff from Human Resources Development
Department Stood first on All India Level in the Hindi
Pragya Examination conducted by Hindi Teaching
Scheme, Department of Official Language, Ministry of
Home Affairs in the month of May, 2004.
One staff of Materials Management Department was
honoured with the Consolation Prize in Hindi Music
Competition organised by National Textile Corporation
(South Maharashtra) under the auspices of Mumbai
Public Sector Undertaking Town Official Language
Implementation Committee.
8.33 POLLUTION CONTROL MEASURES
The Materials Management Department has arranged
for the disposal of garbage and waste items regularly
so as to ensure that such accumulations do not create
any pollution problems.
8.34 ENCOURAGEMENT/ASSISTANCE TO
SMALL SCALE INDUSTRIAL UNITS
In accordance with Government guidelines issued from
time to time, Air India have been procuring items from
Small Scale Industries.
8.35 WELFARE OF SENIOR CITIZENS
During the lean season, Air India offer special senior
citizens fares on the USA/UK/Europe routes for those
aged 60+. These discounts range between 30-40% and
are subject to certain blackout periods. Air India also
offers a 55% discount to senior citizens on the domestic
routes. These were applicable to women aged 63+ and
men aged 65+. However, effective December 6, 2004,
the age limit for both men and women has been reduced
to 60+. keeping with International trends, Air-India
fares are offered on the web in order to promote online
bookings and make available information to passengers
at their convenience. Wheelchairs and assistance is
provided on request.
8.36 ISSUES RELATING TO
DEVELOPMENTAL ACTIVITIES TAKEN
IN THE NORTH-EAST
Air-India has, in association with leading newspapers
in each of the North-Eastern States of India, launched a
recognition programme for students and teachers of
these States. 8 teachers and 8 students were selected
from the Award Winners to visit Singapore, as guests
of Air-India, on an Ambassadorial Visit during the period
Oct.06-09, 2004. During the visit to Singapore, this
group was provided an opportunity to interact with the
students and teachers in Singapore as also get exposed
to the practice of ‘Responsible and Active Citizenship’.
8.37 CITIZEN’S CHARTER
The Citizen’s Charter, is a complete, handy reference
guide to everything the valued passenger would want
to know about Air-India Limited. Information on
reservations, check-in procedures, lounge facilities,
baggage allowance, cargo handling, inflight services,
security regulations, frequent flyer programmes – flying
returns and special promotion schemes, special
88

Annual Report 2004-2005
89
Ø Trained approx. 220 newly recruited cabin Crew
between April and June 2004.
* Operations:
Ø CAT-II/III training, CRM and Human Factors
training and Specialised Operations training in
various areas such as RVSM, RNAV, TCAS,
ETOPS, Fuel Management, MNPS, IRS/FMS etc.
have been imparted to the flight crew on all aircraft
types.
Ø ILS-PRM and LDA-PRM Training has been
commenced for B747-400 Pilots
Ø Flight crew are undergoing EGPWS training on all
types of aircraft.
Ø Aviation Security Training has commenced
Ø 74 Trainee Pilots on A-310 aircraft have joined Air-
India.
* Security Training Center
The National Civil Aviation Security Training
Programmme (NCASTP), which has been recently
approved by the Ministry of Civil Aviation (MCA),
authorizes airport operators, airlines and the police
organization to train the employees working at the
airports. Nine types of training courses will be
conducted under the NCASTP, few of which are as
follows:
Ø AVSEC Screeners Course
Ø Dangerous Goods Regulations Training.
Ø Security Awareness for Staff, Air Crew, Traveling
Public, Ticketing Agents etc.
Ø Basic AVSEC Training.
privileges to single mothers with infants, wheelchair
cases, medical cases, old and infirmed passengers and
senior citizens, simplified and convenient procedure
for receipt and acknowledgement of complaints, is
provided concisely in the brochure.
8.38 HUMAN RESOURCES MANAGEMENT
••
••
• Staff Strength : The Staff Strength of the Company
as on December 31, 2004 is as follows:
Regular India Tr ainees Total Local Grand
Staff based Staff Total
Strength Posted
abroad
14368 * 142 601 15111 389 15500
*Excludes 69 staff on two years’ leave without pay and
02 staff who are on deputation to ICAO/MOCA.
204 employees have superannuated from services of
the company between April 2004 to September 2004
and 164 employees will superannuate between the
period October 2004 to March 2005
••
••
• Training Facilities
* Engineering : 18 technical courses were conducted
in which 336 personnel were trained in various
technical subjects.
* Inflight Services:
Ø Training of Indian Airlines Cabin Crew for VVIP
flights.
Ø Conducted Refresher Course for 23 Flight Pursers
re-designated to the Post of Inflight Supervisors.
89

Ministry of Civil Aviation
90
The NCASTP has been formulated to comply with the
requirements of the Standards & Recommended
Practices (ICAO – Annexure 17), it ensures that the
persons implementing Security Controls are
appropriately trained and possess all competence,
required while performing their duties.
The Security Training Centre, of Air India has complied
with all the requirements of the NCASTP viz.
infrastructure, faculty, training material, resources, etc.
Air India is now awaiting accreditation from the BCAS,
on receipt of which, the Security Training Centre will
be authorized to conduct training sessions for Officers/
Staff of other airlines as well as Security Officials of
Government agencies. During the period October 2003
to September 2004, 1452 Staff have been trained by the
Security Training Centre.
••
••
• Staff Welfare Measures
During the period under review Air-India continued
to provide various welfare facilities to its employees
like subsidised canteen, reimbursement of interest
subsidies on housing loans, allotment of housing
colony flats, use of holiday homes, reimbursement
for use of State owned Holiday Homes / ITDC
properties and participation in the Workers’
Education Scheme.
In keeping with the convention, this year too, the
Company felicitated its 891 employees who have
completed 25 years of service by presenting them
long service mementoes in a function held on
1
st
August, 2004, at Mumbai, Delhi, Chennai,
Kolkatta and various foreign stations.
••
••
• Awards
* Suggestion Awards: Seven employees were
recipients of Suggestion Awards for their
innovations, ideas, which helped Air India save
substantial sums of money and manpower, at the
Annual Awards function held in Mumbai. These
were in the areas of In-house modification of Test
Software for FCC PIN fitted on A310 aircraft, In-
house test procedure oven control modules
installed on leased aircraft, Change of design for
installation of missing broken anchor nuts installed
on CF6050C2 Nose Cowl Assembly, Designing and
fabrication of removal/installation tool for
assembly/disassembly of Wing Leading Panel
assemblies installed on Airbus, Developing an
innovative cabin crew operating pattern for the
optimum utilisation of cabin crew, for successfully
retrieving Air India Equipment which was being
grossly misused at the flight kitchens by other
airlines.
* Special awards: Two employees were given special
awards for distinguishing themselves in the fields
of performing arts, drama, literary work and sports.
*****
90

Annual Report 2004-2005
91
9.1 INCORPORATION OF INDIAN
AIRLINES
Indian Airlines was set up under the Air Corporations
Act, 1953 with an initial capital of Rs.3.25 crores with
its Corporate Headquarters at Delhi. The undertaking
of Indian Airlines was transferred to and vested in
Indian Airlines Limited with effect from 1
st
March, 1994
in pursuance of the Air Corporations (Transfer of
Undertakings and Repeal) Act, 1994. It has four
Regional Offices located at Mumbai, Kolkata, Delhi and
Chennai. The authorized capital of the company at
Indian Airlines Limited
9
91
present is Rs.1,000 crores and the subscribed and paid
up capital is Rs.107.14 crores.
9.2 OPERATIONAL NETWORK
••
••
• Stations airlinked
Number of Stations
Domestic 55*
International 18**
(in 14 countries)
Total 73
*Includes Puttaparthy which is seasonal station.
**Includes Karachi (Operations presently suspended)
Ministry of Civil Aviation
92
• •
• •
• New sectors introduced on International Network
Sector Date of Freq.
Introduction Week/
Aircraft
Guwahati-Bangkok-Guwahati 01.01.2005 2 A320
• •
• •
• Haj Flights
Special flights for Haj Pilgrims were provided with A300/
A320 aircraft in Phase I (outbound carriage to Jeddah)
as under:
* Srinagar-Jeddah (15 A300 flights from 13 Dec’04
to 27 Dec’04 carrying 2990 pilgrims)
* Lucknow-Jeddah (13 A300 flights from 28 Dec’04
to 09 Jan’05 carrying 2581 pilgrims)
* Jaipur-Jeddah (06 A300 flights from 10 Jan’05 to 15
Jan’05 carrying 1193 pilgrims)
* Hub and Spoke flights were operated from Patna,
Aurangabad and Guwahati for onward carriage to
Jeddah by Saudia from Delhi and Mumbai, while
Air India flew pilgrims from Kolkata to Jeddah.
* 15 A320 and 1 B737 Haj Hub and Spoke flights
operated on Patna-Delhi route transporting 1524
pilgrims for onward carriage to Jeddah by Saudia
from Delhi.
* 12 A320 and 5 B737 Haj Hub and Spoke flights
operated on Aurangabad-Mumbai route
transporting 1750 pilgrims for onward carriage to
Jeddah by Saudia from Mumbai.
* 14 A320 Haj Hub and Spoke flights operated on
Guwahati-Kolkata route transporting 1698 pilgrims
for onward carriage to Jeddah by Air-India from
Kolkata.
Flights for the returning pilgrims were operated
from 25
th
January onwards.
9.3 PROFILE OF INDIAN AIRLINES FLEET
The operational fleet of Indian Airlines / Alliance Air at
present is as under:
No. of Average age
Aircraft* as on
31
st
Dec. 2004
Years
Airbus A-300 03 22.2
Airbus A-320 30* 13.6
Boeing 737-200 11** 23.5
Dornier DO-228 02 19.7
Total 46 16.8
*Excludes 16 A320 leased aircraft
**The Boeing 737-200 are being operated by Alliance
Air.
9.4 FINANCIAL PERFORMANCE – 2003-04
After incurring losses continuously for 3 years, the
company has made Operating Profit as well as Net Profit
during the year 2003-04.
The Company has posted an Operating Profit of
Rs.125.10 crores in the year 2003-04 as against the
Operating Loss of Rs.134.73 crores for the year
2002-03. The Net Profit for the year 2003-04 is Rs.44.17
crores as against the Net Loss of Rs.196.56 crores
during 2002-03.
92
Annual Report 2004-2005
93
The turnaround has been achieved by the Company
during 2003-04 due to various cost cutting measures
and increase in passenger carriage by 4.35% as
compared to previous year.
Financial Results for the year 2002-2003 and 2003-2004
and for the period April-September, 2004 vis-à-vis
April-September, 2003 are summarized below:-
The performance of the Company during 2004-05 is
also encouraging, despite the fact that prices of
domestic ATF continued to rise upward and touched
an all time high of Rs.33,600/- per kilolitre in Nov. 2004.
In order to partially offset the huge increase in input
cost mainly due to constant upsurge in ATF prices
globally, the Company twice revised it’s Domestic
Rupee Fares by 10% each in June and October 2004.
(Rupees in Crores)
2002-2003 2003-2004 Apr-Sept., 2003 Apr-Sept. 2004
(*)
Operating Revenue 4101.50 4649.80 2214.55 2549.00
Operating Expenses 4236.23 4524.70 2278.50 2597.90
Operating Profit/(Loss) (134.73) 125.10 (63.95) (48.90)
Non-Operating Revenue 72.02 75.87 3.20 3.20
Non-Operating Expenses 133.85 152.80 42.75 20.70
Profit/(Loss) before tax (196.56) 48.17 (103.50) (66.40)
Profit/(Loss) after tax (196.56) 44.17 (103.50) (66.40)
Foreign Exchange Earnings 1409.74 1414.30 625.00 725.50
(*) As a result of re-grouping, some of the data in Operating Revenue/Expenses etc. have been recast, however, there is no impact on
Operating Loss & Net Loss for the year 2002-03 as the figures remains same.
93
9.5 RESERVES & SURPLUS
The position of the Reserves and Surplus, Loan Funds
as on 31.3.2003 and 31.3.2004 are summarized below:
Particulars As on As on
31.3.2003 31.3.2004
Equity Capital 107.14 107.14
Reserves & Surplus 562.45 566.18
Secured Loans 442.07 406.89
Unsecured Loans 723.59 283.90
(Liability for aircraft & spares)
Net Wor th (446.94) (399.05)
Ministry of Civil Aviation
94
9.6 PERFORMANCE RATIOS
••
••
• The financial performance ratios of Indian Airlines for the last 7 years are as follows:
Particulars 1997-98 1998-99 1999-00 2000-01 2001-02 2002-03 2003-04
Ratio of Operating Profit/ 7.98 8.59 5.63 (2.25) (5.85) (3.28) 2.69
(Loss) to Operating Revenue(%)
Ratio of net Profit (before tax) 44.94 13.46 48.88 - - - 44.96
to equity capital
Ratio of net Profit (before tax) 1.89 0.64 2.84 - - - 16.72
to Capital employed
Ratio of Current Assets to 0.66 0.61 0.53 0.50 0.49 0.48 0.45
Current Liabilities
Ratio of Net Profit (before tax) 59.22 15.01 36.08 - - - -
to Net worth
Operating Ratio (Ratio of Operating 92.02 91.41 94.37 102.25 105.85 103.28 97.31
Expenses to Operating Revenue)
Available Tonne Kilometers 51656 53209 54072 57474 62240 67963 72052
per Employees
Revenue Tonne Kilometers 33106 33632 35484 38348 38781 44007 47715
per Employee
9.7 PHYSICAL PERFORMANCE – 2003-04
Particulars 1997-98 1998-99 1999-00 2000-01 2001-02 2002-03 2003-04
Available Tonne Kilometers 1094.132 1122.922 1120.926 1153.684 1200.315 1308.018 1334.069
(ATKms)(Million)
Revenue Tonne Kilometers 700.896 709.079 740.285 777.342 755.547 845.097 877.475
(RTKms) (Million)
Overall Load Factor (%) 64.1 63.1 66.0 67.4 62.9 64.6 65.8
Revenue Passenger 6.363 6.069 5.927 5.992 5.525 5.654 5.900
Carried (Million)
Freight including excess 82150 86317 91392 91418 80236 92135 93287
baggage (Tonnes)
94
Annual Report 2004-2005
95
9.8 PHYSICAL & FINANCIAL
PERFORMANCE – 2004-05
The Company formulated its Budget Estimates for the
year 2004-05 on the assumption of carriage of 17861
passengers per day on an average.
During the period April to September, 2004, the
Company has earned a total revenue of Rs.2552.20
crores and incurred total expenditure of Rs.2618.60
crores resulting in net loss (provisional) of Rs.66.40
crores which is substantially lower by 35.8% when
compared to the loss of Rs.103.50 crores incurred in
the corresponding period of previous year 2003-04.
Similarly the net loss (Provisional) of Rs.66.40 crores is
lower from the budgeted loss of Rs.67.84 crores during
this period. During the period April – September, 2004,
the domestic ATF prices continued to rise upward and
touched a price of Rs.29,800/- per kilolitre in September,
2004 as compared to Rs.20,830/- per kilolitre prevalent
during September, 2003 and Rs.21,530/- per kilolitre
prevalent during March, 2004. The increase amounts
to 43.1% over September, 2003 rates and 38.41% over
March, 2004 rates (based upon which budget for the
year 2004-05 was formulated).
The improvement in the financial performance during
2004-05 (April/September) is mainly due to increase in
number of passengers by 26.3% over previous year
and 11.1% over budget estimates apart from various
cost cutting measures, adopted by the Company.
The estimated financial performance during the year 2004-2005 compared to budget estimates is as follows:
Budget Anticipated
Estimates
Available Tonne Kilometers (Million) 1439.844 1454.000
Revenue Tonne Kilometers (Million) 959.782 997.000
Passenger Load Factor (%) 61.7 64.5
Overall Load Factor (%) 66.7 68.6
Passenger carried (Million) 6.519 6.946
Operating Revenue (Rupees in crores) 5041.00 5368.00
Operating Expenses (Rupees in crores) 5024.50 5325.25
Operating Profit/(Loss) (Rupees in crores) 16.50 42.75
Total Revenue (Rupees in Crores) 5047.50 5374.50
Total Expenses (Rupees in crores) 5072.25 5365.75
Net Profit/(Loss) (before tax) (Rupees in crores) (24.75) 8.75
Foreign Exchange Earnings (Rupees in crores) 1465.00 1540.00
95
Ministry of Civil Aviation
96
9.10 ENGINEERING
The Company has extensive Engineering &
Maintenance facilities at Delhi, Mumbai, Kolkata &
Hyderabad and its trained workforce is capable of
carrying out all types of aircraft maintenance jobs.
During the year the following major works were carried
out for ensuring smooth and efficient aircraft operations
as also effecting substantial savings in terms of foreign
exchange which would otherwise have been incurred
in getting maintenance jobs done abroad.
Significant achievements made by the Engineering
Department during the year till date are given below:
••
••
• DELHI
Total engineering responsibility of maintenance work
on Airbus A320 and Boeing 737-200 aircraft, their
engines, equipment and components.
* Successful induction of five additional leased A320
aircraft taking the fleet strength to 46.
* Incorporation of Enhanced Ground Proximity
Warning System (EGPWS) retrofit on two Boeing
737-200 aircraft.
••
••
• MUMBAI
* The base has been upgraded to undertake major
maintenance of A320 aircraft. During this period
28 ‘A’ checks and three ‘C’ checks on A320 aircraft
were carried out at Mumbai besides complete major
maintenance work load of A300 fleet.
* Approval from Director of Airworthiness has been
obtained for repair and overhaul of Air India A310
Nose Landing Gear, cleaning and pressure testing
of Primary and Main heat exchangers and reheaters
of A320 aircraft.
96
9.9 ANNUAL PLAN 2004-2005 – A REVIEW
The Company’s annual plan for the year 2004-2005 was
approved by the Government with an outlay of
Rs.226.00 crores. The company has formulated the
Capital Budget Estimates for 2004-2005 reworking its
requirement at Rs.226.00 crores.
It is expected that against the original budget estimate
of Rs.226 crores, the anticipated outgo will be Rs.215.62
crores (approx.). The excess expenditure of Rs.0.26
crores under ‘Aircraft Fleet’ is on account of the
exchange fluctuation.
The expenditure under ‘Building Projects’, ‘Ground
Support Equipment’, “Corporate Computerization” and
“Others” is lower due to economy measures undertaken
whereby capital expenditure has been restricted to
operational requirements only.
Details of the expenditure for the year 2004-05 (budget
estimates) vis-a-vis outgo (provisional) are as under:
(Rupees in crores)
Budget Provi-
Estimates sional
2004-05 2004-05
Aircraft fleet 185.36 185.62
Building Projects 6.19 4.00
Computer/Communication 2.00 1.00
Corporate Computerisation 12.70 10.00
Ground Support Equipment 19.75 15.00
including vehicles & Renovation
of Booking Offices etc.)
Total 226.00 215.62

Annual Report 2004-2005
97
••
••
• KOLKATA
* Maintenance Division of Kolkata has recently
added capability to carry out A320 APU change.
This capability addition will reduce the necessity
of transporting serviceable APU from Kolkata to
Delhi, thereby reducing expenditure and will also
increase operational and maintenance flexibility.
* Boeing APU test stand has been upgraded by
incorporating latest instrumentation and other
state of the art technology and has been shifted to
new location adjacent to APU Centre.
* With increased productivity, availability of
serviceable A320 APUs has improved. On an
average three to four serviceable APUs of A320
are available.
••
••
• HYDERABAD
* Certification of M/s. Silk Air Flights at Hyderabad
and Cochin has been undertaken, besides
providing engineering services to other operators
like Air India, Emirates, Malaysian Airlines, Qatar
Airways and Air Lanka.
* Hangars at Chennai were rented out to M/s. Blue
Dart, Jet Airways, Sahara etc. and a revenue of
Rs.50,37,500/- was earned during this period.
9.11 JET ENGINE OVERHAUL COMPLEX
The Jet Engine Overhaul Complex (JEOC), the
Company’s ultra modern and state-of the-art
Engineering Workshop is fully equipped to handle
engine repair, maintenance and overhaul services.
Jet Engine Overhaul Complex operating under the
approval of DGCA, a Civil Aviation Regulatory
Authority of India and also holding certification as
Foreign Repair Station by FAA (Federal Aviation
Administration, USA), has capabilities to service P&W
JT8D-9A/17/17A Engine fitted on B737 Aircraft and
V2500-AI Engine fitted on A-320 Aircraft.
97
An engineer carriying out inspection on Airbus A320 systms in cockpit

Ministry of Civil Aviation
98
Till Nov’2004, a total of 557 engines (345-JT8D & 212-
V2500) have been successfully serviced by Jet Shop.
The capacity of JEOC has increased from an average of
35 engines in year 1994-97 to more than 55 engines
now.
JEOC has also refurbished one V2500-AI engine of
leased A320 Aircraft under FAA certification.
JEOC is in the process of obtaining ISO 9001-2000
quality certification of its facilities, for which an
application has been submitted and inspection by the
certifying agency M/s. STQC is awaited.
9.12 CIVIL WORKS
The Hangars at Chennai, Mumbai, Kolkata, Engine
Run-up Bay and Blast Fence at Mumbai, Avionics Shop
at Delhi, GSD Hangar Engine Run up Bay, Blast Fence
and Apron at Hyderabad Engineering Base, Structural
repairs and protective/water proofing treatment of the
old cantilever pre-stressed hangar at Mumbai, service
complex for GSD/Engineering at Calicut Airport, Stores
Building at Delhi airport, renovation of CIP Lounge at
Delhi, Mumbai, Hyderabad and Bangalore Airports,
renovation of Sales Office at Delhi and Mumbai have
been completed and commissioned.
Renovation work of CIP lounges and sales office at
Chennai, major structural repairs of buildings in
Housing colonies at Mumbai, construction of new
booking office at Chandigarh, Civil works to be carried
out in respect of Cargo Automation at ten identified
Airports, construction of cleaning bay at Kolkata are
under progress/process.
9.13 PRODUCT IMPROVEMENT
There has been a rapid increase in operations by Private
Operators in the domestic Civil Aviation arena. Further,
low-cost carriers are also starting their operations. In
order to maintain its presence in the market and also to
improve upon its current share of domestic air travel,
the Company continued to lead the market from the
front and adopted pro-active and aggressive marketing
and pricing policies. These initiatives centered around
not only the introduction of special promotional fares
but also offering of value added products and services
both in-flight as well as otherwise in order to enhance
passenger appeal. Details of the product upgrades
implemented and proposed to remain competitive in
the market are given below:
98
Passenger Care

Annual Report 2004-2005
99
* Smart Super Saver
* Super Saver International
* IA Taj Offer
* Flying Returns
* IA Flyaways
* APEX Fares
* Positioning Flight Fares
* Fly Select Fares
* Pay Smart
* IA Co-Brand Cards
– IA AMEX Gold Card
– IA-AMEX Green Card
– IA ABN AMRO Debit Card
* Bid and Fly
* Website & On-line Booking
* Neticket
* IA Cess
* J Smart
* IA Family Ticket
••
••
• Inflight Service Initiatives Implemented And
Proposed
* Training Aids – Procedures & Safety Film
* New Service Manual
* Harmonizing Tray set up
* New Meal Trolley Carts on board
* Stainless Steel Cutlery reintroduced after clearance
from BCAS
••
••
• Fleet Augmentation / Replacement Through
Lease Option
* 16 Airbus A-320 aircraft have been leased-in to
meet the interim capacity requirement and to replace
the ageing A-300 aircraft.
* One more A-320 aircraft will join the fleet shortly.
* 4 ATR-42 aircraft leased for exclusive operations
in and to/from North East.
* 5 Airbus A-319 aircraft proposed to be leased for
replacing the B-737 fleet operated by Alliance Air.
* 12 Wide Body aircraft proposed to be leased-in.
* 6 more ATR-42 aircraft proposed to be leased-in
for operation to short sector – regional routes.
••
••
• Fleet Augmentation / Renewal Proposed Through
Purchase Option
Indian Airlines submitted a Project Report to the
Ministry of Civil Aviation in April 2002 for acquisition
of 43 aircraft comprising nineteen (19) A319, four (4)
A320 and twenty (20) A321 from Airbus Industrie during
the period 2003-04 to 2007-08 at a net Project Cost of
Rs.10,089 Crores.
The new aircraft are envisaged to replace the entire
fleet of Airbus A-300 aircraft and Boeing B-737 aircraft
in a phased manner as well as cater to the projected
annual traffic growth of around 5% during the five
year period.
••
••
• Marketing Initiatives Implemented And Proposed
* Corporate House Scheme
* Bumper Super Saver
* Bumper Super Saver – J Class
99

Ministry of Civil Aviation
100
* Improved magazine Selection in ‘J’ Class
* After meal mouth freshener in ‘J’ Class
* Better soap & Dispenser in aircraft toilet
* Trolley Service for ‘J’ Class with round casseroles
* Round Casserole for improved presentation in ‘J’
class
* Popular brands of Sweets of Alpenliebe, Cofietoes,
Mali Candy
* Nimbupani on sectors ex-Delhi/Mumbai
* Premium brands of Coffee and Tea
* Bone China Casserole in ‘Y’ class on Metro routes
* Bar service introduced on some more select
international sectors
* Bone China crockery in ‘J’ Class extended to
international flights
* Amenity kits introduced in ‘J’ Class on select
international flights
* Introduction of Winter Menu:-
Ø Breakfast
– Light options introduced in South Indian variety
– Greater variety of Danish pastries and muffins
Ø Hi Tea
– Hot snack options increased
– Sandwiches with variety of fillings in J class
– Better choice in dessert for J class, e.g. tea, fancy
cake, cookies etc.
Ø Lunch / Dinner
– Light cold meal option rich in proteins and low in
carbohydrates
– Balanced composition in veg and non veg
– Introduction of items like bread pudding with
mango sauce, gajar halwa with vanilla sauce, etc.
– Choice of dessert.
••
••
• Service Upgrades On Ground Implemented And
Proposed
* DCS implemented at domestic on-line stations.
* Baggage tag printers installed at 22 stations. Plans
to install at 29 more domestic stations by April’05.
* Auto ticketing at all IA-Booking Offices (except
Agatti) & 58 Airport Ticketing Offices of IA in
India.
* City check-in facility at Delhi (MBO & PHBO),
Mumbai, Kolkata & Chennai.
* Neticket Facility – Extended to Agents also
* Call Centre set up at Delhi & Bangalore
* FFP – Extended to Bangladesh & Nepal w.e.f. 18
th
Aug ‘04, Sri Lanka 1
st
April ‘04.
* Implementation of SITA-CUTE.
* Auto ticketing at the remaining 8 domestic airport
offices (excluding Agatti) and IA’s stations abroad.
* Extension of City check-in facility Bangalore and
Hyderabad.
* EMI Scheme similar to ICICI with Citi Bank
* Bookings through Reliance Mobile
* Extension of call Center facility to Chennai,
Hyderabad, Kolkata and Mumbai.
100

Annual Report 2004-2005
101
* FFP Alliance Partnership with GE’s – SBI Gold Card
Programme.
* FFP – Tie-up with Lufthansa Airlines Miles & More
Loyalty programme.
••
••
• Cabin Ambience
* Action taken to upgrade:-
– Aircraft Carpets
– Cabin upholstery
– Passenger seats
* Upholstery including curtains changed during ‘C’
check or earlier, if required
* Carpets replaced during ‘C’ check or earlier, if
required.
* Reporting and rectification system introduced for
cabin maintenance/ambience during Night halt-
– ‘A’ Check
– ‘C’ Check
* Aircraft Cabin Ambience
– New Design for seat upholstery, curtains and
carpets – NIFT
– Other Cabin refurbishments
– Toilet soap dispenser
– Tissue paper dispenser/disposable toilet seat
cover/Toilet seat cover holder.
••
••
• Ground Support Initiatives
* Equipment upgraded by
– replacing old Equipment
– Inducting additional requirement
* Major items are:
– Ground Cooling Unit 07
– Low Floor airconditioned Passenger coaches 06
– Aircraft Push Back Tractor 08
– Ambulift 08
– Air Starter 13
– Ground Power Unity (Electrical) 22
– Passenger Stepladders 17
– Container Pallet Loader 40
* Equipment proposed to be purchased in 2004-05
– Aircraft Push back Tractor 01
– Passenger Stepladders 15
– Container Pallet Transporter 04
101
Passenger Step Ladder on the Flight

Ministry of Civil Aviation
102
9.14 CARGO PROMOTIONAL ACTIVITIES
••
••
• Indian Airlines has signed Special Pro-rate
Agreement (Cargo) with Lufthansa, Cathay Pacific
and El-Israel Airlines.
••
••
• 18 tons of relief material were carried to Patna and
Guwahati.
••
••
• Cargo Automation project initiated through global
tender for interactive track and trace for shippers.
••
••
• For export promotion ex- Inland Cargo Complexes
for dissemination of information to shippers, a new
facility offered through Shipment Notification
System – SNS via e-mail and SMS.
••
••
• Introduction of Productivity Linked Incentive
Scheme for Cargo Agents linked with new concept
of Loyalty Bonus scheme.
••
••
• Printing of new Cargo Tariff booklet.
••
••
• Quality Standard Certification ISO 9001:2000
surveillance checks by M/s. LRQA being
conducted.
••
••
• Indian Airlines Cargo participated in the Air Cargo
Agents Association of India (ACAAI) Conference
at Kuala Lumpur from 25
th
– 28
th
November, 2004.
9.15 HRD INITIATIVES
••
••
• Commercial – Customer Service Excellence
Intervention
Programme developed for delivery of high level of
customer service delivery, spontaneously and
routinely. Programme design includes identifying,
monitoring and addressing deviations in
performance from laid down standards and taking
corrective steps. Transfer the training expertise
to internal facilitators is a part of the programme.
Initially, Customer Service Excellence Intervention
programmes have been conducted by an outside
agency for frontline staff and officers at Delhi
Airport Northern Region.
15 programmes were held for staff and officers in
Northern Region Commercial Department.
The Performance Enforcement System to monitor
performance on 7 parameters is in place for Delhi
Airport. This will be an on going process.
A proposal is being worked out for the Customer
Service Excellence Intervention for Mumbai airport
staff in the second phase.
••
••
• Sales and Marketing Programmes
All Station Managers entrusted to carry out the
job of marketing and redesignated as Area
Marketing Manager. Special week long sales and
marketing sessions have been conducted for
existing Sales Personnel and the Area Marketing
Managers.
These programmes have been carried out by an
outside agency. Two such programmes have been
held for core sales personnel. Nine (9) of such
programmes have been held for Area Marketing
Managers and other sales personnel, in all covering
over 225 sales personnel.
102

Annual Report 2004-2005
103
••
••
• Executive development programmes
A ten day Management Development programme
had been tailor made with the help of Amity
Business School, NOIDA for senior executives of
the organization. Seventeen (17) executives
attended the programme.
••
••
• Computer Training by NIIT
* Headquarters:
In collaboration with NIIT, Indian Airlines has
organized a 40 hours PC familiarization training at
its premises at Safdarjung Airport for employees
of Headquarters and Northern Region posted at
Safdarjung Airport. Twenty six (26) batches have
undergone this training till the end of August 2004.
One batch for Directors and GMs had also been
organized.
Four (4) batches of advanced training on MS Excel
and MS Power Point has also been conducted.
Three batches of advanced data based
management, VB 6.0 and SQL have been conducted
for a period of three weeks (60 hours) till 20
th
December, 2004.
* Western Region:
NIIT has been conducting computer training in
the Western Region from 17
th
August, 2004.
Till date 223 participants have been trained.
Trainings will be for another six months.
••
••
• MOU
In the Memorandum of Understanding signed with
the Ministry of Civil Aviation, training of
employees is one of the parameters.
The total number of employees trained from April to
November 2004 is 5975. This does not include technical
and mandatory training of pilots, aircraft engineers and
flight dispatchers.
••
••
• Ab-initio training for Cabin crew at Hyderabad
An advertisement for filling up of 250 cabin crew
was issued. The selections have been completed.
Two batches of 53 cabin crew have completed their
training and 3 batches are in the process of
undergoing training. The duration was of 8
weeks. The module consists of mandatory
technical subjects, soft skills, cabin services,
grooming/etiquette and personality development,
announcements/voice culture, first aid, yoga/
physical fitness etc.
••
••
• Management Training Centre
The total programmes held from January to
November 2004 are 30 and the number trained is
707. The programmes organized by MTC during
this period are given below:
* Management Development Programme for
Newly Promoted Officers/Managers
* Seven Spiritual Laws for Success
* Effective Personality Development through
Leadership
* Wrap-up of Management Trainees (XXXIII
Batch)
* Personal Branding & Images Management for
Professional Success
* Challenges & Opportunities for Today’s Career
Woman
103

Ministry of Civil Aviation
104
* Induction Programme for Asstt. Manager
(Data Commn. & Computer Offr.) & Trainee
Computer (Tech.)
* Striking Balance Between Home & Career
* Achieving Human Excellence at Kolkata
* Six Thinking Hats
* Strategic Negotiations
* Effective Trade Union Management
* Transactional Analysis for Managerial
Effectiveness
* Standing Orders & Disciplinary Procedure
* Consultative Sales Training
* CME for Pharmacy Officers
* Business Management Workshop – Ist Phase
* Business Management Workshop – IInd
Phase
* Internal Audit Programme
* Effective Skills for Strategic Negotiation
* Communication to Win
* Team Building through Outbound Experience
* Personality & Personal Effectiveness
* Success Strategy
9.16 COMPUTERISATION
The Departure Control System (DCS) is implemented
at domestic outline stations & 10 International Stations
on IA Network. During the year 2002-03, 100% up time
of IBM main frame at the two central sites was achieved
thereby ensuring the availability and reliability of
system access for all users.
9.17 SCHEDULED CASTE/TRIBE WELFARE
Special Cells have been formed under the direct
supervision of Liaison Officer (Corporate) at
Headquarters and one each in the four regions viz.
Northern, Southern, Eastern and Western. Adequate
number of Scheduled Caste/Tribe employees man these
Cells and are primarily responsible to ensure
implementation of reservation orders in the Company
and also to deal with individual grievances and
representations submitted by Scheduled Caste/Tribe
employees. Periodical meetings are held with Scheduled
Caste/Tribe Associations both at the Central and
Regional level.
9.18 USE OF HINDI
In order to ensure progressive use of Official Language
Hindi in official work, 57 Official Language
Implementation Committees have been constituted at
Corporate Headquarters, Regional Headquarters and
all Stations and the Official Language Implementation
Committee meetings were held regularly. All efforts
were made to achieve the targets laid down in the annual
programme issued by the Ministry of Home Affairs for
the year 2004-05.
During this period, the Sub-Committee of the Committee
of Parliament on Official Language carried out official
language inspection of Indian Airlines offices located
at Hyderabad Base, Bhavnagar & Jamnagar and
appreciated the progress made in the field of Hindi.
The Ministry of Civil Aviation also carried out
inspection of Patna, Chandigarh, Agra, Bangalore,
Hyderabad and Chennai stations of Indian Airlines.
The Official Language Department of Corporate
Headquarters also carried out inspection of 7 stations
and 4 departments.
With a view to create a congenial atmosphere for the
use of Hindi in Indian Airlines, Hindi Fortnight was
104

Annual Report 2004-2005
105
celebrated with great zeal at all India level. To mark the
occasion, a Hindi fortnight was also celebrated at
headquarters from 15
th
September, 2004 to 30
th
September, 2004. Dy. Managing Director gave prizes
to the winners of the various competitions organized
on this occasion. A Rolling Rajbhasha Shield for
excellent official language implementation in official
work was awarded to Medical Department of
Headquarters. Varanasi, Pune & Trivandrum Stations
of A, B & C region was awarded for excellent official
language implementation in official work. One officer/
employee each from Corporate Headquarters, Central
Training Establishment, Hyderabad Base and all
Regions have been awarded Sarvashretha Vayaktigat
Puruskar for doing maximum work in Hindi in day-to-
day working. Mrs. Shakuntala Lalwani, Personnel
Officer, Engineering, Headquarter was awarded a special
prize of official language implementation.
An appeal was also issued on the occasion of Hindi
Diwas by the Chairman & Managing Director. A
Rajbhasha Sangosthi for officers working at
Headquarters was organized.
In order to facilitate Officers/Employees doing their
official work in Hindi as many as 174 Officers and
Employees were trained in 11 Hindi Workshop Training
Programmes.
Corporate Headquarters had got the financial sanction
of Rs.10,000/- in the current financial year for the
purchase of Hindi books. Books of Rs.3000/- were
purchased and the remaining will be purchased soon.
Similarly, other Regional Headquarters viz. Northern,
Southern, Eastern, Western Region and CTE
Hyderabad/Base also purchased Hindi books.
9.19 VIGILANCE
••
••
• Important Activities
* Complaints received through Vigilance Topic on
IA website
Central Vigilance Commissioner – Shri P. Shankar
inaugurated Vigilance topic on IA website on 6
th
November 2003 during the vigilance awareness
week. There has been a good response from the
passengers/outsiders as Vigilance Department
received 40 complaints/suggestions during the
year 2004-05 (till December 2004). These
complaints/suggestions were forwarded to the
concerned Departments/Authorities for taking
further action besides looking into the same, which
had vigilance angle.
* Regular post & surprise checks in respect of high-
density flights
Vigilance officials frequently conduct surprise
checks in respect of reservations, ticketing and
other facets having interaction with the travelling
public. Scrutiny of reservation data and records
revealed that certain unscrupulous agents indulge
in blocking seats by feeding fictitious ticket
numbers and indulge in other irregularities of
postponing remittance of sale proceeds to Indian
Airlines. Vigilance Department has taken up the
matter with the Regional Director recommending
stern action against the delinquent Agent(s)
besides recovering the loss caused to such
irregularities in reservations.
105

Ministry of Civil Aviation
106
9.20 SOCIO-ECONOMIC
RESPONSIBILITIES
Indian Airlines has been providing air-connectivity over
a large domestic network comprising number of
uneconomical services in remote/far flung and tourist
destinations being served for socio-economic reasons.
Indian Airlines also offers a number of fair concessions
on humanitarian/social grounds like defence personnel
& their families, senior citizens, students, blind persons,
cancer patients, physically impaired persons etc. Indian
Airlines, quite often, is called upon to perform
operations in times of natural calamities, defence
requirements and other emergency situations.
••
••
• Tsunami - Relief Operations
In order to provide relief to the residents of Port
Blair in the aftermath of Tsunami hitting Indian
Airlines coasts on 26
th
December, 2004, Indian
Airlines/Alliance Air operated following flights to
transport men and relief material:
* 146 flights with B737 fleet of Alliance Air Limited
(a wholly owned subsidiary of Indian Airlines)
were operated from 26
th
December, 2004 to 10
th
January, 2005 on Kolkata-Port Blair and Chennai
Port Blair routes carrying 7658 passengers from
Port Blair to the mainland 3250 passengers from
mainland to Island.
* Special A300 services were also operated between
Mumbai-Chennai, Delhi-Chennai, and Ahmedabad-
Chennai for bringing in 1708 Paramilitary forces to
Chennai for onward carriage to Port Blair.
* 30 Special Cargo flights were operated on Kolkata-
Port Blair route upto 10
th
January, 2005 and Approx.
325 Tons of material handled.
9.21 MEDICAL
IA Medical Department of Headquarters/different
Regions organized Talks/Seminars & Programmes on
health related issues like Women’s Health, Diabetes,
Heart attack, Blood Donation Camp etc. at Headquarters
as well as at Regional level. Indian Airlines also
sponsored an event organized for public awareness
against drug abuse of a “Mass Run” organized by
Department of Social Welfare in Delhi. To re-enforce
the Government agencies effort to control Dengue fever
during the outbreak in Aug/Sept 2004, Medical
Department issued guidelines about dengue and the
preventive measures, for the benefit of Indian Airlines
employees and their families.
In August, 2004 Medical Department with the help of
an NGO organized street plays in Indian Airlines
residential colonies and work places to sensitize the
employees and their families about the adverse effects
of smoking and alcohol consumption. These plays
also imparted information on Mother & Child Health
and promoted measures for population control.
Water borne diseases being very common, advisories
were issued for periodical cleaning and chlorination of
106
Alliance Air operating relief flights for Port Balir

Annual Report 2004-2005
107
water tanks in all office premises and residential
colonies, as well as periodical monitoring of the quality
of water, by getting the, samples tested from
Government recognized laboratories.
Bio-medical waste disposal is being carried out as per
the laid down norms at Airlines House and Safdarjung
Dispensary.
9.22 SPORTS
••
••
• Cricket
S/Shri V.V.S. Laxman and Yuvraj Singh were members of
the Indian team for the Three Test series and One day
series against Pakistan.
S/Shri V.V.S. Laxman, Harbhajan Singh were members
of the Indian team for the Asia Cup which finished
runner-up to Sri Lanka.
S/Shri V.V.S. Laxman, Harbhajan Singh and Yuvraj Singh
were members of the Indian team for the ICC Champions
Trophy in England.
S/Shri V.V.S. Laxman, Harbhajan Singh and Yuvraj Singh
were members of the Indian team in the Test Series
against the visiting Australians.
S/Shri V.V.S. Laxman and Harbhajan Singh were members
of the Indian team in the Test Series against the visiting
South Africans.
S/Shri Harbhajan Singh and Gagandeep Singh were
members of the Indian team for the two test series against
Bangladesh.
S/Shri Harbhajan Singh and Yuvraj Singh were members
of the Indian team for One day series against
Bangladesh.
Shri Harbhajan Singh was conferred with the Prestigious
“Arjuna Award” for the year 2003.
Indian Airlines won the All India Rani Surya Mukhi
Memorial tournament, Sadbhavna cup, Om Nath Sood
Cricket tournament, Lala Raghuvir Cricket Tournament,
All India Indian Airlines Gold Cup and finished runner
up in the Shahibzada Ajit Singh Cricket tournament,
All India Jubeliant Cricket Cup and B.D. Chandiwalla
Cricket Tournament.
••
••
• Hockey
Shri Dilip Tirkey was conferred with the prestigious
“Padma Shri” award for the year 2003.
Shri V.B. Singh was appointed as an Umpire for the
Champions Trophy held at Lahore.
Indian Airlines won the Him Gold Cup and finished
Runner-up in the Lal Bahadur Shastri Memorial hockey
tournament held at Mandi and New Delhi respectively.
Shri Jagbir Singh has been honoured with the Laxman
award by the Government of Uttar Pradesh for his
contribution in the field of hockey.
••
••
• Carrom
S/Shri M. Natraj and E. Mahimairaj defeated R.M.
Shankara and Maria Irudayam in the doubles finals of
the Senior National Carrom championships at Goa.
Shri M. Natraj won the Federation Cup held in Akola.
Shri R.M. Shankara finish runner-up in the SAARC
Carom championships held in Delhi in July 2004.
Shri R.M. Shankara won the Federation Cup in
Ramagundam and teamed up with Maria Irudayam to
finish runner-up in the Doubles event.
107

Ministry of Civil Aviation
108
Shri R.M. Shankara won the World Cup at Colombo
and was also instrumental in India winning the team
championships and the Doubles title.
••
••
• Chess
Ms. S. Meenakshi became the Sixth Women Grand
Master in India.
Ms. S. Vijayalakshmi won the Silver and S. Meenakshi
won the Bronze in the Commonwealth championships
at Mumbai. Master Parimarjan Negi won the Silver
Medal in the Under-14 category of the same tournament.
Tejas Bakre became the eleventh Grand Master in India.
Ms. S. Meenakshi represented India in the Women’s
World Chess Championships held at Georgia.
Indian Airlines won the National Team Chess
Championships at Pune.
S/Shri Tejas Bakre and Rahul Shetty qualified to
participate in the National “A” Chess championship.
Ms. S. Vijayalakshmi was member of the Indian team in
the 36
th
Chess Olympiad in Spain.
Master Parimarjan Negi participated in the World Youth
Championship for Boys U-12 in Greece and won the
Bronze Medal.
••
••
• Shooting
Shri Zorawar Singh won the Gold Medal and Shri
Birendeep Singh won the Silver Medal in the Trap event
of the SAF Games at Islamabad, Pakistan. Shri Vivek
Singh won the Bronze Medal in the Free Pistol in the
same games.
In the 9
th
International Junior competition at Suhi,
Germany Ms. Sweta Choudhary and Annu Raj Singh
won the silver Medal in the team event and Ms. Sweta
won the Silver Medal in the individual event. Shri
Zakir Khan won the Gold Medal in the team event.
Indian Airlines participated in the 48
th
National Shooting
championships at Hyderabad and won Nine Gold
Medals, One Silver and One Bronze Medal.
Shri S.M. Faisal has been honoured with the Laxman
award by the Government of Uttar Pradesh in the field
of shooting.
9.23 AIRLINE ALLIED SERVICES LIMITED
Indian Airlines had set up a wholly owned Public
Limited Company in 1983 known as Airline Allied
Services Limited (AASL). The objects of the Company
as enumerated in the Memorandum and Articles of
Association envisaged providing support services to
the core activities of Indian Airlines for e.g. setting up
of hotels, flight kitchen etc. In the year 1988
Memorandum and Article of Association of AASL were
amended to include the following mandate:-
* To establish, maintain, operate international and
domestic Air Transport Services, scheduled and
non-scheduled, for the carriage of passengers, mail
and freight and for any other purpose.
* To buy, sell, hire, let on hire and deal in aeroplanes,
flying machines, aircraft and the component parts
and all kinds of machinery and appliances for use
in connection therewith.
108
Annual Report 2004-2005
109
Airline Allied Services Limited started airline operations
with B-737 aircraft under the brand name of ‘Alliance
Air’. The company commenced its operations effective
15
th
April 1996. Alliance Air is at present, operating
services to 44 stations with 11 B-737 aircraft taken on
lease from Indian Airlines. There is a complete synergy
and cooperation between Indian Airlines & Alliance
Air in all facets of Airline Allied Services Ltd. operations
such as engineering, ground handling, marketing,
ticketing facilities etc.
••
••
• PHYSICAL PERFORMANCE OF ALLIANCE
AIR
The physical & financial performance of Alliance Air
during the years 2002-2003, 2003-04 and upto November
in the years 2003-04 and 2004-05 is as under:
109
PARTICULARS 2002-03 2003-04 Apr-Nov. Apr-Nov.
2003 2004
(Prov.)
Available Tonne Kms. (Million) 170.01 171.33 114.03 99.47
Revenue Tonne Kms. (Million) 101.68 106.52 69.41 63.26
Available Seat Kms. (Million) 1793.45 1862.95 1228.75 1085.25
Revenue Passenger Kms. (Million) 1059.47 1121.42 720.05 667.69
Load Factor % 59.81 62.17 60.87 63.60
Seat Factor % 59.07 60.2 58.6 61.52
Number of Passengers (Million) 1.419 1.582 0.998 1.009
Effective Fleet during the year 12.19 15 15 15
• Financial Performance of Alliance Air
(Rupees in Crores)
PARTICULARS 2002-03 2003-04 Apr-Nov. Apr-Nov.
2003 2004
(Prov.)
Operating Revenue 502.00 616.64 400.03 412.79
Operating Expenses 596.77 651.42 452.51 470.55
Operating Profit/(Loss) (94.77) (34.78) (52.48) (57.76)
Prior Period items 0.14 0.23 0.00 0.00
Non-Operating Revenue 12.43 37.21 23.33 23.33
Non-Operating Expenses 0.00 0.00 0.00 10.00
Profit/(Loss) before tax (82.48) 2.66 (29.14) (34.43)
Profit/(Loss) after tax (82.48) 2.05 (29.14) (34.43)

Ministry of Civil Aviation
110
• ATR – OPERATIONS TO NORTH EAST
Alliance Air has taken on lease 4 ATR-42-320 aircraft
for dedicated operations in the North Eastern Region.
These aircraft have been deployed exclusively in the
North East for a period of 5 years on dry lease basis.
The lease period commenced from December, 2002.
The leased aircraft are being operated in the North
Eastern Region on the basis of agreed budgetary grant
of Rs.35 crores per annum i.e. Rs.175 crores during the
five year period, to be contributed by Ministry for
Development of North-Eastern Development. The
deficit, if any, will be met by Alliance Air / Indian Airlines
with increase in fares and other concessions expected
from the Government like reduction of ATF prices,
lowering of Airport Charges, including savings from
Landing and Navigation charges in the North East etc.
* The first aircraft arrived in India on 19
th
December,
2002 whereas the second aircraft on 23
rd
December,
2002. The remaining two aircraft arrived in
February, 2003.
* The inaugural flight took off on 25
th
December, 2002
and operated on sector Kolkata-Guwahati-
Dimapur-Agartala-Kolkata.
* The first commercial flight operated on 2
nd
January,
2003.
* Gradually the flight operations increased. The
ATR is operating a total of nine stations i.e.
Kolkata, Guwahati, Silchar, Dimapur, Agartala,
Imphal, Aizwal, Lilabari, Shillong.
* Guwahati made an operational base for 1 ATR
aircraft effective July, 2004.
* Frequency of operations to/from/within North East
increased from 52 flights per week in Winter 2002
to 123 flights per week in Winter 2004 and city pair
links increased from 74 per week to 141 per week.
* Seats offered on North-East routes increased from
7518 per week in Winter 2002 to 9617 per week in
Winter 2004.
*****
110
Annual Report 2004-2005
111
10.1 ORGANISATION
Pawan Hans Helicopters Limited was incorporated in
October, 1985 (under the name of ‘Helicopter
Corporation of India Limited’) as a Government
Company under the Companies Act, 1956 with the
primary objective of providing helicopter support
services to the oil sector in offshore exploration, operate
in hilly and inaccessible areas and make available charter
flights for promotion of travel and tourism. The
Registered Office of the Company is located at New
Delhi and its Regional Offices are at Mumbai and New
Delhi. It has a team of dedicated highly motivated and
skilled manpower, which includes pilots, engineers,
executives and support staff. Pawan Hans is headed
by Chairman & Managing Director.
10.2 CAPITAL STRUCTURE
The Company’s authorised capital is Rs.120.00 crores
and the present paid up capital is Rs.113.76 crores out
of which Rs.89.26 crores is held in the name of President
of India and Rs.24.50 crores in the name of Oil & Natural
Gas Corporation Limited.
Pawan Hans Helicopters
Limited
10
10.3 FLEET PROFILE
PHHL has emerged as one of Asia’s largest helicopter
operator having a well balanced operational fleet of 32
helicopters. The Company’s operational fleet profile as
on 31.12.2004 has been as follows :-
Helicopter type No. of helicopters
Dauphin AS365N 17
Dauphin AS365N-3 4
Bell-407 3
Bell 206L4 3
MI-172 3
Robinson R-44 2
Total 32
10.4 OPE RATIONAL MILESTONES
Pawan Hans is the first aviation company in India to
get ISO 9002-2000 Certification for its entire gamut of
activities. The Company achieved flying of 3,35,000
hours and 12,00,000 landings on its fleet since its
formation.
111
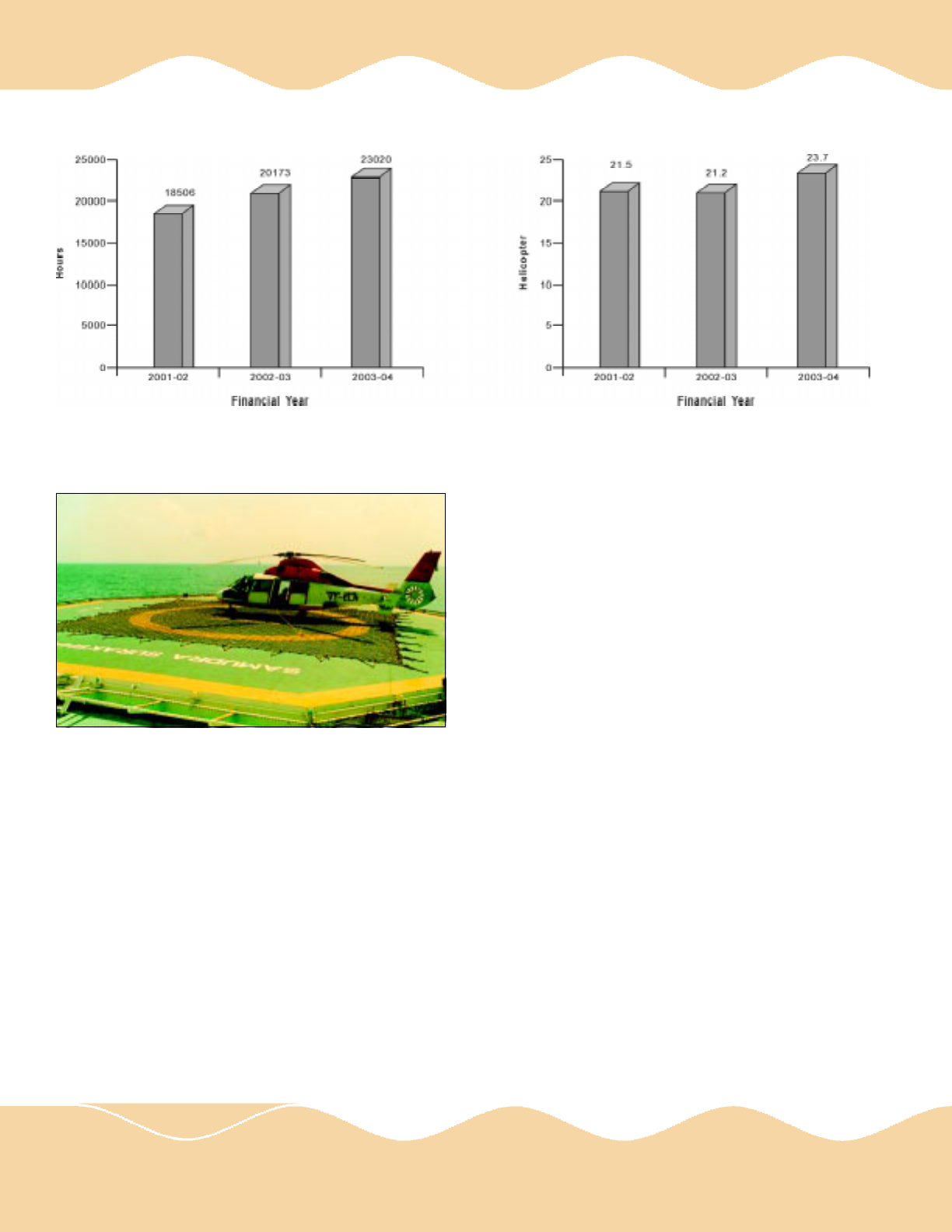
Ministry of Civil Aviation
112
10.5 DEPLOYMENT OF THE HELICOPTER
FLEET
••
••
• Operations for ONGC
The Company operates ten Dauphins and one MI-
172 helicopter on contract basis to ONGC for
carrying its men and vital supplies round the clock
to drilling rigs situated in Bombay off-shore
platforms.
– PHHL generates over 65% of it’s revenue from
ONGC at Mumbai and other locations for
transportation of its men & material.
– PHHL operates to 35 Rigs (mother platforms and
drilling rigs) and 100 production platforms (wells)
within a radius of 130 nm. from the main land at
Mumbai.
– 8 Dauphins operate daily from Mumbai carrying
out 17-20 sorties with a monthly utilization of 800
hours. In addition, 2 Dauphins operate from other
locations of ONGC as well. One MI-172 is also
flying on contract with ONGC.
– 30 landings daily per helicopter during production
sorties. 250 men are carried to various ONGC off-
shore locations every day.
– 2 Dauphins are stationed overnight at the main
platforms in addition to a dedicated Night
Ambulance to meet any emergency evacuation.
••
••
• Other Customers
PHHL provides helicopter support services to
several State Governments namely Arunachal
Pradesh, Punjab, Meghalaya, Tripura, Sikkim,
Lakshadweep, Andmans & Nicobar. It is also
providing helicopter services to some PSUs like
Oil India and NHPC, Ministry of Home Affairs
112
Pawan Hans Helicopter during operation for ONGC

Annual Report 2004-2005
113
(MHA), Guwahati and Hardy. PHHL had run the
helicopter services from Augustmuni to the Holy
shrine of Kedarnath in May-June, & September-
October, 2003 and September-October, 2004. The
company plans to resume the services from May
2005 onwards.
••
••
• Helicopter Service in the North Eastern Region
Pawan Hans operates flights from 24 destinations
covering 46 sectors by 120 weekly flights under
the agesis of the State Governments of Meghalaya,
Tripura, Sikkim and Arunachal Pradesh.
* Arunachal Pradesh
PHHL has provided a Dauphin helicopter SA365N
to Government of Arunachal Pradesh from
December 1995 which is being utilized by the State
Government for services connecting Itanagar with
Guwahati, Mohanbari, Pasighat, Roing, Tezu, Ziro,
Namsai, Along, Yingklong, Miao, Changlang,
Daporijo etc. In addition one MI-172 helicopter
has been deployed from August 2002 for ferrying
passengers and carrying cargo (air maintenance).
* Meghalaya
PHHL has leased one Dauphin helicopter on wet
lease to the Government of Meghalaya w.e.f. 15
th
February 1999. The State Government has been
operating daily passenger flights on the Guwahati-
Shillong-Tura sector and other sectors within the
State.
* Sikkim
PHHL has provided a 5-seater Bell helicopter on
wet lease to the Government of Sikkim since 31
st
October 1998. The State Government has been
operating daily passenger/tourist flights on
Gangtok-Bagdogra-Gangtok sector (6 days in a
week) and other flights (joyride to Kanchanjunga)
for carrying tourists.
* Ministry of Home Affairs
MHA has been utilizing PHHL’s Dauphin
helicopter since 1996 every year. The helicopter is
based at Guwahati and being utilized for
transportation of Ministers and Senior Officers of
the Central Government to important centers in
North East.
* Tripura
PHHL has provided a Bell 407 helicopter on wet
lease to the Government of Tripura w.e.f. 25
th
September 2002. The State Government has been
utilizing this helicopter for regular passenger
services within the State.
* NHPC
PHHL has provided a 5 seater Bell helicopter to
NHPC w.e.f. 27
th
October 2000. The helicopter is
based at Itanagar, Arunachal Pradesh and is being
utilized by them to meet their own requirements.
* Oil India Ltd.
PHHL has provided a 3 seater Robinson R-44
helicopter to Oil India Ltd. w.e.f. 10
th
May 1994.
The helicopter is based at Guwahati, Assam and is
being utilized by them to meet their own
requirements.
113

Ministry of Civil Aviation
114
10.6 ENGINEERING / MAINTENANCE
ACTIVITIES
The Company has established state-of-the-art
maintenance facilities in Mumbai & Delhi, approved
by DGCA, for maintenance of its fleet of helicopters.
Meticulous maintenance checks on helicopters are
carried out and extensive workshops with in-house
facilities provide the back up. Maintenance capability
has been upgraded to carry out major ‘G’ Inspections
(Airframe overhaul at 5,000 hours) on Dauphin
helicopters totally in-house without any foreign
assistance which leads to foreign exchange savings
on account of lower cost of repairs/inspections. During
the year 2003-04, a total of 32 inspections consisting of
T/2T/5T(500 hrs./1000 hrs./2500 hrs.) inspection and 4
‘G’ inspections (5000 hrs.) on Dauphin helicopters were
carried out by the Company from within its resources.
Pawan Hans has been appointed as an approved
Maintenance Centre to carry out services on Dauphin
series helicopters and is part of the Eurocopter’s network
of authorized Maintenance Centres world wide.
The enhancement in workshop facilities during the
financial year 2003-2004 include bench checks of fire
detectors, ATC Transponder and overhaul of Main
Rotor Hub Assembly installed on Bell 407 helicopters.
The overhaul of Main Rotor Hub of Bell 407 helicopter
has already been carried out successfully at Company’s
Northern Region which has lead to substantial savings
in foreign exchange.
A new system of recording of flight time for maintenance
planning as approved by the manufacturers and DGCA
was taken up. The revision has been implemented for
Dauphin N3 helicopters w.e.f. 05.08.2003 and Dauphin
N helicopters w.e.f. 01.01.2004 after receipt of approval
of DGCA for the change to the new basis. Following
the above system not only reduced the repair/overhaul/
inspection costs but also reduced the number of
helicopters under major maintenance, component
replacement etc. and in turn increased the availability
of helicopters for flying.
During the year serviceability of helicopter and on time
dispatch have shown remarkable improvement. Major
maintenance of Bell 206L4 helicopters Allison engines
has been carried out in-house instead of sending these
engines to foreign Repair agencies. Further major
maintenance inspections and major component
changes of Bell 206L4 helicopter at bases such as
Sikkim, Agartala and Itanagar was introduced during
the year.
Pawan Hans also provides maintenance & operations
support for a Dauphin AS-365N3 helicopter of
Government of Karnataka and a Robinson R-44
helicopter of a religious organization at Delhi.
10.7 M ATERIALS MANAGEMENT
During the year 2003-04 procurement of MI-172 spares
have been streamlined by having agreement for product
support with the manufacturer of the helicopters.
Material management directives for better control
relating to non-moving inventories was issued in
August, 2003. Further by fixing of inventory levels all
procurements have been made based on joint review
by Engineering and Material Departments and spares
are ordered on forecasted projections. Quantum of
slow moving inventory has been reduced considerably
over the years by utilizing such items during major
inspections. Air Consolidation Services were
streamlined by combining freight, forwarding, custom
clearance and door delivery of consignment, which
resulted in improvement in procurement process.
10.8 INFORMATION SYSTEM &
TECHNOLOGY PLAN
In order to implement Information System &
Technology Plan in the critical functional areas of
Operations, Engineering, Materials & Finance, an
114

Annual Report 2004-2005
115
agreement for crucial integrated software development
was signed with M/s.Tata Consultancy Services Ltd.
which would enhance efficiency, effectiveness and
customer satisfaction. The development work has
reached an advanced stage and process of
implementation has commenced in certain functional
areas.
10.9 TRAINING
The operating and maintenance standards of Pawan
Hans are one of the highest in the world. All aircrew
must pass proficiency tests every six months.
Maintenance crew undergo regular refresher courses.
10.10 FINANCIAL PERFORMANCE
Since the financial year 1991-92 Pawan Hans has been
continuously making profit and paying dividend to the
Government and ONGC. The financial performance
during 1997-98, 1998-99, 1999-2000, 2000-2001, 2001-
2002, 2002-03, 2003-04 and 2004-05 is as under:-
Particulars 1997-98 1998-99 1999-2000 2000-01 2001-02 2002-03 2003-04 2004-05
A ) Revenue Estimates 157.37 178.54 175.85 191.96 195.86 205.02 224.00 225.14
B) Expenditure Estimates
i) Operating & non- 100.32 106.19 99.38 129.17 115.59 131.33 143.52 156.60
Operating expenses
ii) Depreciation & 5.65 7.78 7.44 9.98 11.06 14.21 15.26 19.29
Obsolescence
Reserve
Total 105.97 113.97 106.82 139.15 126.65 145.54 158.78 175.89
C) Profit before prior period/ 51.40 64.57 69.03 52.81 69.21 69.48 65.22 49.25
extraordinary Adjustments
D) Prior Period/ 24.09 22.48 38.16 22.19 22.25 4.20 12.62 13.35
Extra-ordinary adjustments
E) Interest on GOI dues including - - (288.33) (11.69) - (39.31) - -
arrears of earlier years.
F) Proit/(Loss) after 75.49 87.05 (181.12) 63.31 91.46 24.37 77.84 62.60
Adjustments
G) Provision for Income Tax 13.75 15.00 42.50 25.30 32.15 8.98 25.15 29.50
H) Net Profit/(Loss) after tax 61.74 72.05 (223.62) 38.01 59.31 15.39 52.69 33.10
I) Dividend (paid/payable) 12.51 14.79 10.52 11.38 13.65 13.65 17.50 -
10.11 S TAFF QUARTERS
To meet the acute shortage of residential
accommodation in Mumbai, Company has acquired
land from Airports Authority of India on lease for
building 242 flats out of which 50 flats have been
allocated to Airports Authority of India.
10.12 FLEET AUGMENTATION
The Company signed an agreement for purchase of
two new Dauphin AS365N3 helicopters in August,
2003. The first Dauphin N3 helicopter has been delivered
in August, 2004 and the second in October, 2004. The
Company has also purchased one new Bell 407
helicopter in December, 2004. Further, evaluation of
tenders for two medium helicopters is underway.
115

Ministry of Civil Aviation
116
10.13 STEPS TAKEN TO IMPROVE PUBLIC
GRIEVANCE REDRESSAL
MACHINERY
Pawan Hans does not have direct services for the general
public and is dealing mainly in long term contract with
selected customers like ONGC, Oil India Ltd. State
Governments and PSUs etc. Therefore complaints
received are minimal and are being dealt with promptly
within the stipulated time. Pawan Hans has a prescribed
public grievance procedure including PGRAM to settle
any public grievance. Further there exists a Public
Grievance Redressal Machinery dealing with the
complaints by Director at Corporate Office and
Grievance Officer at Regions.
10.14 POLLUTION CONTROL
Pawan Hans is endeavoring to maintain a pollution free
environment and has been planting trees around its
office premises in Delhi and Mumbai.
10.15 VIGILANCE
The Vigilance Department is headed by the Chief
Vigilance Officer. The thrust of the activities of the
Department are on preventive vigilance whereby the
employees are made aware of the extant rules and
procedures of the Company and are motivated to abide
by them. The rules themselves are also scrutinized in
order to fill up the gaps where rules are either non-
existent, or are antedated, or are considered to be
inadequate to deal with a given situation. Instructions
are issued from time to time for better documentation
and filing procedures, and proper upkeep of records.
Identification of and plugging the sources of pilferage,
if any, is an on-going exercise. The emphasis is on
regular inspections and greater interface with the staff
so as to streamline functioning and enlighten the staff
about the serious consequences of adoption of shortcut
methods and deviation from established procedures.
Periodic counselling of the staff regarding greater
transparency in their decision making is an important
activity of the Vigilance Department that is expected to
bring about an attitudinal change for the betterment
and improve the work culture and discipline in the
Company.
10.16 USE OF OFFICIAL LANGUAGE
More than 80% of the Officers and staff members
possess working knowledge of Hindi and as far as
possible most of them do their official work in Hindi.
Hindi dictionaries and other help literature have been
provided to officers and staff to facilitate their working
in Hindi. All documents covered under Section 3(3) of
the Official Languages Act were issued bilingually i.e.
both in Hindi and English. Provisions of Rule 5 of the
Official Languages Rules were also complied with.
10.17 CITIZEN CHARTER
PHHL has a limited clientele such as ONGC, various
State Governments etc. as such PHHL does not have
direct public contact. The State Governments in various
States in the North East have been utilizing the services
of PHHL for running passenger services in their States.
Citizen Charter has been provided in the web site i.e.
www.pawanhans.com.
10.18 EFFORTS TOWARDS ACHIEVING
EXCELLENCE
PHHL has laid a strong foundation in terms of trained
manpower and excellent safety standards. The
Company looks forward to a bright future.
*****
116
Annual Report 2004-2005
117
11.1 INTRODUCTION
The Hotel Corporation of India Limited (HCI) is a Public
Limited Company wholly owned by Air India Limited and
was incorporated on July 8, 1971 under the Companies
Act, 1956 when Air India decided to enter the Hotel
Industry in keeping with the then prevalent trend among
world airlines. The objective was to offer to the
passengers a better product, both at the International
Airports and at other places of tourist interest, thereby
also increasing tourism in India.
11.2 D ISINVESTMENT
As per the recommendations of the Disinvestment
Commission, the following properties of the Hotel
Corporation of India have been divested under the
guidance of the Ministry of Disinvestment :
Hotel Corporation of India
Limited
11
11.3 DISINVESTMENT OF THE REMAINING
UNITS
The process of disinvestment in respect of remaining
units was again re-initiated in 2003 and Expression of
Interest was called for disposal of Centaur Hotel Delhi
Airport ( including Chefair, Delhi ) and Chefair Flight
Catering (including Dining Facilities, Mumbai) through
an advertisement which appeared on 14.10.2003. The
Inter Ministrial Group of Ministry of Disinvestment
had shortlisted 39 parties out of 46 parties whose
response was received and 20 parties desposited the
Earnest Money and shown the seriousness. These QIPs
were provided with Confidential Information
Memorandum and these QIPs accessed the data room
and interacted with the management and physically
visited the properties. The process of dues diligence
was over in May, 2004. Thereafter no progress has
taken place.
S. No. Date of Sale Description of Property Name of Purchaser Amount realized on sale
1. 26.3.2002 Indo-Hokke Hotels Ltd. Inpac Travels Pvt. Ltd Rs.6.51 crores
Rajgir
2. 31.5.2002 Centaur Hotel, Juhu Beach Tulip Hospitality Rs.153 crores.
Mumbai Services Ltd.
3. 5.6.2002 Centaur Hotel, Batra Hospitality Pvt. Ltd. Rs.83 crores.
Mumbai Airport
117
Ministry of Civil Aviation
118
As regards disposal of Centaur Lake View Hotel,
Srinagar, it was decided by the Central Government to
dispose off the same to the Government of J&K at
negotiated terms. Core issues were identified and the
property was got valued by an individual Valuer and
soon a decision in this regard would be taken to transfer
the property to the Government of J&K.
11.4 SHARE CAPITAL
Present Authorised Share Capital Rs. 41.00 Crores
Subscribed Issued & Paid up Share Capital Rs. 40.60 Crores
Net worth as on 31.03.2004 Rs.119.24 Crores
11.5 FINANCIAL RESULTS
For the financial year 2003-04, due to disinvestment of the two
major units viz., Centaur Hotel Juhu Beach and Centaur Hotel
Mumbai Airport, there was a substantial reduction in the revenue
of the Company. However in spite of the reduction in revenue,
the performance of the Company was better than the previous
year, in view of reduction in Staff Cost due to introduction of
VRS whereby 327 employees were relieved under VRS upto
March 31, 2004. The Financial Results of the Company for 2003-
04 are summarized below:
118
(Rupees in Lakhs)
PARTICULARS 2002-03 2003-04 2004-05
(Revised Estimate)
Total Revenue 5177.09 4074.92 4990.35
Total Operating Expenditure 6300.68 4758.69 4755.45
Gross Operating Profit/(Loss) (1123.59) (683.77) 234.90
Interest 72.71 181.51 230.00
Cash Profit/(Loss) (1196.30) (865.28) 4.90
Depreciation 191.50 144.59 151.05
Net Profit/(Loss) Before Extra Ordinary Items (1387.80) (1009.87) (146.15)
Prior Period Adjustments 160.50 (31.73) ( 8.85)
Extraordinary Item-VRS &Terminal Benefits 1121.90 439.85 -
Net Profit/(Loss) After Extra Ordinary Items (2349.20) (1481.45) (155.00)
Net Sale Proceeds of Units 19737.68 - -
Net Profit/(Loss) After Tax 17388.48 (1481.45) (155.00)
Income Tax 1391.68 26.33 -
Net Profit/(Loss)Available for Appropriation 15996.80 (1507.78) (155.00)
Transfer To General Reserve 1738.80 - -
Dividend 2030.00 - -
Profit/(Loss) After Appropriations 28.00 (1507.78) (155.00)

Annual Report 2004-2005
119
11.6 POST DISINVESTMENT ISSUES
The issue of settlement of Net Current Assets and
other obligations in both the properties viz.Centaur
Hotel Mumbai Airport and Centaur Hotel Juhu Beach,
Mumbai is yet to be settled as the reports of the
Transaction Auditors were qualified one and
inconclusive. In case of Centaur Hotel Mumbai Airport,
the matter was referred for Arbitration and in case of
Centaur Hotel, Juhu Beach, Mumbai , on three divergent
issues, the matter has been referred to the Ministry of
Civil Aviation for adjudication as was agreed between
the Buyer and the Company.
11.7 REVIEW OF PERFORMANCE
With the improved trend in the Hotel and Tourism
Industry, the business at the hotels in Delhi and
Srinagar as well as the Chefair Flight Catering Units
has shown substantial increase. The Company has
already shown growth of 24% in the first quarter, 15%
in the second quarter and 36% in the third quarter as
compared to the corresponding period last year. In the
recent past, the occupancy of the Delhi Hotel has
increased by 40% as compared to the previous year. In
the current season, it is expected that the hotel would
generate substantial revenue due to increased
occupancy levels.
Similarly, there has been improvement in the business
propositions at Centaur Lake View Hotel, Srinagar.
During the year 2003-04, a number of prestigious events
like Inter-State Council Meeting, Congress Chief
Minister’s Conference, Vice Chancellor’s Conference
etc. were held. During the current financial year i.e.
2004-05, there has been a tremendous increase in
occupancy during the season, in view of the boom in
tourists traffic, from 40% to 75%, yielding additional
revenue.
At the Chefair Flight Catering- Mumbai, 130 additional
flights have been obtained from Air India in the current
financial year 2004-05, thereby increasing the meals
uplifted by 25% and the revenues by approx. Rs.3
crores. It is expected that during the year, further
additional flights would be catered for, to Air India.
11.8 EMPLOYEES
As on 31
st
March, 2004 the Company had on its payroll
a total of 1789 employees as against 2196 as on 31
st
March, 2003. The total number of employees will further
reduce due to VRS, retirement, on superannuation and
resignation etc. The Management’s relations with the
employees continued to be good and cordial during
the year under review.
11.9 FUTURE PLANS
In pursuance of the decision of the Government, soon
the Centaur Lake View Hotel, Srinagar would be
disposed off to the Government of J&K and financial
bids woulds be called for Centaur Hotel Delhi (including
Chefair Flight Catering, Delhi) and Chefair Flight
Catering, Mumbai as the Government has already called
for Expression of Interest for sale of these two
properties. With this all Units of the Company would
be disposed off and the shell company would be
merged with the parent company with the proceeds
realized.
119

Ministry of Civil Aviation
120
11.10 IMPLEMENTATION OF OFFICIAL
LANGUAGE POLICY.
In regard to the implementation of Official Language
Policy, the directives received from the Government
from time to time are being followed.
11.11 TRAINING & DEVELOPMENT
Employees are sponsored to attend various Seminars,
Conferences and short duration Refresher Courses
organized by various Agencies in order to acquaint
themselves with Modern Management, Technical
Concept and latest innovations in the Hotel Industry.
120
*****
Annual Report 2004-2005
121
12.1 INTRODUCTION
In accordance with the instructions of the Department
of Women and Child Development, a cell headed by a
lady Deputy Secretary as Nodal Officer, is in existence
in the Ministry of Civil Aviation, for overseeing the
work relating to women’s welfare and for taking suitable
measures to provide convenient and hassle free work
environment to the women members of the staff. Further,
as per the guidelines of the Hon’ble Supreme Court of
India, a complaint committee headed by the same lady
officer has also been constituted to examine complaints
relating to sexual harassment of women at work places
and to suggest remedial measures to prevent such
harassment. All the organisations under the Ministry
have also set up similar cells and complaints committees
to look after matters relating to women welfare and to
look into complaints relating to sexual harassment of
women employees. Instructions received from
Department of Women and Child Development,
National Commission for Women etc. from time to time,
are circulated to all organisations under this Ministry,
for necessary implementation. The position of women’s
welfare/ cases of sexual harassment in the Ministry and
its organisations is being monitored periodically and
necessary action is taken wherever called for.
12.2 DIRECTORATE GENERAL OF CIVIL
AVIATION
The meetings of the Women’s Cell in the Directorate
General of Civil Aviation are held periodically. All the
ladies working in DGCA attend these meetings and the
topics of general interest concerning ladies are
discussed in these meetings. There has been no serious
problem relating to ladies that could be reported during
the year 2004-05.
12.3 BUREAU OF CIVIL AVIATION
SECURITY
A separate common room has been earmarked for women
for attending to their needs for medical emergency/
rest. Problems of the women employees as and when
reported, are promptly attended to and resolved
amicably, keeping in view specific requirements of
Government Policy on the subject. As a part of
modernization of work procedures, women employees
of the Bureau are also being imparted computer training
and also in use of other modern office automation
equipment.
Women Welfare
12
121

Ministry of Civil Aviation
122
12.4 COMMISSION OF RAILWAY SAFETY
The offices of the Commission are generally located in
Railway Office Complexes and the facilities provided
therein such as toilets, creche, tiffin room etc. are availed
by the female employees of the Commission also. The
women employees also participate and hold office in
Mahila Samiti, the women’s welfare organisation of
railways. The instructions on welfare of women
employees, issued by Government of India from time to
time are being implemented.
12.5 AIRPORTS AUTHORITY OF INDIA
Women Welfare Association of Airports Authority of
India, known as Kalyanmayee, carries out societal
mission of AAI. Besides bringing out the social and
cultural awareness of its members and their families,
Kalyanmayee reaches out to souls in-need. The
branches of Kalyanmayee organize programmes for
mental, physical and spiritual upliftment of its members.
Its activity encompasses arranging literary camps,
health awareness programmes and helping the villages
close to the Airports in the Regions. Kalyanmayee has
endeavoured to wipe out many a tear of the Tsunami
victims when the calamity struck, by financial aid.
To enhance the productivity and leadership qualities
of women officials of Airports Authority of India, they
are nominated / sponsored for various training
programmes in India and abroad also.
12.6 AIR INDIA LIMITED
Air India is nominating women employees to various
training programmes/ seminars and conventions both
in India as well as abroad, organized by outside agencies
like Bombay Chamber of Commerce and Industry,
Bombay Management Association and Employers’
Federation of India on various issues concerning the
women including the issue of sexual harassment. Air
India has also nominated its women employees to
various Conferences and Seminars organized by WIPS
(Women in Public Sector), an organisation which has
been constituted under the aegis of SCOPE.
On the occasion of the World Women’s Day on 8
th
March, 2004, Air India operated its first flight AI-470
on Mumbai- Delhi- Singapore sector with all women
cockpit crew. Capt. Rashmi Miranda and Capt. Kshmata
Bajpai, piloted the flight, operated with an A 310 aircraft.
12.7 INDIAN AIRLINES LIMITED
Indian Airlines is amongst the very few organizations
in the world to employ women in highly skilled
vocations such as flying or even maintenance of aircraft.
Indian Airlines was the first scheduled airline in the
world to enroll a woman Pilot (Durba Banerjee) in
August 1966 who later became the first woman Pilot on
the wide-bodied Airbus-300. Indian Airlines created
world history by operating a flight with all women crew
in January 1986 with Saudamini Deshmukh commanding
an F-27 flight from Kolkata to Silchar and back. Indian
Airlines have as many as 40 women Pilots, of which 3
are Executive Pilots. There are 12 women Aircraft
Engineers and 30 Aircraft Technicians. Indian Airlines
is a life member of Forum of Women in Public Sector
(WIPS), and actively participates in all the activities of
this Forum.
122

Annual Report 2004-2005
123
As per the guidelines issued by the National
Commission for Women, Indian Airlines has formed
Women Cells at Headquarters and in each of the four
Regions to follow up development activities for women.
These Cells are functioning effectively.
In pursuance of the Order of the Supreme Court in the
case of Vishakha and Others Vs. State of Rajasthan,
the following actions have been taken:-
••
••
• List of Do’s and Don’ts prepared by National
Commission for Women has been displayed at work
places.
••
••
• In addition to the existing Women Cells, Separate
Cells to look into the complaints received regarding
sexual harassment have also been formed at the
Headquarters and in all the Regions and these have
been given wide publicity.
••
••
• The two sets of Standing Orders concerning
Discipline & Appeals have been amended to
include sexual harassment in the list of misconduct.
12.8 PAWAN HANS HELICOPTERS LIMITED
Women Cells have been set up separately in all offices
of the company. Pawan Hans has been making
consistent efforts to promote all round development
and ensure provision of all essential amenities for the
women employees. The company has also been
sponsoring women employees for in-house training as
well as to outside specialised institutions for their skill
upgradation.
12.9 HOTEL CORPORATION OF INDIA
A women’s Cell has been constituted at the head office
of the company, which looks into the issues concerning
women’s welfare.
12.10 INDIRA GANDHI RASHTRIYA URAN
AKADEMI
The welfare of women employees and girl trainees are
looked through normal administrative channels in
IGRUA as per Government regulations and the girl
flying trainees have equal opportunities for award of
scholarships to outstanding candidates provided by
JRD Tata Trust.
*****
123
